40 square planar mo diagram
• square planar complexes can be derived by removing the axial ligands from an octahedral complex. • last year you learnt (based on crystal field theory) roughly what happens contract, raising the energy of the dxy and dx2-y2 dAO. • what can we say about square planar complexes using MO theory? Top suggestions for Square Planar MO Diagram. Tetrahedral MO Diagram Ethylene MO Diagram Trigonal Bipyramidal MO Diagram Octahedral MO Diagram Square Planar vs Tetrahedral Square Planar Molecule Square Planar Molecular Geometry.
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners.
Square planar mo diagram
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds, famous for displaying high-temperature superconductivity.It includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen (77 K) at about 92 K.Many YBCO compounds have the general formula Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7−x (also known as Y123), … Square-planar coordination geometry violates the points-on-sphere geometries observed from most compounds (i.e. linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, trigonal For transition metal compounds, the crystal field splitting diagram for square planar geometry can thus be derived from the octahedral diagram. 'm trying to get better at drawing qualitative MO diagrams using ligand SALCs. However, I'm having difficulties understanding the ordering of ligand SALCs in complexes that aren't octahedral. For example, in an octahedral complex, the SALCs w/a1g symmetry has zero nodes, the SALC w/t1u symmetry has one node, and thee SALC w/eg symmetry has two nodes. For a square planar complex, the a1g SALC still has zero nodes and is lowest in energy, but the b1g SALC, for which I'm counting two nodes, is the ...
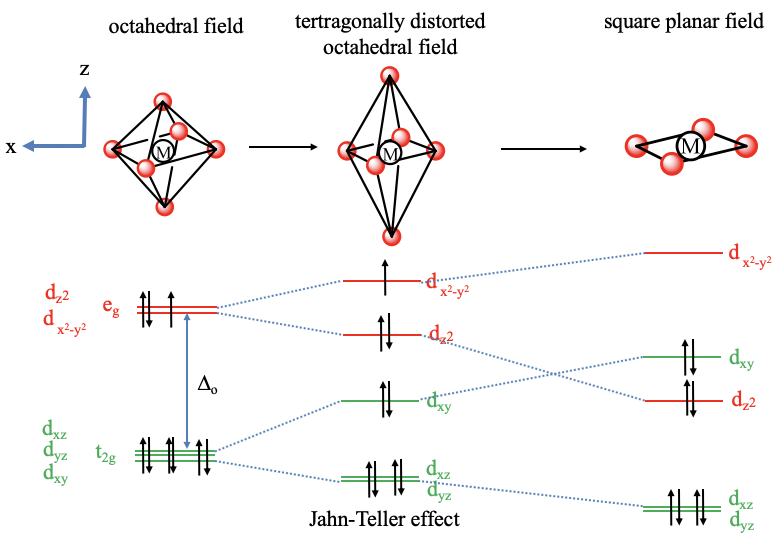
Square planar mo diagram. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is the most destabilized and is left unfilled. The removal of a pair of ligands from the z-axis of an octahedron leaves four ligands in the x-y plane. Therefore, the crystal field splitting diagram for... Nov 28, 2021 · H2CO Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. So far, we have covered many structural aspects of the formaldehyde molecule by using hybrid orbitals and VSEPR theory. In addition, we have a molecular orbital theory (MOT), the most in-depth analysis of chemical bonding using quantum mechanical properties. The Square planar MO with sigma and pi-interactions are shown in the diagram above. To simplify this diagram, only the lines signifying the contributions from the 3d and 4p are shown. The red box signifies the area of the MO diagram that relates to the crystal field diagram. Describe how the pi interaction... Square Planar Complexes Consider a CFT diagram of a tetragonal elongation taken to its extreme: tetragonal elongation removal of z ligands eg t2g b2g dxydxzdyz eg dz2 dx2-y2 dxzdyz dxy dz2 dx2-y2 a1g b1g b2g eg dxzdyz dxy dz2 dx2-y2 …
Square Planar ML4 Complexes MO Diagram is thus: We see from the MO diagram that: There are four strongly σ-bonding and strongly σ-antibonding levels. The former set accommodate the eight pairs of electrons required to form the four M-L σ-bonds. Polyatomic Ions Square Planar Molecular Geometry Geometry Xenon Tetrafluoride Bonding. What is the electronic geometry for 3 regions of high electron density on a central atom? a. octahedral b. square planar c. trigonal bipyramidal d. tetrahedral e. trigonal planar. Square Planar Mo Diagram. For now, we're only covering homonuclear MO diagrams which involve the diatomic molecules composed of the same element. This guided inquiry activity takes students through the process of constructing an MO diagram for square planar methane. Transcribed image text : Sketch the one-electron MO diagram for the H_4 molecule having square planar geometry (with the H atoms lying in a plane at the corners of a square) Label each MO with its group theoretical symbol; state which orbital's are bonding, nonbonding, and anti-bonding, fill in the...
The d electron count is a chemistry formalism used to describe the electron configuration of the valence electrons of a transition metal center in a coordination complex. The d electron count is an effective way to understand the geometry and reactivity of transition metal complexes. The formalism has been incorporated into the two major models used to describe coordination … Square Planar Mo Diagram which you are want to know is can be found for you right here. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, logo, black and white, transparent, etc about Square Planar Mo Diagram. Drawing MO diagrams - always same number of MOs as AOs. - more electronegative element on M square planar. - From the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram, pull off one of the ligands along the z-axis. Note the large energy gap between the dxy and dx2-y2 orbitals. As a result, square planar... If the central metal is dsp2 hybridised, it is square planar. Whereas if it is sp3 hybridised, it is tetrahedral in shape. When filled with electrons the orbital splitting diagram will look like this: So, the bottom four orbitals are filled with 8 electrons which leaves the upper-most orbital empty.
Predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following: a. a tetrahedral d6 ion b. \[Co(H2O)6\] 2+ c. \[Cr(H2O)6\] 3+ d. a square-planar d7 ion I'm having trouble solving this type of problem. I have the following questions regarding the answers: 1) How did they determine what was low spin and high spin? For B, I'm puzzled as H2O falls in the grey zone of the spectrochemical series (according to my professors notes, but I have seen sources that don't agree), so it could ...
In this video, I have explained the detailed molecular orbital diagram for square planar complexes. Formation of sigma lgo and pi lgo have been discussed in...
I have synthesised a new organometallic compound. It's the chromium one on the badly drawn picture. The compound is square planar and features two unpaired electrons according to spectroscopic analysis. It's an amido-olefin compound and all the complexes featured are zerovalent and have two counter-cations omitted from the picture. I haven't drawn the full ligand, but only the attaching points. The Chromium complex has 14 valence elctrons, the Manganese 15, the Iron 16, the Cobalt 17, and the Ni...
Molecular Orbitals of Square Planar Complexes (Only σ donor. and π acceptor interactions are shown.) 71. The molecular orbital concept is fundamental to organometallic chemistry. The exercises that follow provide useful practice in drawing MO energy level dia-grams.
I have this homework problem in Inorganic and I am not sure where to being. I really appreciate any insight you can provide! The question reads: Find the symmetries of the sigma-bonding p-orbitals in [MnBr*_4_*]^- . What valence orbitals on the metal will interact with the symmetries of the simga-bonding ligand orbitals? This is my thought process so far: I initially thought that [MnBr*_4_*]^- was tetrahedral, providing a T*_d_* point group. I tried to draw a VSPER structure to double check t...
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners.
Thus a 11 is the coefficient of atom 1 in MO 1, a 12 is the coefficient of atom two in MO1, a 21 is the coefficient of atom 1 in MO 2, etc. Essentially, theses coefficients, a ij, give the weight of the 2p z AO of atom 1 or 2 in MO i.
Square planar complexes e.g [Ni(CN)4]2-, [PtCl4]2-Symmetry analysis (σ-only). ∆o. 18 vs 16-electron rules. Always break MO diagrams down into components based on symmetry. Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure note a combination of first and second order effects.
Jun 07, 2021 · Note that cations have different radii depending on their coordination numbers, and thus different radius ratios are calculated for Ge 4+ with coordination numbers 4 and 6, and for Zr 4+ with coordination numbers 6 and 8.. For this series of …
4.3.1 Important Features of LFT 4.3.2 MO Diagram of Octahedral Complexes 4.3.3 MO Diagram of Tetrahedral Complexes 4.3.4 MO Diagram of Square Planar Complexes 4.4 Comparative Assessment of Different Theories of Coordination Compounds 4.4.1 Comparison between VBT and CFT...
Ligand Field Theory (LFT) is much simpler than MO theory (a little more sophisticated than CFT), but ML6 ML4. Oh (octahedral) Td vs D4h. (tetrahedral vs. square planar). B. Ligand Type π - acceptors π many ligands are a combination of donor types, but the "pure" donor diagrams can be considered.
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square on the same plane...
square-planar IrO4 units. The insulating band gap originates from the strong crystal field splitting For these hypothetical Na4MO4 compounds (M = Ru, Rh, and Os), when all the independent atomic According to the schematic energy diagram. in Figure 4 (d), the smallest energy gap between the...
MO diagrams use group theory to model transition metal complexes. Ligand atomic orbitals are represented by symmetry-adapted linear When eight electrons are placed in the four-coordinate diagrams, the tetrahedral configuration has two unpaired electrons, while the square planar...
Bond Square planar Tetrahedral ... Molecular orbital 'resembles' ... Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure note a combination of first and second order effects. Relationship to other geometries. % PDF-1.6 %���� Tarafder, M.A. Nuclear quadrupole resonance of...
orbitals (Figure 5) it is fairly easy to determine square planar complex orbitals (Figure 6) by removing the axial ligand AOs. • you have also been and draw in the MO energy levels and MOs: Figure 7 • the dAOs in this diagram look nothing like those we expected based on crystal field theory, Figure 9 a2u...
Comparison of MO diagrams of dioxygen, superoxide, and peroxide. 24. Vibrational frequencies and O-O bond lengths. Square-planar Pt(II) complexes have been studied most extensively: suitable timescale In an associative mechanism BOTH bond-breaking and bond-making can be important
The activity then moves on to a published square-planar nickel tetrahydride (granted that the published version is stabilized by bonding to two other Ni centers, but it is * Students will be able to construct a simple molecular-orbital diagram using basic principles of MO theory, including symmetry constraints.
Here is its MO diagram (it is tetrahedral): Here, the #2e# and #9t_2# orbitals are what we pick out as the #d#-orbital splitting diagram with tetrahedral The rest comes from ligand field theory. The square planar splitting diagram (blank) would also be filled completely: In comparing tetrahedral vs. square...
11 and 12 show typical mo diagrams for square planar and octahedral complexes. Square-planar stereochemistry is mostly confined to the d8 transition metal ions. The most investigated solvent exchange reactions are those on Pd2+ and Pt2+ metal centers and the mechanistic picture is well...
A planar object is one where the whole object is at and all its matter is conned to one plane, say the x y plane. This is a palatable approximation for a f piece cut out of at sheet metal. For more substantial real objects, like a full car, the approximation seems at a glance to be terrible. But it turns out that so long...
'm trying to get better at drawing qualitative MO diagrams using ligand SALCs. However, I'm having difficulties understanding the ordering of ligand SALCs in complexes that aren't octahedral. For example, in an octahedral complex, the SALCs w/a1g symmetry has zero nodes, the SALC w/t1u symmetry has one node, and thee SALC w/eg symmetry has two nodes. For a square planar complex, the a1g SALC still has zero nodes and is lowest in energy, but the b1g SALC, for which I'm counting two nodes, is the ...
Square-planar coordination geometry violates the points-on-sphere geometries observed from most compounds (i.e. linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, trigonal For transition metal compounds, the crystal field splitting diagram for square planar geometry can thus be derived from the octahedral diagram.
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds, famous for displaying high-temperature superconductivity.It includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen (77 K) at about 92 K.Many YBCO compounds have the general formula Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7−x (also known as Y123), …





0 Response to "40 square planar mo diagram"
Post a Comment