39 methane molecular orbital diagram
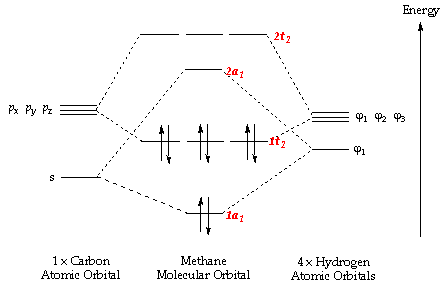
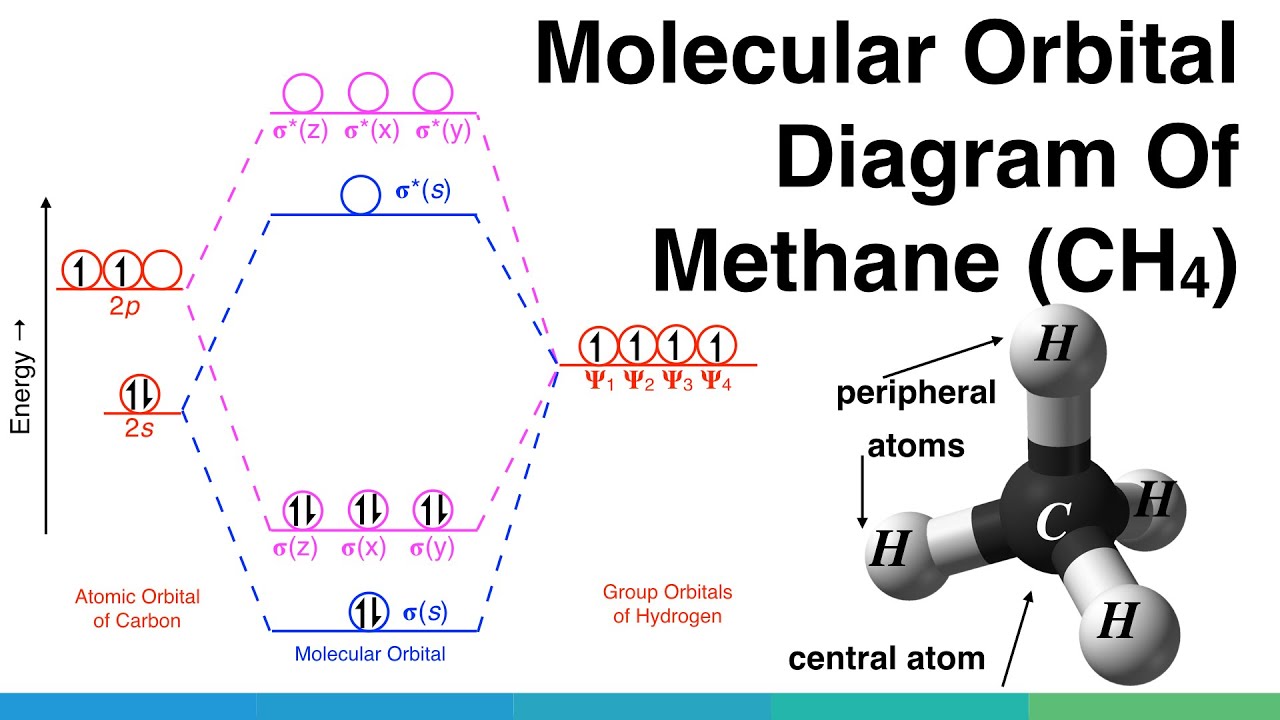
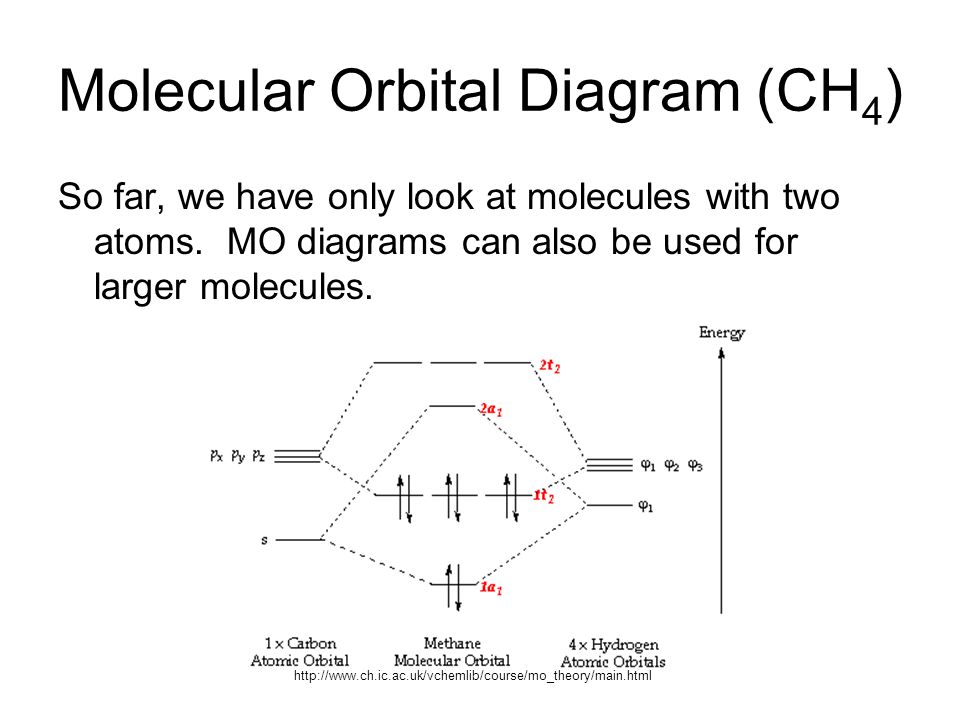
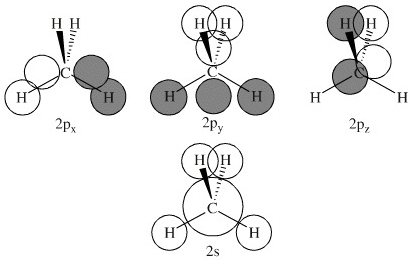
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Methane. Sigma and pi covalent bond models have proven to be valuable tools for describing the structure and reactivity of simple molecules, such as methane and ethene. However, such models do not accurately represent the electron distribution within the molecules. In the case of methane, this model implies four ... Properties and bonding. Methane is a tetrahedral molecule with four equivalent C-H bonds.Its electronic structure is described by four bonding molecular orbitals (MOs) resulting from the overlap of the valence orbitals on C and H.The lowest-energy MO is the result of the overlap of the 2s orbital on carbon with the in-phase combination of the 1s orbitals on the four hydrogen atoms.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in . A Molecular Orbital Approach to Bonding in Methane methane (CH4) molecule . A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti-bonding.
Methane molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti‐bonding molecular energy levels is provided below. (McQuarrie & Simon, Physical Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, p. 388) Methane has eight valence electrons, so according to the aufbau and Pauli exclusion principles the two lowest energy molecular orbitals ... Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us. Here is an energy level diagram showing how the 4 hydrogen 1s orbitals.Jan 18, · Using LCAO to Construct MOs for ... p-orbitals; 3p-orbitals; 3d-orbitals; 4f-orbitals; Compare shape and size of 1s, 2s and 2p orbitals; Molecular Orbitals. Hydrogen; Nitrogen; Fluorine; Ammonia; Methane; Ethylene (Ethene) Acetylene (Ethyne) Allene; Formaldehyde(Methanal) Acrolein; Carbon Monoxide; Hydrogen Fluoride; Allyl Anion; Butadiene; Benzene; Aromaticity of cyclic polyenes ...
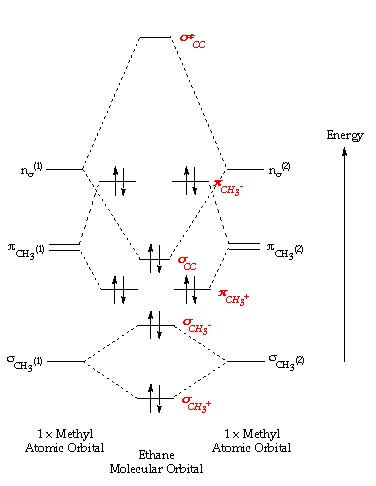
Methane molecular orbital diagram. The hydrogens bond with the two carbons to produce molecular orbitals just as they did with methane. The two carbon atoms bond by merging their remaining sp 3 hybrid orbitals end-to-end to make a new molecular orbital. The bond formed by this end-to-end overlap is called a sigma bond. The bonds between the carbons and hydrogens are also sigma ... Methane has four valence molecular orbitals (bonding), consisting of one orbital with one nodal plane (lowest occupied) and three degenerate (equal energy) orbitals that do have a nodal plane. For the energy diagram and pictorial view of the orbitals - please see below: Ethane: Chapter 2. Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Introduction to Hydrocarbons 2.1: Classes of Hydrocarbons molecules that are made up of carbon and hydrogen The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us. It should reconcile our valence-bond idea of electrons localized between carbon and hydrogen with the "delocalized" picture typical of the MO approach. It should tell us (quantitatively) about the energies of different electrons.
The three molecular orbitals (MOs) of methane in the ground electronic state (X 1 A 1 ), namely, the core MO, 1 a1 and the valence MOs, i.e. 2 a1 and three-fold energy degenerate MOs 1 t2, are studied in both coordinate space and momentum space. They are compared with the corresponding atomic orbitals (AOs) of a 'free' carbon atom in its ... Methane is a pentatomic, tetrahedral molecule. It is formed by combination of one carbon atom with 4 hydrogen atoms. In the molecule of methane, the carbon a... Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4. The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with four 1s atomic orbitals of the hydrogen. Determining CH 4 molecular geometry should be easier. In methane, the four hybrid orbitals are located in such a manner so as to decrease the force of repulsion between them. Nonetheless, the four orbitals do repel each other and get placed at the corners of a tetrahedron. CH 4 has a tetrahedral shape. The sp 3 hybrid orbitals have a bond angle ...
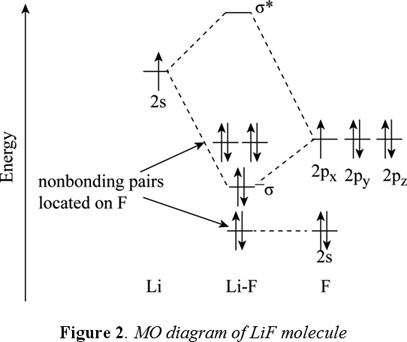
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine. x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbitals. Showing the s and p orbitals. ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11. CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2 Color conventions: Hydrogen atoms are shown in gray. The formation of molecular orbitals in ethane Ethane isn't particularly important in its own right, but is included because it is a simple example of how a carbon-carbon single bond is formed. Each carbon atom in the ethane promotes an electron and then forms sp 3 hybrids exactly as we've described in methane. This animation explains the methane molecule through the Molecular Orbitals TheoryFor more Chemistry animations check out the youtube channel Lili Tosta: htt...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
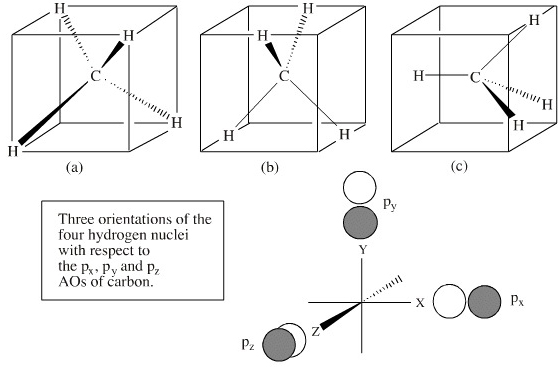
square planar methane. With no lone pairs, the electronic and molecular geometry are the same. Technique for constructing LGO's: I Draw Lewis structure and assign VSEPR geometry (already done above) II Assign a point group to the molecular geometry III determine the central atom's VB hybrid orbitals for the electronic geometry
A Molecular Orbital Approach to Bonding in Methane methane (CH4) molecule . A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti-bonding. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals.
Polyatomic Species: Molecular Orbitals. Polyatomic species like methane, CH 4, can be described in terms of molecular orbital theory, however, the diagrams can be very difficult to visualise. However, structures built up from hybrid atomic orbitals are much easier comprehend.
This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. The students generate ligand-group orbitals (LGOs) for the set of 4 H(1s) orbitals and then interact these with carbon, ultimately finding that such a geometry is strongly disfavored because it does not maximize H/C bonding and leaves a lone pair on C.
Click Images to Large View Methane Molecule Stock Image F0048582 Science Photo. Nitrogen Molecular Orbital Diagram. CH4 Hybridization. 02 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram. Structure 3D. Hybrid Orbitals. N2 Molecular Orbital. Li2 Molecular Orbital Diagram.
Solved Generate The Mo Diagram For Ch4 As Square Planar And Ch4 As Tetrahedral Why Does Ch4 Not Exist As A Swaure Planar But It Does As A Tetrahed Course Hero
molecular orbitals. 2.The number of molecular orbitals formed is the same as that of the number of atomic orbitals combined. 3.The additive overlap results in the bonding molecular orbital while the subtractive overlap results in the antibonding overlap. 4.The energy of bonding molecular orbitals is lower than their nonbonding counterparts ...
Please explain me the orbital diagram and electron Dot structure of ccl4, h2o, nh3,ch4. why does graphite have high melting or boiling point if their bonding is weak. give one property of hydrogen chloride which agrees with it being a covalent compound. A covalent hydrocarbon molecule having four single covalent bond.
Hybrid Orbitals In order to explain the structure of methane (CH 4), the 2s and three 2p orbitals are converted to four equivalent hybrid atomic orbitals, each having 25% s and 75% p character, and designated sp 3. These hybrid orbitals have a specific orientation, and the four are naturally oriented in a tetrahedral fashion.
Molecular Orbital Analysis of Ethene Dimerisation π Molecular Orbitals of 1,3- Butadiene essentially the same theory about how acids and bases behave. π Molecular Orbitals of Ethene The diagram to the right shows the relative energies of the atomic p orbitals, the resulting π molecular orbitals and the electron.
c. Complete the molecular orbital diagram for methane, shown below, by doing the following: i. Label the atomic orbitals of C by writing their Mulliken symbols under the orbital(s). ii. Label the symmetries of the H 1s SALCs on the right-hand side of the diagram. iii. Add molecular orbitals to the center of the diagram and label their symmetries.
p-orbitals; 3p-orbitals; 3d-orbitals; 4f-orbitals; Compare shape and size of 1s, 2s and 2p orbitals; Molecular Orbitals. Hydrogen; Nitrogen; Fluorine; Ammonia; Methane; Ethylene (Ethene) Acetylene (Ethyne) Allene; Formaldehyde(Methanal) Acrolein; Carbon Monoxide; Hydrogen Fluoride; Allyl Anion; Butadiene; Benzene; Aromaticity of cyclic polyenes ...
Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us. Here is an energy level diagram showing how the 4 hydrogen 1s orbitals.Jan 18, · Using LCAO to Construct MOs for ...
A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti‐bonding molecular energy levels is provided below. (McQuarrie & Simon, Physical Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, p. 388) Methane has eight valence electrons, so according to the aufbau and Pauli exclusion principles the two lowest energy molecular orbitals ...

Scielo Brasil Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built
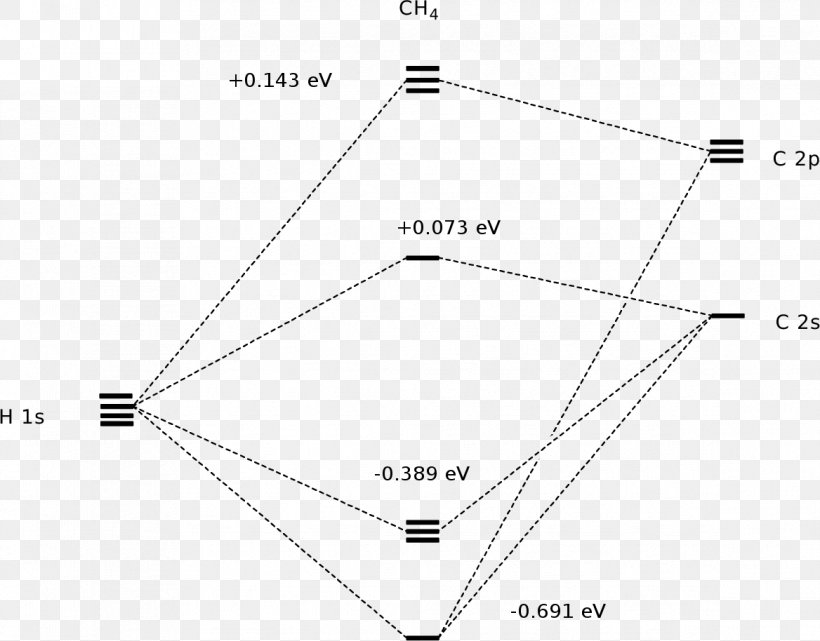
Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular Orbital Theory Methane Molecule Png 1168x914px Molecular Orbital Diagram Area Atomic Orbital

Chemistry Molecular Orbital Diagram Heteronuclear Molecule Molecular Orbital Diagram Angle Chemistry Molecule Png Pngwing


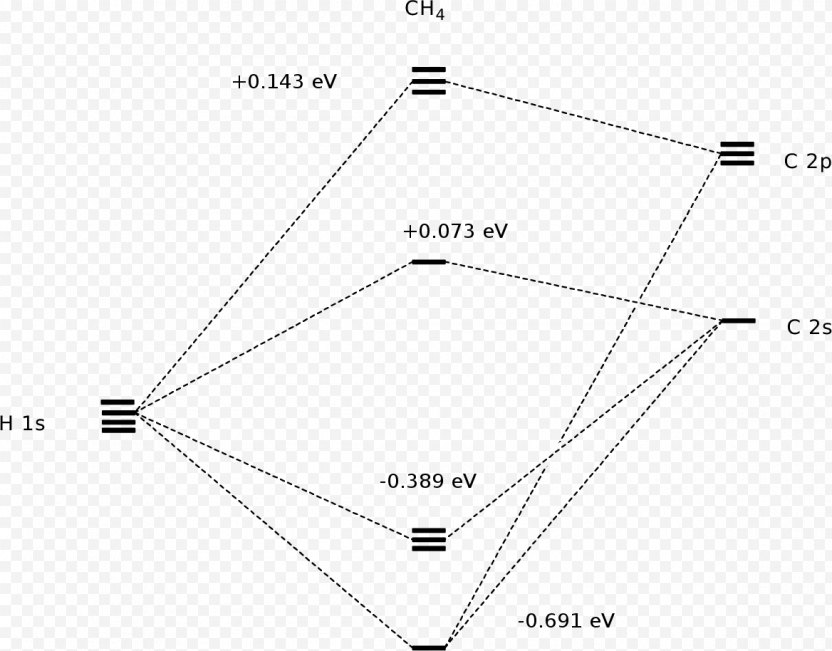












0 Response to "39 methane molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment