42 muscles of respiration diagram
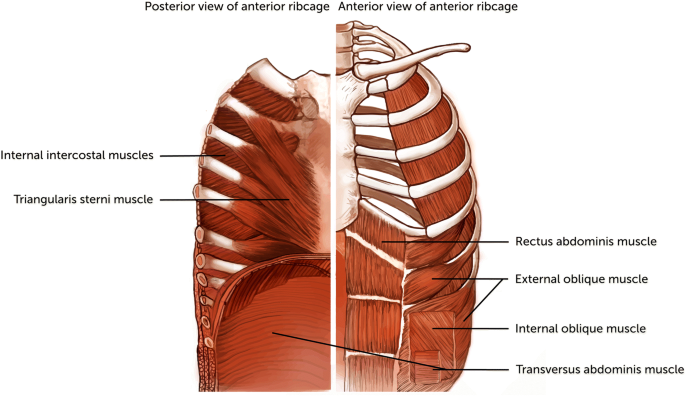
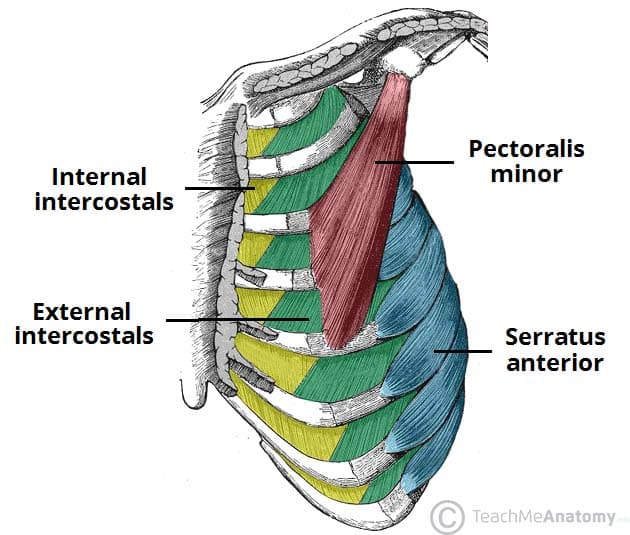
Original Editors - Rachael Lowe. Top Contributors - Khloud Shreif , Andeela Hafeez , Candace Goh , Vidya Acharya , Rachael Lowe , Admin , George Prudden , Kim Jackson , Evan Thomas , Tomer Yona , WikiSysop , Lenny Vasanthan T and Lucinda hampton -. The muscle fibres of the external intercostal group run forwards and downwards and those of the internal intercostal group run backwards and downwards from rib to rib (Fig. During violent respiratory effort even the platysma and all other muscles of the trunk take part in respiration.
Respiratory system. The human respiratory system is adapted to allow air to pass in and out of the body, and for efficient gas exchange to happen.

Muscles of respiration diagram
Cell respiration is the process of creating ATP. It is "respiration" because it utilizes oxygen. In anaerobic respiration, this is where the process ends, glucose is split into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. When oxygen is present, pyruvic is broken down into other carbon compounds in the Kreb's Cycle. The muscles of respiration and the lungs themselves are elastic, so when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax there is an elastic recoil The medulla oblongata is the primary respiratory control center. Its main function is to send signals to the muscles that control respiration to cause... the muscles of respiration are those muscles that: • contribute to inhalation and exhalation • by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. Respiratory muscles of carnivores. 1. M. scalenus dorsalis 2. M. scalenus medius 3. M. serratus dorsalis cranialis 4. M...
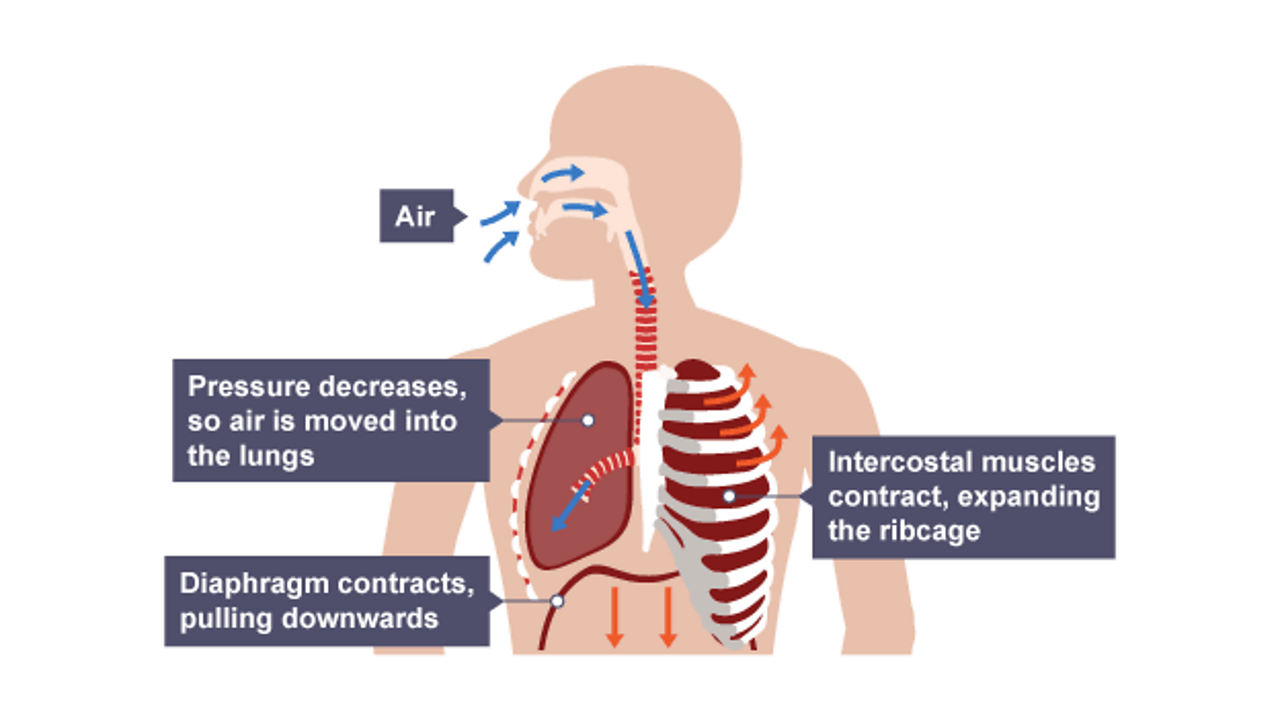
Muscles of respiration diagram. The respiratory muscles relax and the chest cavity contracts. The elastic lungs recoil and pushes air out through the air passages where it is emptied into Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood are monitored by the respiratory center in the brainstem. This in turns control the rate of respiration... (a) Lateral view of the intercostal muscles. (b) Inferior view of the diaphragm Learn with flashcards, games and more — for free. The Human Respiratory System - explore anatomy of the upper and lower respiratory tracts, from nasal passages to the lungs, using interactive Finally, the muscles of respiration, including the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, work together to act as a pump, pushing air into and out of the... Respiratory System For Kids: Diagram, Parts, Functions, And Facts. External respiration: The gaseous exchange between the external air and the blood inside the lungs is known as external Lungs cannot expand on their own and require muscles of respiration for inhalation and exhalation.
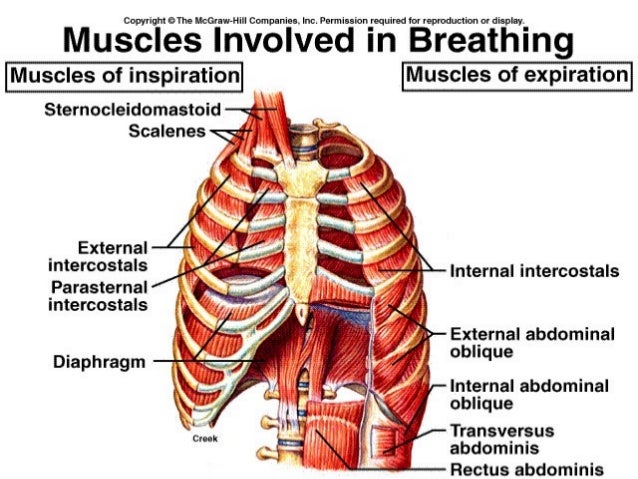
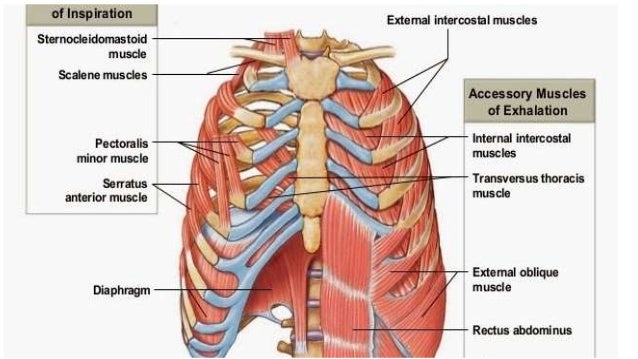
Muscles of respiration (inspiratory muscles). Respiratory System: Muscles - Respiratory Medicine | Medical Education Videos. Along with the diaphragm, the intercostal muscles are one of the most important groups of respiratory muscles. These muscles are attached between the ribs and are... External respiration: pulmonary ventilation (breathing) and gas exchange in the pulmonary capillaries of This diagram shows the locations of pressures involved in the pressure gradients needed for FIGURE 27-6 Movement of the rib cage during breathing. A, Inspiratory muscles pull the ribs upward... We can use more muscles than the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to move the ribs and sternum, and these are the accessory muscles of respiration.Music by... Respiratory Structures: Nasal Cavity Oral Cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchiole Left and Right Bronchii Left and Right Lung Alveoli Sac Alveolus Pulmonary Respiration at rest: What causes expansion of the thoracic cavity and therefore breathing? Muscles - Actively contract/passively relax.
The muscle of this region that is important in breathing is the serratus anterior. It overlies the lateral part of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the axilla. These vital organs of respiration inside the thorax are the site responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. These soft and spongy... Diagram of the Human Respiratory System (Infographic). The primary organs of the respiratory system are the lungs, which function to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide as we breathe. Muscles of Respiration. During quiet breathing, the predominant muscle of respiration is the diaphragm. As it contracts, pleural pressure drops, which lowers the alveolar pressure, and draws air in down the pressure gradient from mouth to alveoli. Respiration — In biochemistry, respiration may refer to: *Cellular respiration, the process in which the chemical bonds of energy rich molecules such as glucose are converted into energy Il respire par un système de trachées se divisant en trachéoles, et apportant directement l air aux cellules.
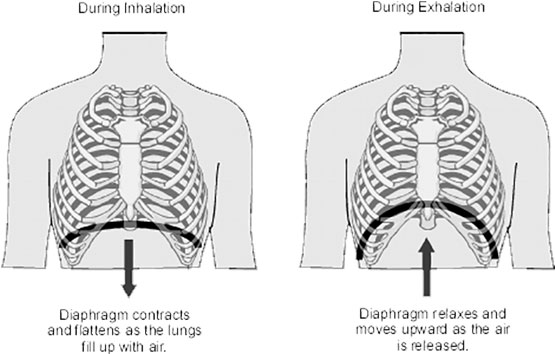
Diagram of the respiratory system. Air enters the body via the nose (preferably) or the mouth. Inhalation is active, because it requires muscle contraction. The major muscle of respiration is a sheet-like dome shaped muscle called the diaphragm that is located below the lungs.
Respiratory muscles mediate the movement of air into and out of the body. The bronchioles lead to the respiratory zone of the lungs, which consists of respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and the alveoli, the multi-lobulated sacs in which most of the gas exchange occurs.
Respiratory system. Respiration rate (RR) at rest. Tidal volume (TV) at rest. 1) local vasoconstriction (contraction of smooth muscles of vessel wall); 2) platelets adhesion (involving Willebrand's factor), their activation and secretion of platelets granules (involving thromboxan A2...
Expiratory Muscle Dysfunction In Critically Ill Patients Towards Improved Understanding Springerlink
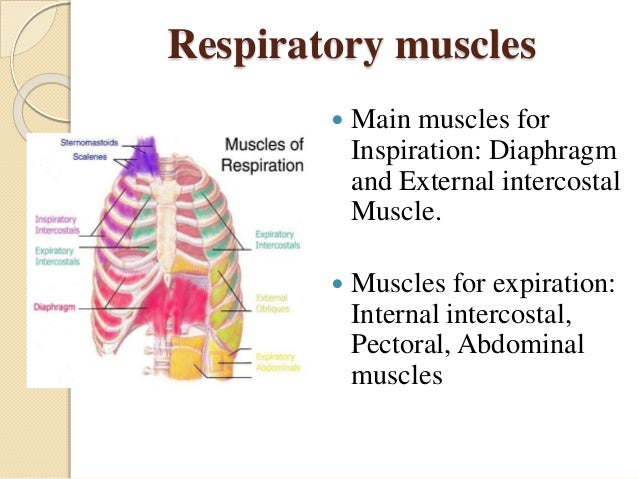
The muscles of respiration are those muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during quiet breathing.
Schematic diagram of the action of the external intercostal muscles. Excluding the cortical respiratory controls described above, which override spontaneous respiration, we have to examine the neurological mechanisms of quiet breathing and its reflex modification for changed circumstances...
Mechanics of Breathing. Muscles of Respiration. Topics. Muscles of expiration. internal and external oblique muscles, rectus abdominis, transversus abdominis.
Respiration. Respiratory System: Primary function is to obtain oxygen for use by body's cells & eliminate carbon dioxide that cells produce. Breathing is an active process - requiring the contraction of skeletal muscles. The primary muscles of respiration include the external intercostal muscles...
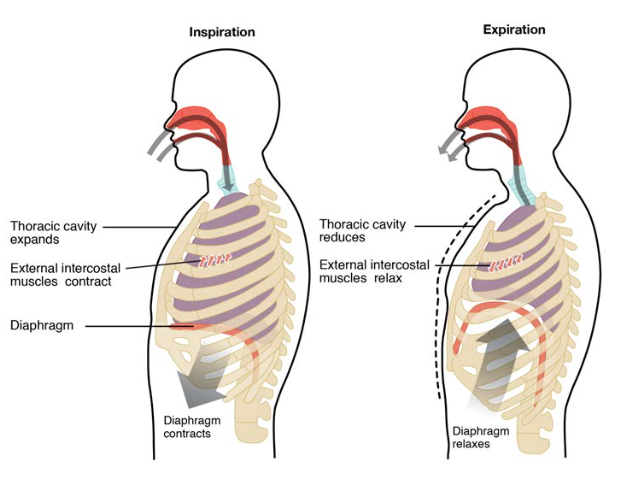
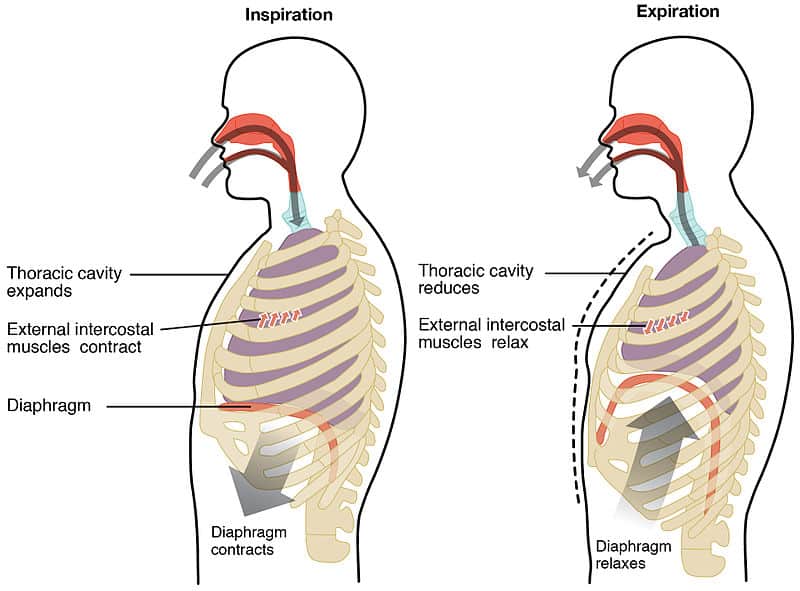
Fig 2 - Diagram showing the process of inspiration and expiration at rest. Active inspiration involves the contraction of the accessory muscles of breathing (in addition to those of quiet Opened chapter Respiration Overview. The processes of inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out) are...
respiratory muscles length at lung volume different than RV, FRC, and TLC during respiration. EMG. signal is depicted from the vicinity near the electrode The human chest wall is a complex structure, and the contribution of its different components to effi-. cient respiration has been the subject of...
Muscles of respiration (diaphragm and intercostal muscles) along with accessory muscles of respiration described. Respiration involves Inspiration and Expiration which are accompanied by the alternate increase and decrease of the volume of thoracic cavity.
Human respiratory system, the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. The major organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm. Learn about the anatomy and function of the respiratory system in this article.
the muscles of respiration are those muscles that: • contribute to inhalation and exhalation • by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. Respiratory muscles of carnivores. 1. M. scalenus dorsalis 2. M. scalenus medius 3. M. serratus dorsalis cranialis 4. M...
The muscles of respiration and the lungs themselves are elastic, so when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax there is an elastic recoil The medulla oblongata is the primary respiratory control center. Its main function is to send signals to the muscles that control respiration to cause...
Cell respiration is the process of creating ATP. It is "respiration" because it utilizes oxygen. In anaerobic respiration, this is where the process ends, glucose is split into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. When oxygen is present, pyruvic is broken down into other carbon compounds in the Kreb's Cycle.









/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12404/anatomy-of-respiratory-system_english.jpg)











0 Response to "42 muscles of respiration diagram"
Post a Comment