41 nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram
The poor catalyst stability in acidic oxidation evolution reaction (OER) has been a long-time issue. Herein, we introduce electron-deficient metal on semiconducting metal oxides-consisting of Ir ... Molecular Orbital Diagram Of N2. ... High temperature combustion in the presence of nitrogen gas, such as in automobile engines, can generate nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide. Both gases are poisonous on their own, while they also play a role in the production of peroxyacetyl nitrate , a major component of smog, and nitric acid, which is part ...
Name each molecular compound. CHEBI:16480 - nitric oxide. Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical, i.e., it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (·N=O. or ·NO).
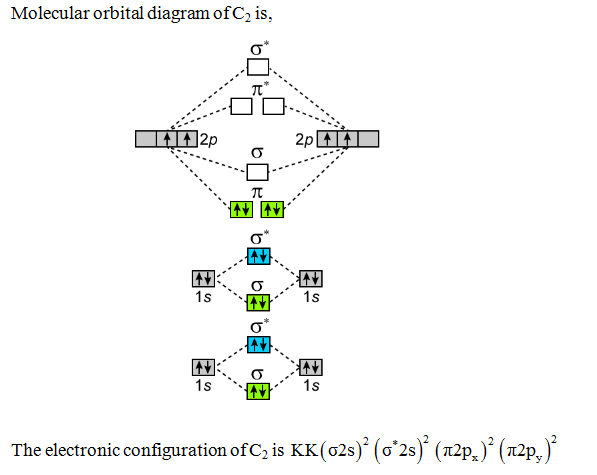
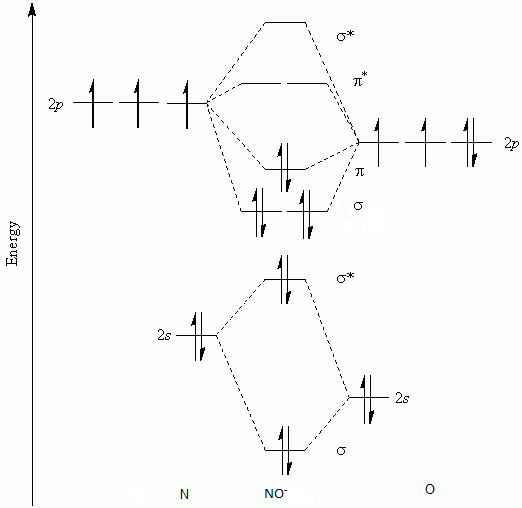
Nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram
Results #1. Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it ? The bond order Can have a negative quantity Can have a negative quantity Has always an integral value Has always... Beryllium (Be) is a metal and Chlorine (Cl) is a non-metal. Beryllium Chromate Dihydrate. Example #2: ferrous oxide The electrons removed when nitrogen and oxygen are ionized also come from 2p orbitals. HSO 4 − Hydrogen sulfate . To oxidize nitrogen to nitric oxide, there should be high temperature. ... Now the next topic to cover is the molecular orbital diagram of nitrous oxide. N2O Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular orbital diagrams say about the mixing of orbitals in a compound. Using a MO diagram, the bond order of a compound can be determined which gives us an idea about bond length, bond stability as well.
Nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram. Like nitrous oxide, it has a linear molecular structure, but with the great difference that the N = O bond also has the character of a triple bond. NO is rapidly oxidized in air to produce NO 2 , thus generating more stable molecular orbitals with a more oxidized nitrogen atom (+4). 2NO (g) + O 2 (g) => 2NO 2 (g) Is nitrous oxide the same as nitric oxide? Nitric oxide (NO) is often confused with nitrous oxide (N2O, sometimes called "laughing gas"), the anesthetic whose second nitrogen atom creates a completely different structure with different chemical properties. Nitric oxide's single unpaired electron creates its immense signaling power. HNO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Bond Angle, and Shape. The chemical formula HNO2 represents Nitrous Acid. HNO2 is also known as. Dioxonitric (III) acid. It is a weak acid and exists only in specific conditions, i.e., in solution (cold and dilute), as a gas, or in the form of nitrite salts. As we discussed before, NO is polar. This is because the non-bonding orbitals give rise to partial + and - charges on O and N sides. Conclusion. An elaborate explanation has been given about nitric oxide and its bonding nature. We have drawn the most suitable Lewis Structure and found out the Molecular geometry i.e. the three-dimensional ...
Calculate Bond Order From Molecular Orbital Diagram. Collected from the entire web and summarized to include only the most important parts of it. Can be used as content for research and analysis. ... Nitric oxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule. Reaction of O 2 with N 2 at high temperatures in internal combustion engines ... The highest occupied molecular orbitals are mainly located on oxygen atoms. On the other hand, the distribution of LUMO orbitals is minimal on the nanocluster. Considerable changes in the frontier molecular orbitals are stem from the interaction between CH 4 S molecule (complex C) and Ca 12 O 12 nanocluster. A molecular orbital that is formed by addition overlap (i.e., when the lobes of atomic orbitals overlap with the same sign) of two atomic orbitals is known as bonding molecular orbital. It is represented as ψ MO = ψ A + ψ B Its energy is lower than the atomic orbitals from which it is formed. It favours bonding. No it is not paramagnetic.O2^2- has 2 electrons more than O2.Pi 2p molecular orbitals get completely filled hence it is diamagnetic. Molecules such as N 2 and ions such as Na + and [Fe (CN) 6] 4â that contain no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic. ...
Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the main environmental pollutants produced by fossil combustion, which caused acid rain, ozone depletion, and photochemical smog .In recent years, most countries have formulated quite strict policies to suppress NO emissions into the atmosphere [2,3].Therefore, the conversion of NO to harmless substances including nitrate (NO 2 −), nitrogen (N 2) and ammonia (NH 3 ... Introduction. First being recognized as an endothelium-derived relaxing factor, 1 nitric oxide (NO) is continually appreciated for its diverse roles in virtually every cell function. Synthesis and metabolism of NO are tightly regulated in living cells. 2 - 4 Dysregulation of NO homeostasis is associated with various diseases, for example, cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory diseases, and ... Molecular Orbital and Energy Decomposition Analysis Renato P. Orenha,[a, b] Marcus V. J. Rocha,[b, c] Jordi Poater,*[d, e] S8rgioE.Galembeck,*[a] and F. Matthias Bickelhaupt*[b, f] 1. Introduction Nitric oxide (NO) is involved in alarge number of physiological and physiopathological processes, such as abiological messen- molecular orbitals of nitric oxide. It is interesting to note that in homonuclear dioxygen molecules, all EDT's are strongly forbidden by the central point (invers ion) symmetry and only weak ...
a) Sulphuric Acid. b) Hydrochloric Acid. c) Nitric Acid. d) Phosphoric Acid. Answer. a) Sulphuric Acid. 6. A gas cylinder of the capacity of 20 dm3 is filled with gas X, the mass of which is 10 g. When the same cylinder is filled with hydrogen gas at the same temperature and pressure the mass of the hydrogen is 2 g.
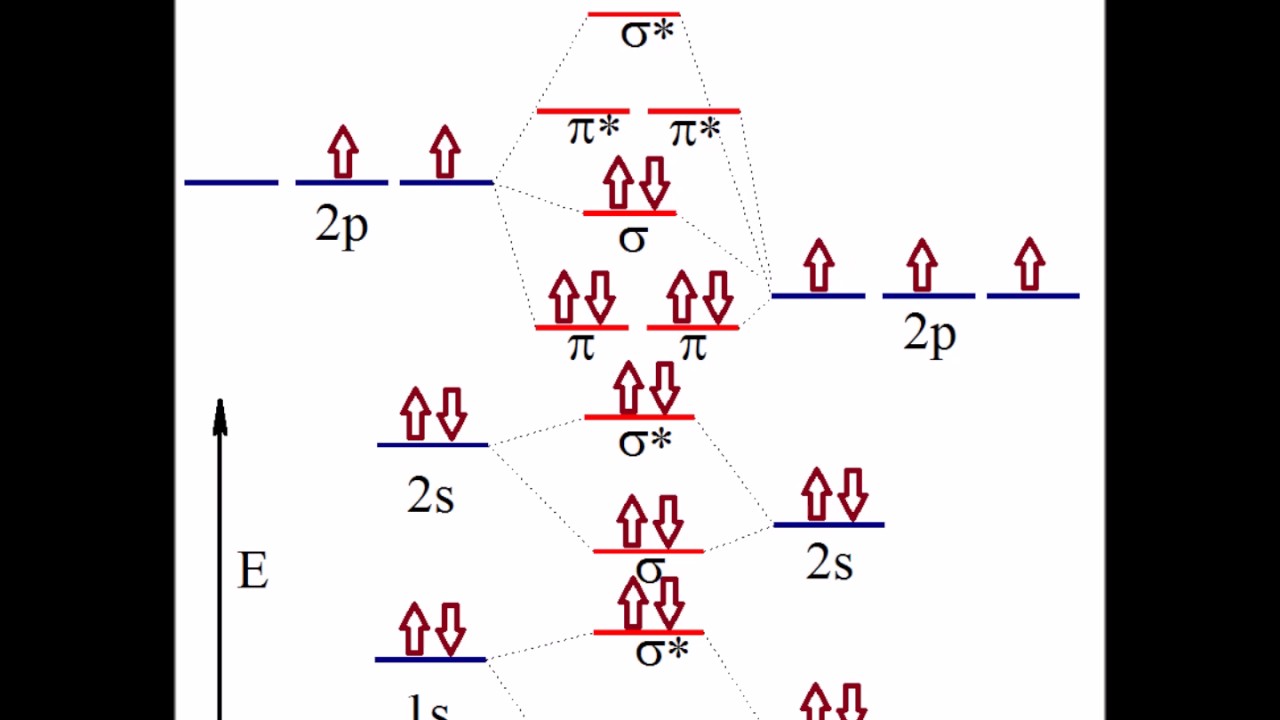
Molecular orbital diagram of dinitrogen molecule, N 2. There are five bonding orbitals and two antibonding orbitals (marked with an asterisk; orbitals involving the inner 1s electrons not shown), giving a total bond order of three. ... Nitric oxide (NO) is the simplest stable molecule with an odd number of electrons. In mammals, including ...
2. CO and NO—Chemistry. Both CO and NO are diatomic gaseous oxides of carbon or nitrogen, respectively. CO is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air [].NO is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen and also is a colorless gas [].Spectroscopic data are available in the literature and databases: Fourier Transform Infrared (SpectraBase Spectrum ...
Molecular terms of dioxygen and nitic oxide are presented. Electron spin resonance spectra of diatomic molecules corresponding to these terms are discussed. Gas-phase ESR can be a convenient method of monitoring paramagnetic pollutants in the atmosphere. We ran additional calculations in molecular physics for terms of these molecules and Zeeman transitions.
Compounds of Nitrogen: We know that nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the earth's atmosphere. The element nitrogen is a group 15 elements. It is non-metal and exists in the gaseous state. The gaseous nitrogen (N2) comprises about 78% by the volume of our atmosphere. Nitrogen combines with other elements to form several compounds.

The Negative Ion Chemistry Of Nitric Oxide In The Gas Phase Chacko 2006 Mass Spectrometry Reviews Wiley Online Library
Nitric oxide is a relatively unstable, diatomic molecule that possesses a free radical (i.e., an unpaired electron). The molecule can gain or lose one electron to form the ions NO− or NO+. In the chemical industry, nitric oxide is an intermediate compound formed during the oxidation of ammonia to nitric acid.
Di helium cation (He2+) possess three electron over all two are present in bonding sigma molecular orbital and are paired and one electron in antibonding sigma orbital which is unpaired. From above discussion hope you have guessed that only dihydrogen H2 is diamagnetic species.
The UV spectrum of nitric oxide shows absorption below 200 nm due to weak electronic transitions to unoccupied orbitals, and the onset of photoionization to nitrosonium NO+ by ejection of the unpaired electron from the n* orbital. As expected for an antibonding electron, the ionization threshold is fairly low with 9.26 eV.
Now the next topic to cover is the molecular orbital diagram of nitrous oxide. N2O Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular orbital diagrams say about the mixing of orbitals in a compound. Using a MO diagram, the bond order of a compound can be determined which gives us an idea about bond length, bond stability as well.
Beryllium (Be) is a metal and Chlorine (Cl) is a non-metal. Beryllium Chromate Dihydrate. Example #2: ferrous oxide The electrons removed when nitrogen and oxygen are ionized also come from 2p orbitals. HSO 4 − Hydrogen sulfate . To oxidize nitrogen to nitric oxide, there should be high temperature. ...
Results #1. Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it ? The bond order Can have a negative quantity Can have a negative quantity Has always an integral value Has always...
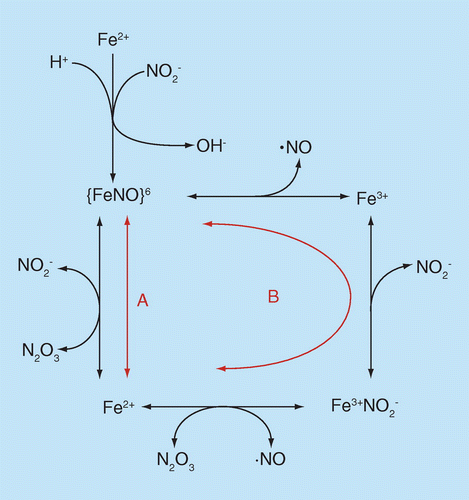
Nitric Oxide A Brief Overview Of Chemical And Physical Properties Relevant To Therapeutic Applications Future Science Oa
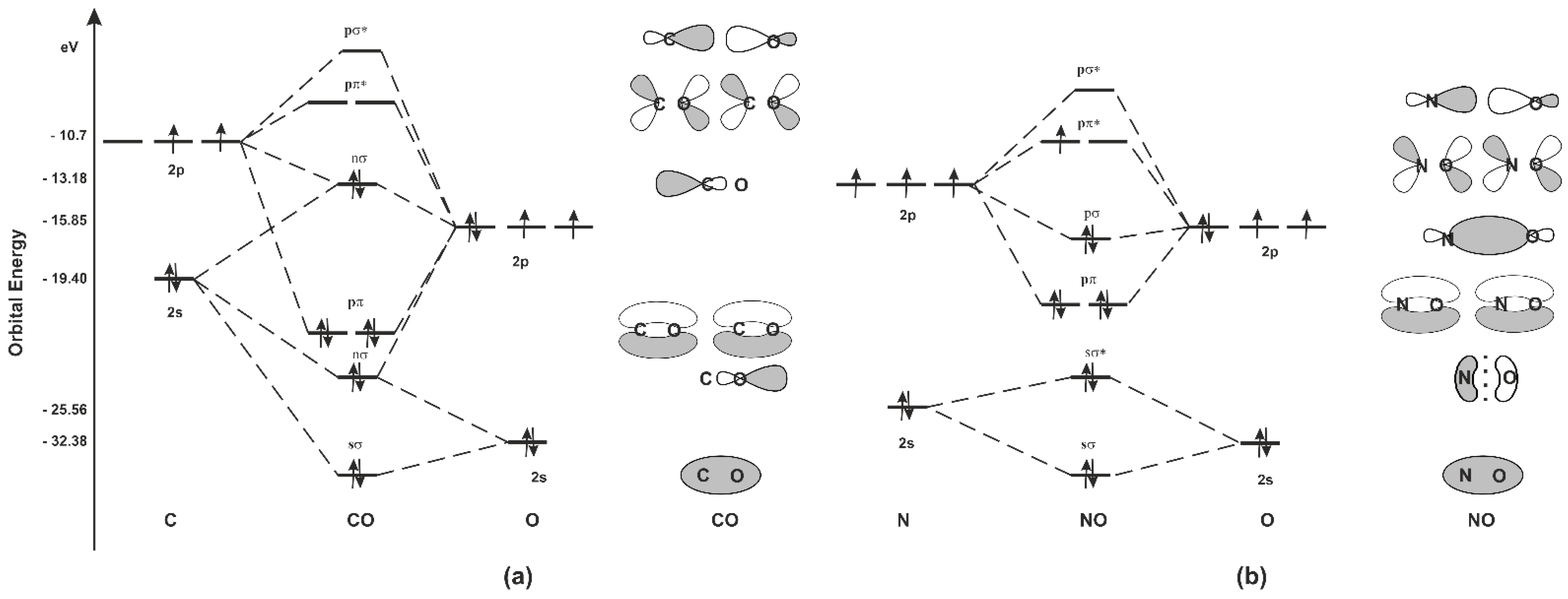
Ijms Free Full Text Carbon Monoxide And Nitric Oxide As Examples Of The Youngest Class Of Transmitters Html
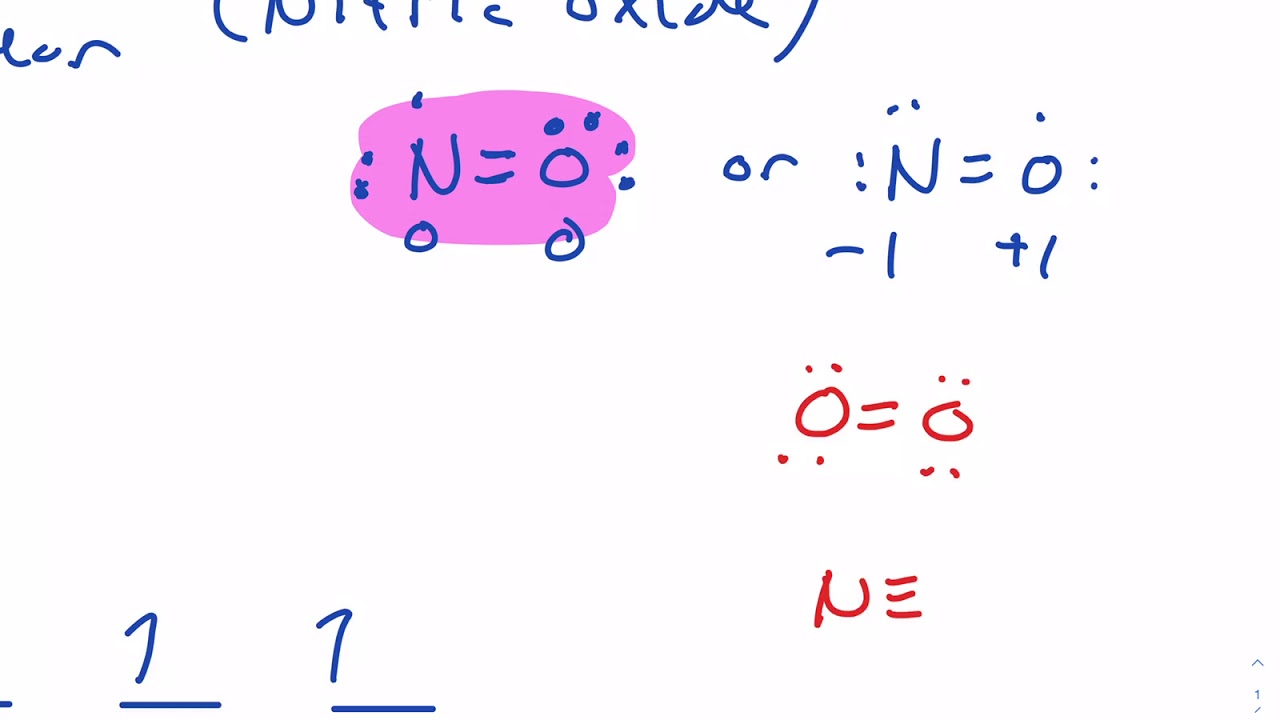

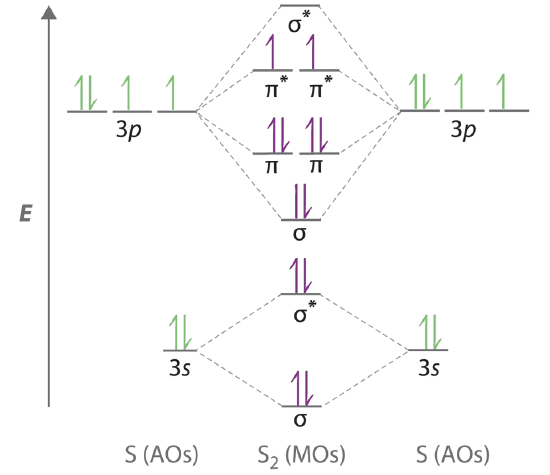



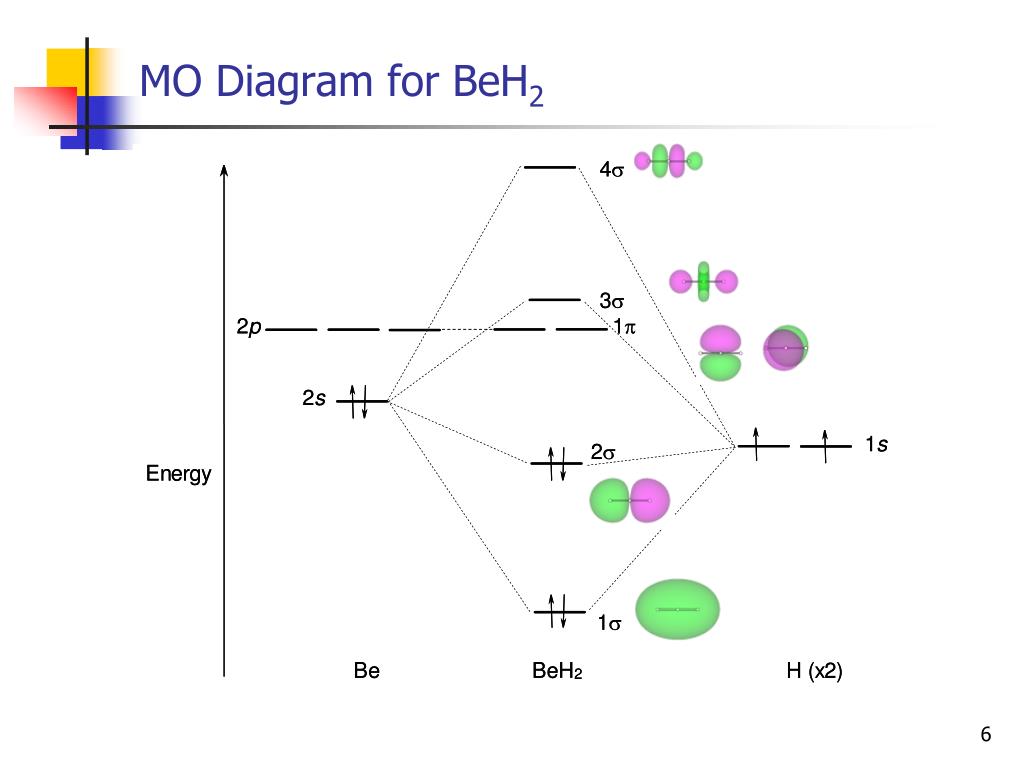

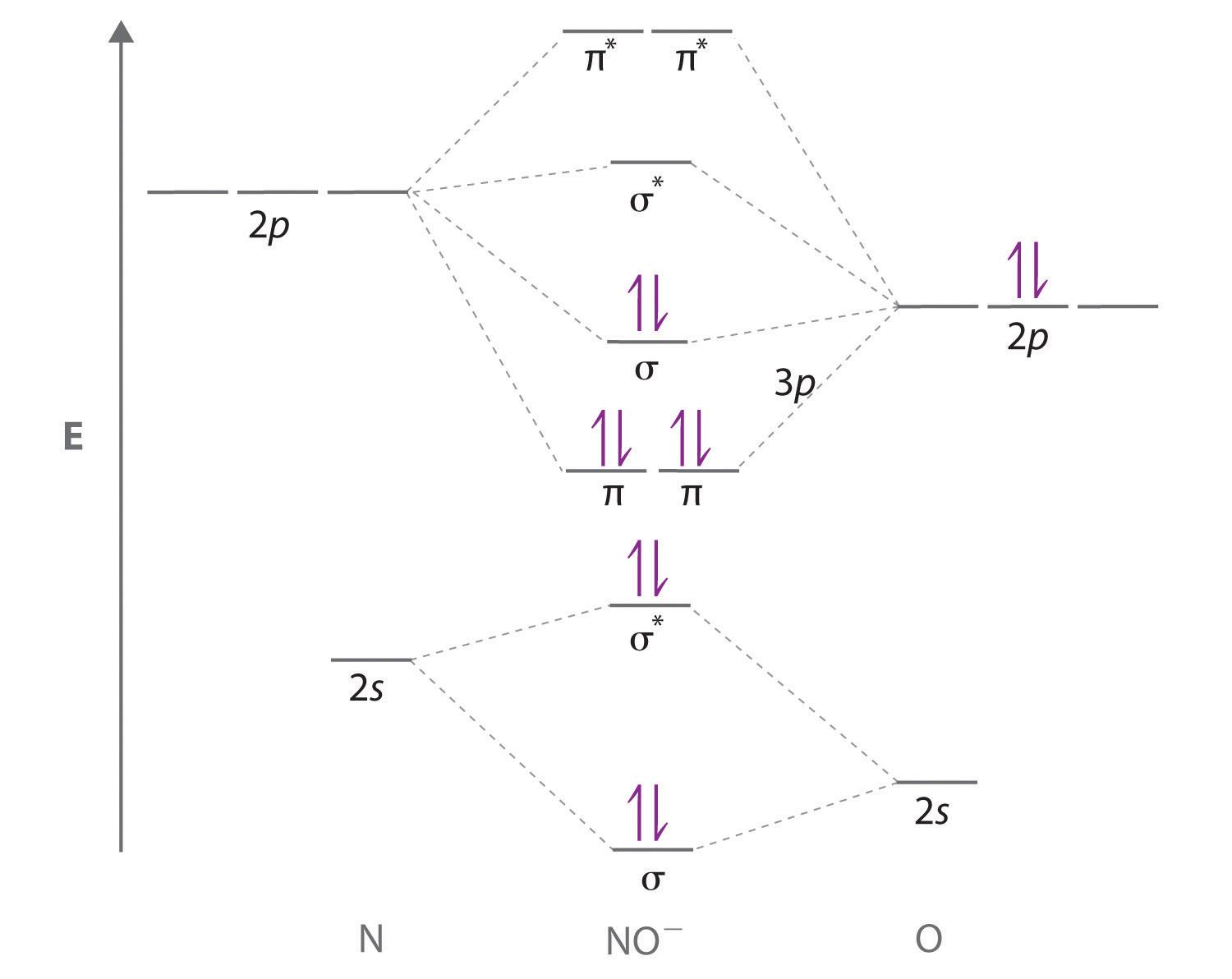




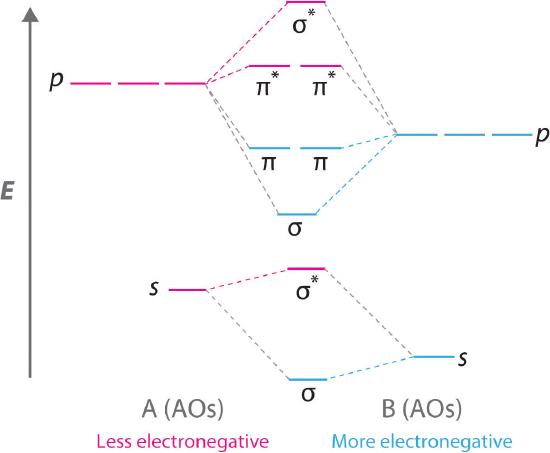


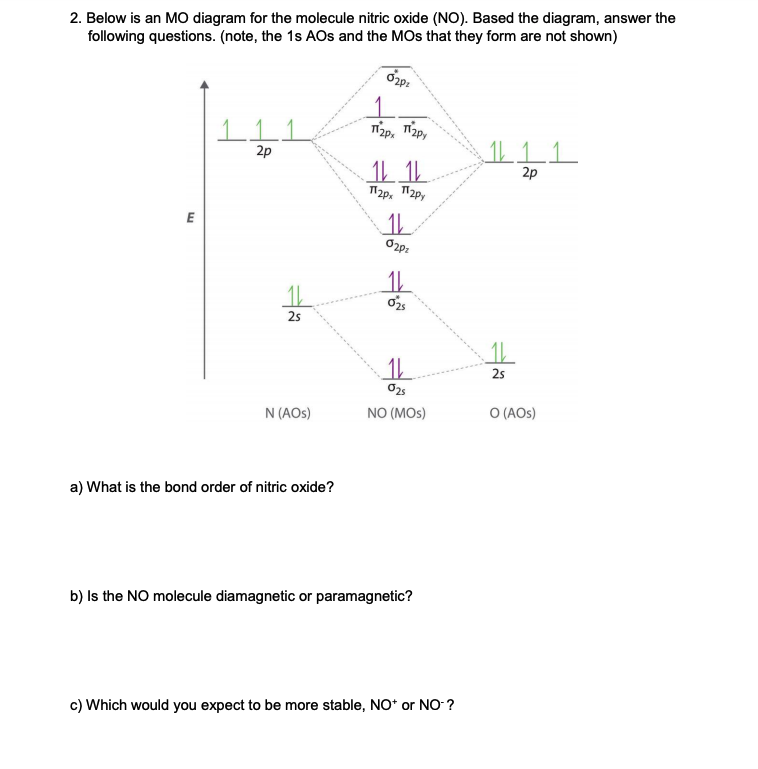
0 Response to "41 nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment