37 molecular orbital diagram h2-
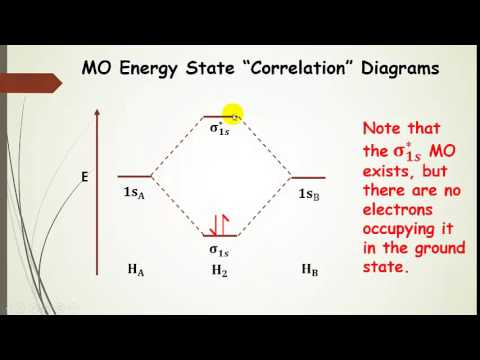
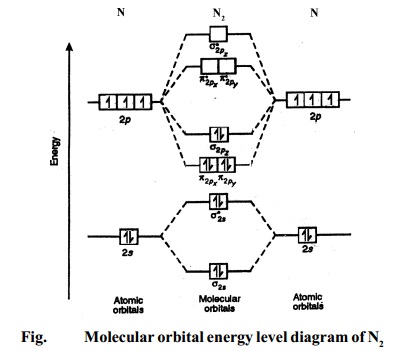
10 Mar 2016 — 1. Hydrogen molecule, H2. It is formed by the combination of two hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom in the ground state has ... The MO diagram also shows the AOs from which each MO is formed. There are four molecular orbitals derived from the 1s and 2s orbitals. Bond order = (8 - 4) / 2 H2 : ( 1s)2 The molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule is given in Fig 29. An orbital view of the bonding in ethyne.
Molecular Orbital Theory is primarily used to explain the bonding in molecules that cannot be explained by Valence Bond Theory. These are molecules that generally involve some form of resonance. Resonance implies that a bond is neither single nor double but some hybrid of the two.

Molecular orbital diagram h2-
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... 5:31He has two electrons with electronic configuration 1s2. Thus He molecule will have total 4 electrons and its ...8 Jun 2020 · Uploaded by Edmerls In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one-electron ...
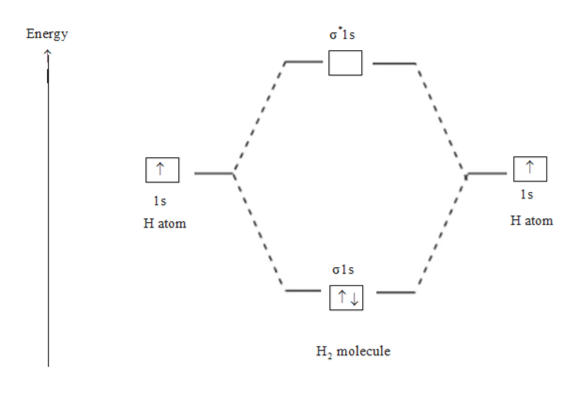
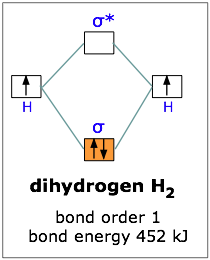
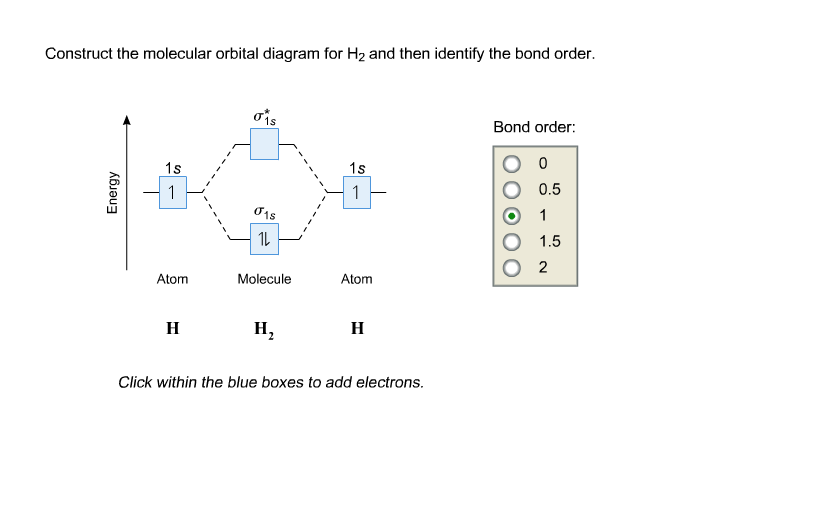
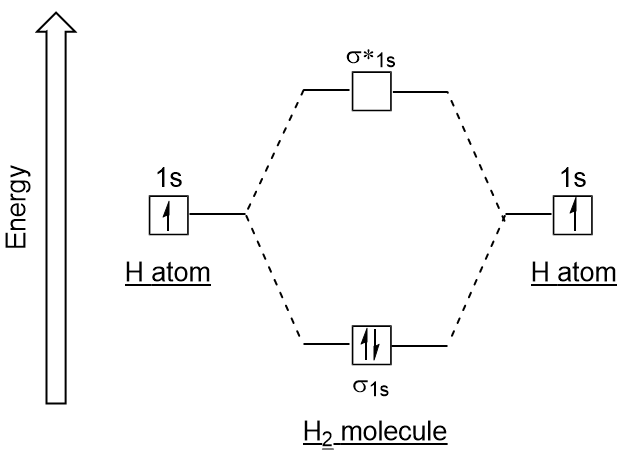
Molecular orbital diagram h2-. 22 Dec 2020 · 1 answerExplain about the molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule. · 1. Electronic configuration of H atom 1s · 2. Electronic configuration of H, ... 3 Feb 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ... According to the molecular orbital theory, molecular orbitals of a molecule is formed by combination of its atomic orbitals and electrons are distributed ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason The concept used to solve this problem is based on molecular orbital diagram. A molecular orbital diagram is used to explain ... Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
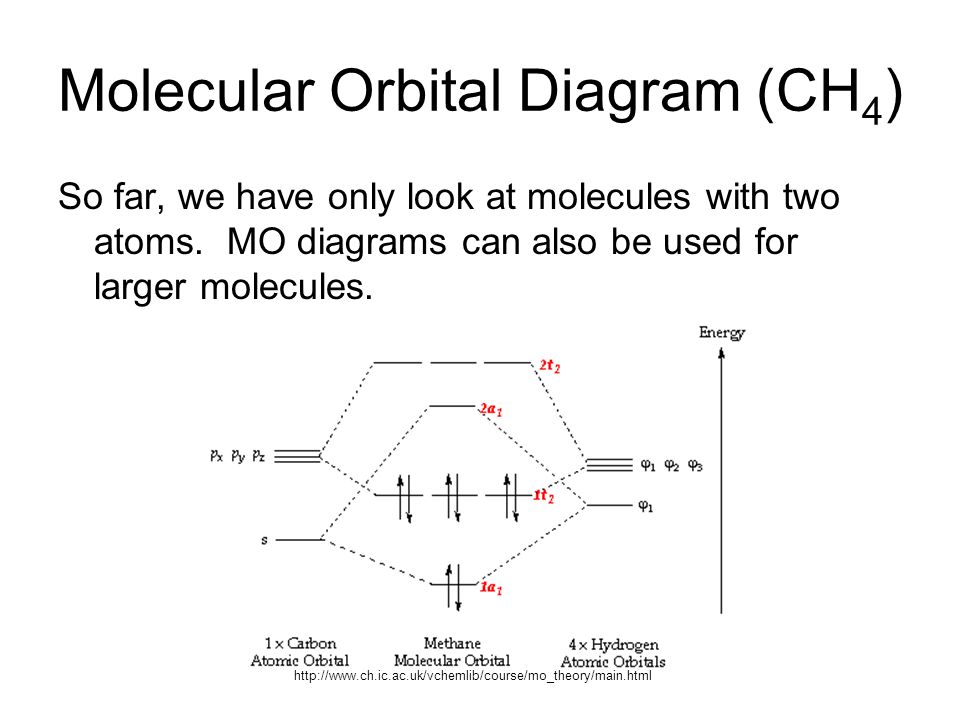
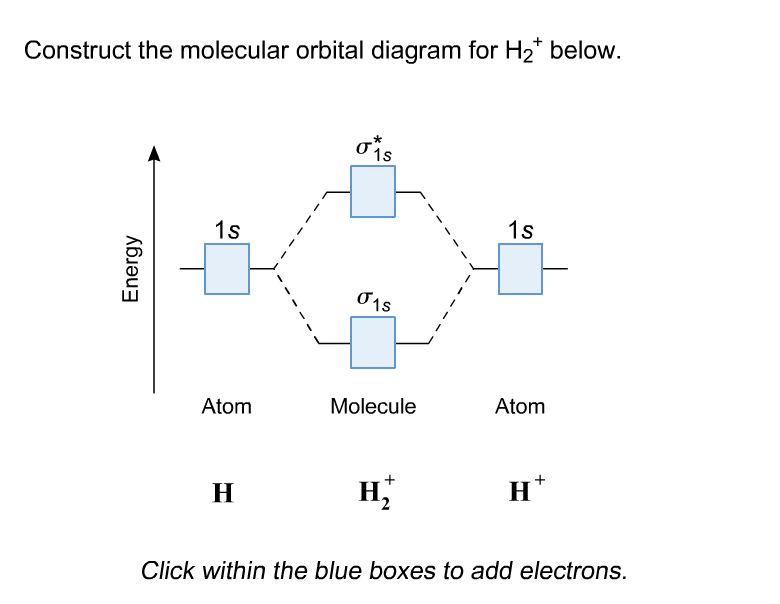
Its molecular orbitals are constructed from the valence-shell orbitals of each hydrogen atom, which are the 1s orbitals of the atoms. Two superpositions of ... 28-10-2021 · The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be: The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of … 04-03-2021 · Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ... 07-11-2021 · OF2 Molecular Geometry. We have already found the 2D Lewis Structure diagram of the Oxygen Difluoride molecule. Now, we are going to decipher the 3D molecular shape. Via Lewis Structure, we have realized the type of bond formed and the number of lone or unbonded pairs of valence electrons present in an OF2 molecule.
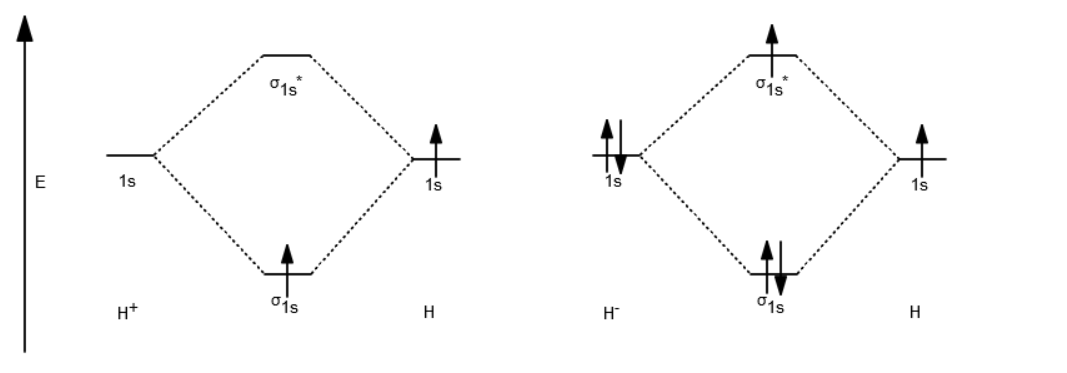
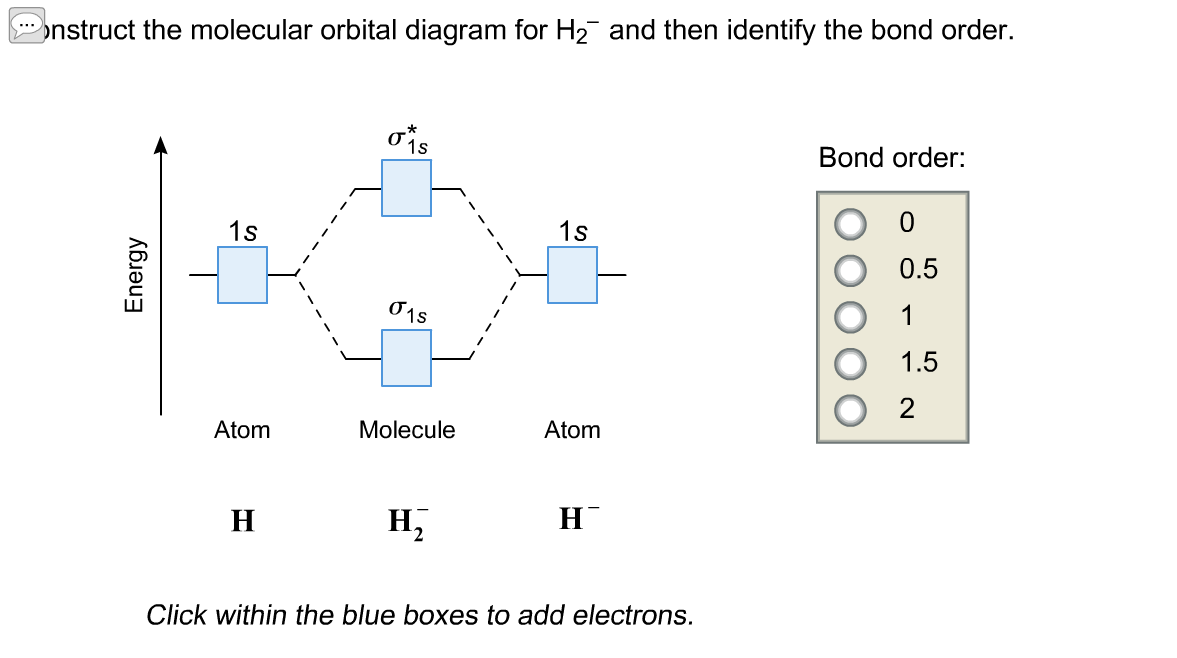
01-04-2017 · I'm assuming you mean "H"_2^(-) vs. "H"_2^(+). Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals. Bond Order in Molecular Orbital Theory. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the same result. Bond order is also an index of bond strength, and it is used extensively in valence bond theory ... In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one-electron ... 5:31He has two electrons with electronic configuration 1s2. Thus He molecule will have total 4 electrons and its ...8 Jun 2020 · Uploaded by Edmerls
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Number Molecule Atom Bond Order Multiple Bonds
Chapter 1 Molecular Orbital Concepts A Concepts Of Mo Theory 1 Strong Covalent Bonds Consider The Pi Bond Of Ethene In Simple Molecular Orbital Terms The Qualitative Results Would Be The Same For Any Pi Or Sigma Bond Q The Overlap Of The Two
When An Electron Of H2 Is Promoted To The Excited State Does The Molecule Continue To Exist Or Does Its Bond Break Quora
Explain About The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Hydrogen Molecule Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

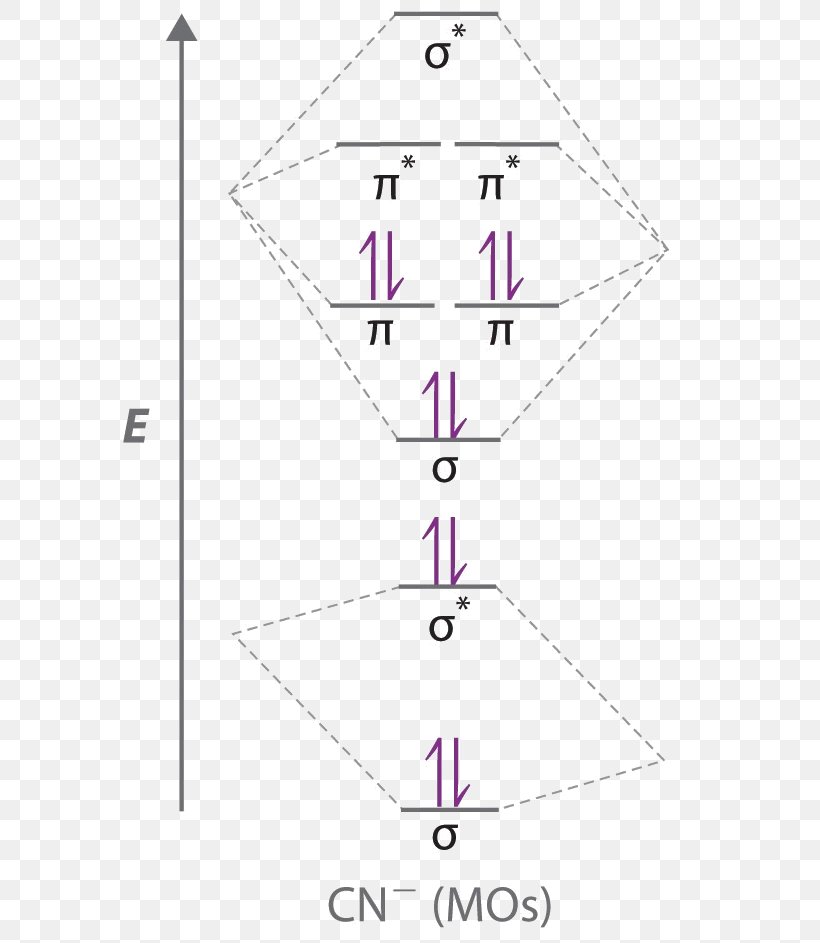
Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Antibonding Molecular Orbital Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Angle Text Chemistry Png Pngwing















0 Response to "37 molecular orbital diagram h2-"
Post a Comment