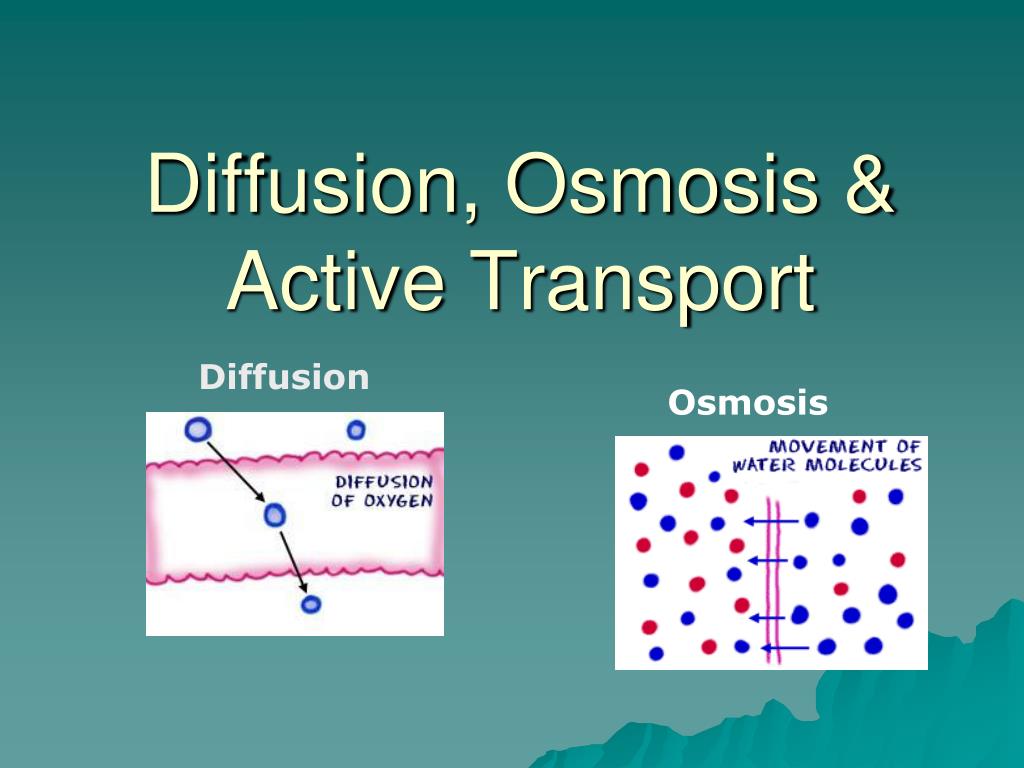
40 diffusion and osmosis diagram
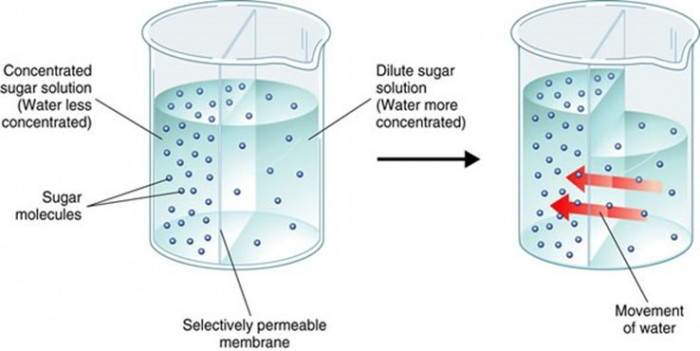
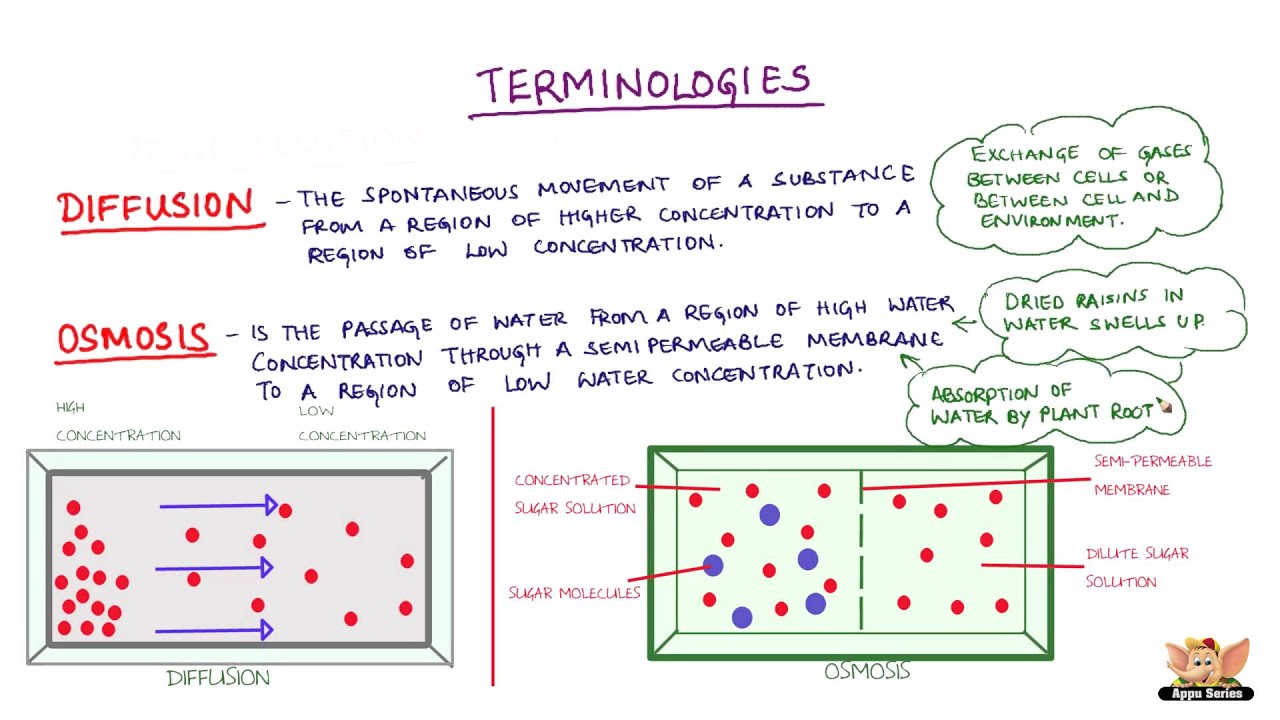
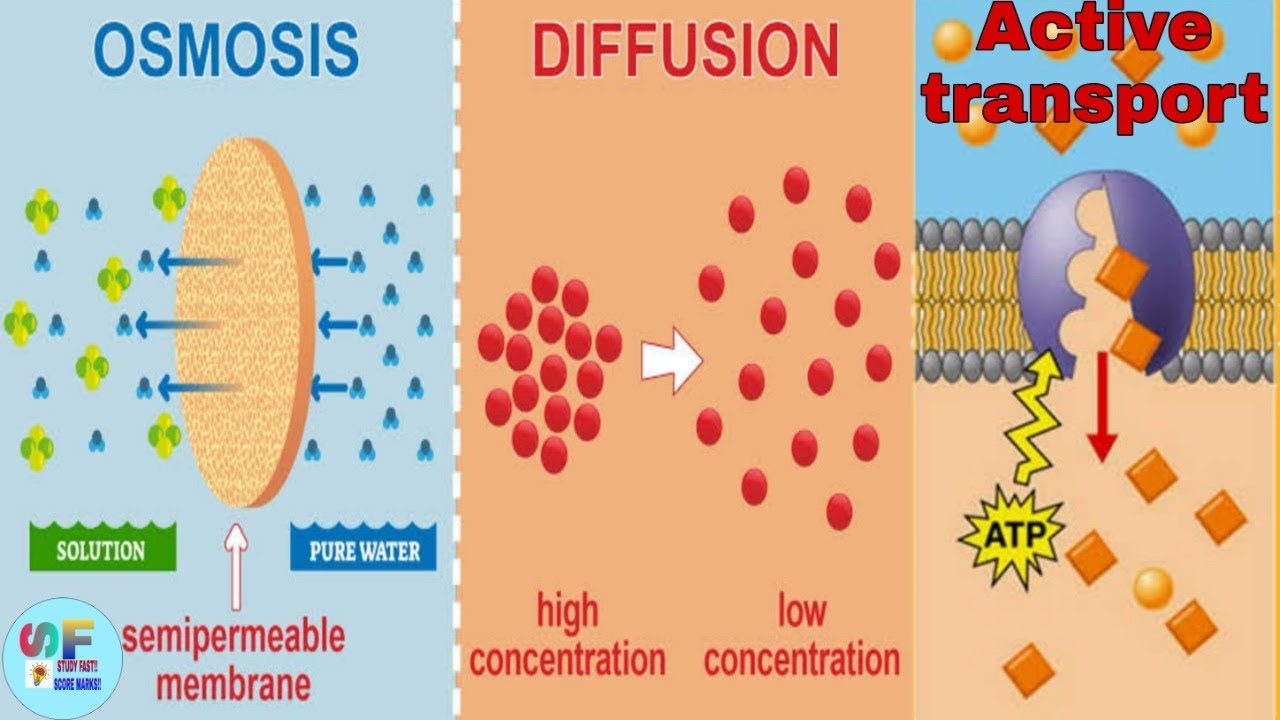
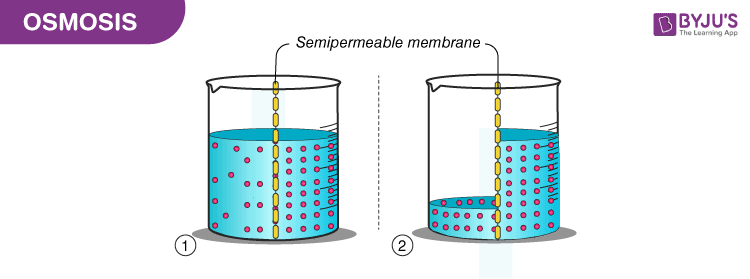
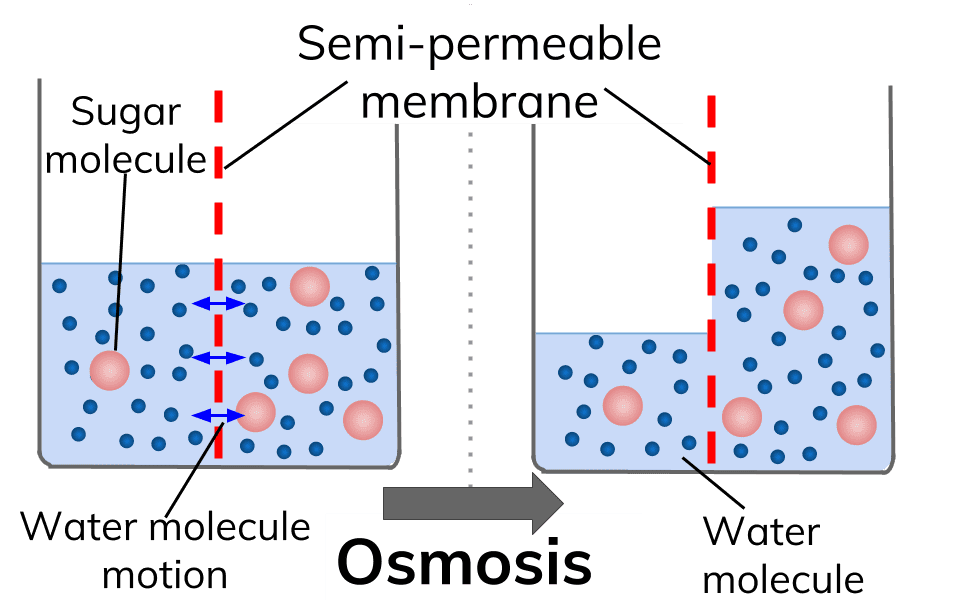
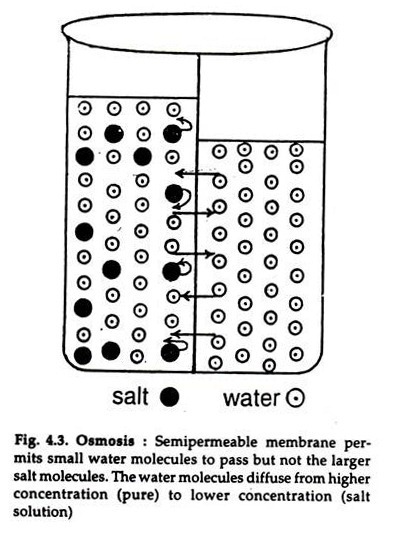
What is Osmosis? By definition, osmosis is the movement of any solvent through a selectively permeable membrane into an area of higher solute concentration, the result of which will be an equalizing of solute concentration on either side of the membrane.. This equilibrium is important for the efficient and optimized function of cells; as mentioned before, balance is the preferred state in a ... Osmosis is a special form of diffusion in which water molecules diffuse in the presence of semipermeable membrane from hypotonic solution to hypertonic solution. All diffusing molecules are known to possess some kinetic energy, called free energy. Free energy of pure water is higher than that of the same in a solution.
Diffusion sees molecules in an area of high concentration move to areas with a. Create a Venn diagram comparing osmosis and diffusion. Osmosis and diffusion play essential, but distinct roles in the human body. Diffusion sees molecules in an area of high concentration move to areas with a lower concentration, while osmosis refers to the process ...

Diffusion and osmosis diagram
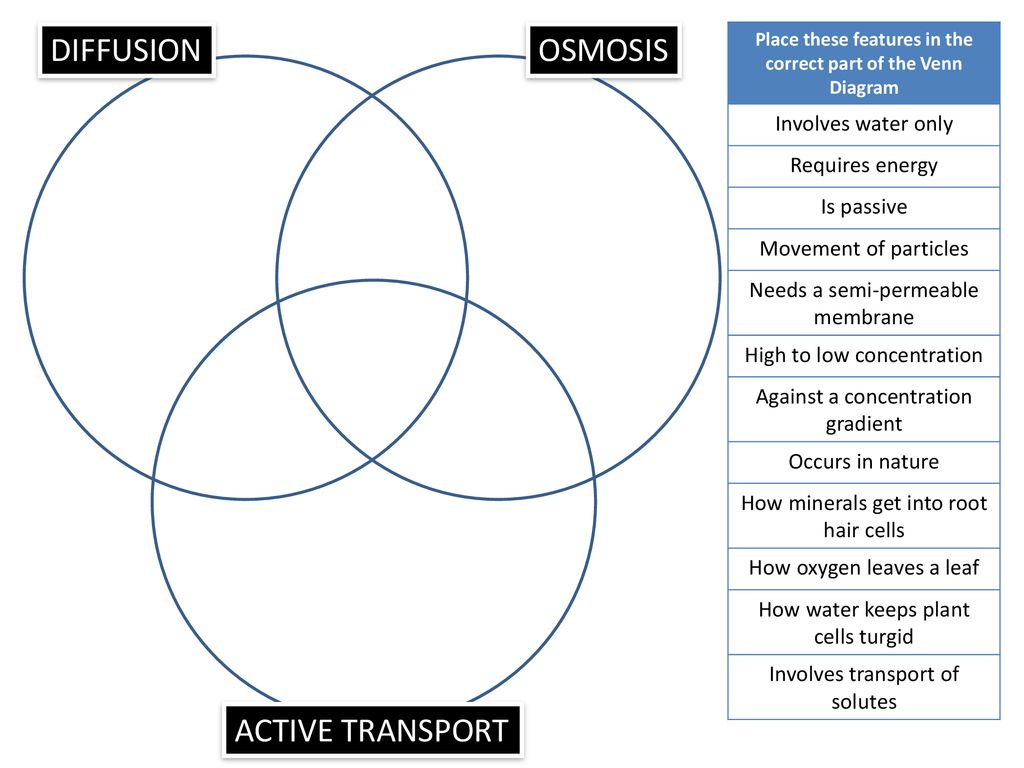
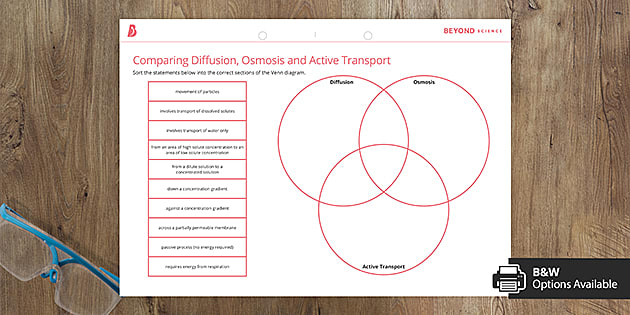
Osmosis is a type of passive transport occurring commonly in biological systems where solvent molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane towards a region of high solute concentration. Nature of the membrane. Diffusion occurs through any permeable membrane. Osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane. Nature of the process. This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Digestion and Absorption essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Digestion and Absorption by visiting the associated Learn Page. Diffusion, osmosis & active transport venn diagram - Google Slides. Place these features in the correct part of the Venn Diagram. Involves water only. Requires energy. Is passive. Movement of particles. Needs a semi-permeable membrane. High to low concentration. Against a concentration gradient.
Diffusion and osmosis diagram. Osmosis on the other hand only occurs between two solvents. Osmosis also takes much less time to occur than diffusion. A Venn Diagram showing Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport. You can edit this Venn Diagram using Creately diagramming tool and include in your report/presentation/website. A Venn Diagram showing Diffusion vs Osmosis. Venn Diagram Of Diffusion And Osmosis. Venn Diagram Of Diffusion And Osmosis. Tracy Tetreault. 116 followers . ... One page of doodle sketch notes on diffusion and osmosis packs in information and allows students to be creative. The activities are easy and fun, involving gummy worms (or other gummy candy) and tea bags. ... Osmosis can only function in a liquid medium, but diffusion can occur in all three mediums (solid, liquid and gas). Furthermore, osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane, while diffusion does not. The intake of water in plants is an example of osmosis. Diffusion is observed when a drop of food colouring is added to a glass of water, where ... Osmosis and Diffusion ( Venn Diagram) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. We were unable to load the diagram. You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel ...
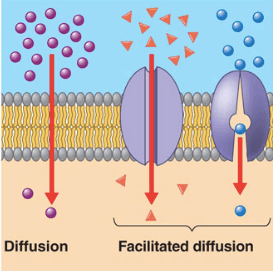
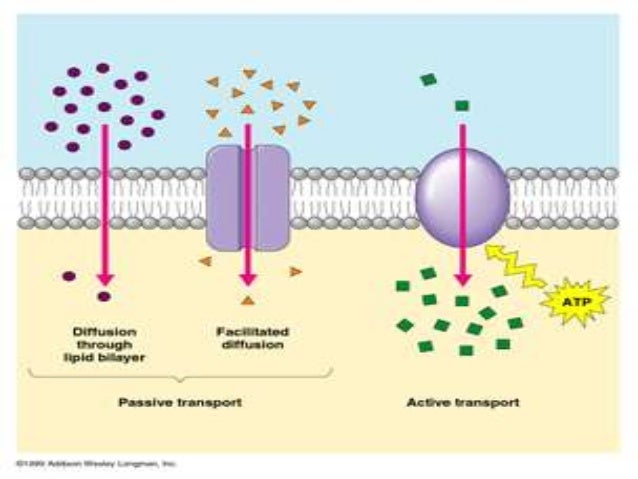
The below mentioned article explains about the osmosis and diffusion with the help of suitable diagrams. Diffusion: The movement of molecules of a solute in a solvent from higher to lower concentration is diffusion. The concentration of a solute in a solvent depends on the number of its molecule in a given volume of solvent. Osmosis and diffusion are related processes that display similarities. Both osmosis and diffusion equalize the concentration of two solutions. Both diffusion and osmosis are passive transport processes, which means they do not require any input of extra energy to occur. In both diffusion and osmosis, particles move from an area of higher Diffusion increases entropy (randomness), decreasing Gibbs free energy, and therefore is a clear example of thermodynamics.Diffusion operates within the boundaries of the Second Law of Thermodynamics because it demonstrates nature's tendency to "wind down", to seek a state of less concentrated energy, as evidenced by increasing entropy.. Osmosis is the process of diffusion of water across a ... Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Name: _____ Diffusion. is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. It is a natural, random process. This means that it does not require extra energy input. These are pictures of molecules frozen at two different times.
Start studying Osmosis, Diffusion, Active Transport. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Basic Characteristics of Osmosis. Requires a semipermeable membrane. A slow and spontaneous process. Occurs in liquid medium. Requires no energy expenditure and thus also called passive diffusion. Movement of water occurs from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential. The process continues until the concentration of ... Diffusion does not depend on solute potential, pressure potential, or water potential. Osmosis depends on solute potential. Diffusion mainly depends on the presence of other particles. Osmosis mainly depends on the number of solute particles dissolved in the solvent. Diffusion is a passive process. #DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS CHALLENGE ANSWER KEY #Download file | read online labeling, diagram reading, and coloring exercises Putting It All Together including multiple-choice quizzes and case studies Challenge Yourself! with critical thinking questions and puzzles
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet. Diffusion. is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. It is a natural, random process. This means that it does not require extra energy input. 1a. These are pictures of molecules frozen at two different times.
Share the following explanation with students, using the diagram on the board: • Tell students to recall that diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Osmosis refers to the movement of water moleculesacross a membrane trying to achieve equilibrium.
Osmosis and the Movement of Water. Water moves across cell membranes by diffusion, in a process known as osmosis. Osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, with the solvent (water, for example) moving from an area of low solute (dissolved material) concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
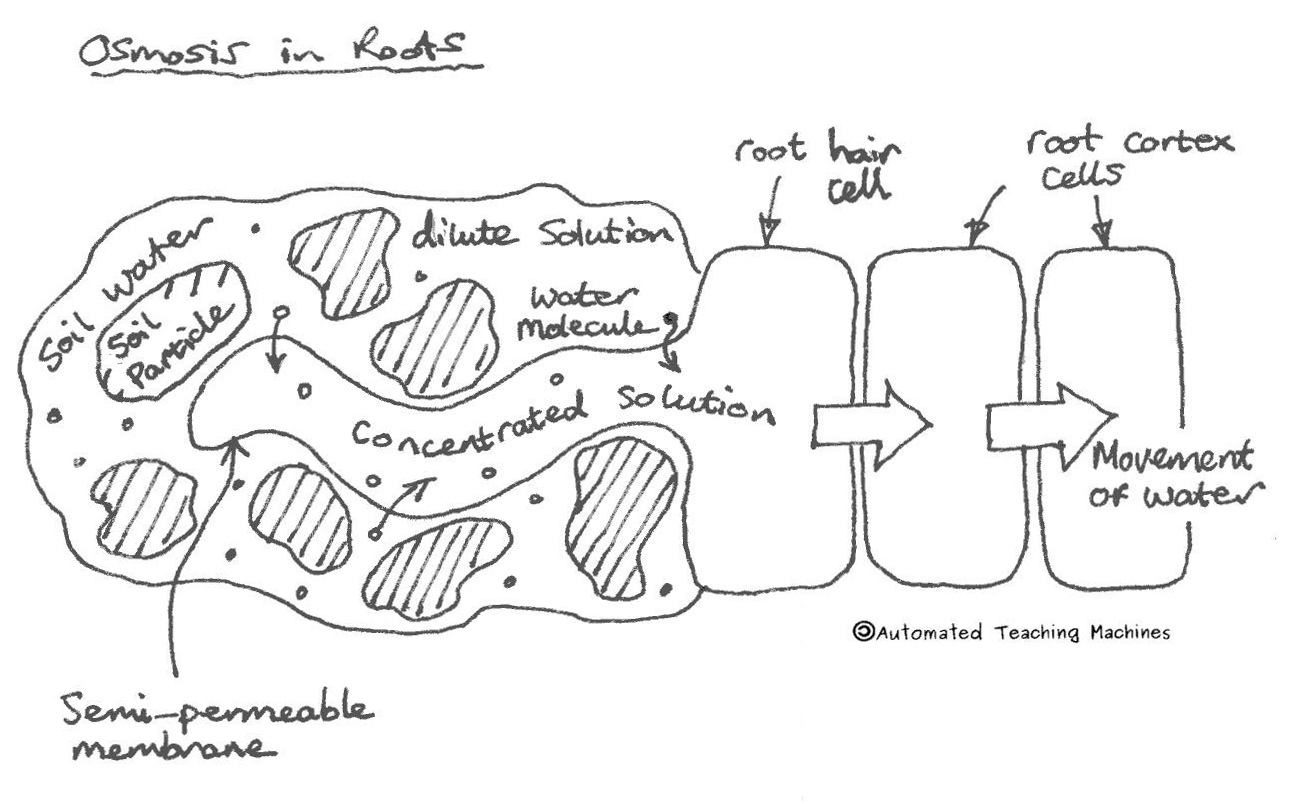
ADVERTISEMENTS: Process of Diffusion in Plant Cell (With Diagrams)! Diffusion: The movement of various substances into a plant, usually from the soil, out of which the green plant synthesises the numerous complex organic compounds, is accomplished, principally through the agency of the process known generally as diffusion. In some cases, however, the operation of the […]
Ven diagram of osmosis vs diffusion. Diffusion and osmosis are both passive transport processes, meaning they require no energy input to move substances. Both processes are essential to the proper ...
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet. Diffusion. is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. It is a natural, random process. This means that it does not require extra energy input. 1a. These are pictures of molecules frozen at two different times.
Diffusion and Osmosis The cell membrane plays the dual roles of protecting the living cell by acting as a barrier to the outside world, yet at the same time it must allow the passage of food and waste products into and out of the cell for metabolism to proceed.
osmosis-and-diffusion-venn-diagram. Ven diagram of osmosis vs diffusion. Diffusion and osmosis are both passive transport processes. Students place comments into the correct sections of a Venn diagram. Page 2 contains correct answers. can be projected onto IWB or page 1.
Osmosis Osmosis is a special example of diffusion. It is the diffusion of water through a partially permeable membrane from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution - down the water potential gradient) Note: diffusion and osmosis are both passive, i.e. energy from ATP is not used.
Solid, liquid or gas, diffusion can take place in any of these media. Osmosis can take place only in a liquid medium. No requirement of semi-permeable membrane for diffusion to occur. Semi-permeable membrane is a must for osmosis to take place. There is the equalization of concentration to occupy the available space.
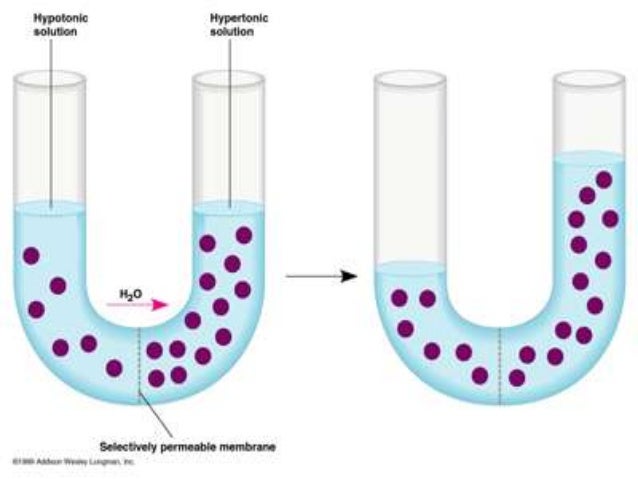
DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS CHALLENGE KEY The following questions refer to the diagram below. The solutions in the two arms of the U-tube are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. At the beginning of the experiment the volumes in both arms are the same, and the level of the liquid is therefore at the same height.
Diffusion, osmosis & active transport venn diagram - Google Slides. Place these features in the correct part of the Venn Diagram. Involves water only. Requires energy. Is passive. Movement of particles. Needs a semi-permeable membrane. High to low concentration. Against a concentration gradient.
This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Digestion and Absorption essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Digestion and Absorption by visiting the associated Learn Page.
Osmosis is a type of passive transport occurring commonly in biological systems where solvent molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane towards a region of high solute concentration. Nature of the membrane. Diffusion occurs through any permeable membrane. Osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane. Nature of the process.













(96).jpg)






0 Response to "40 diffusion and osmosis diagram"
Post a Comment