41 the diagram shows a lever. the mechanical advantage of the lever is
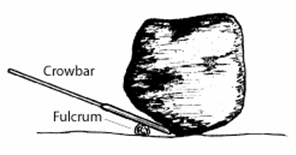
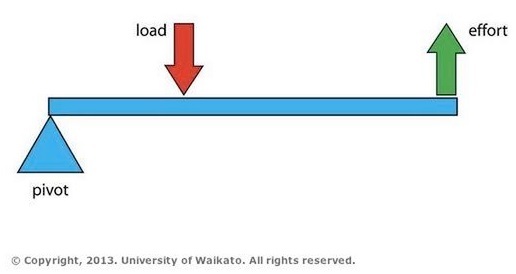
In the diagram below, two forces act on the lever. This is a schematic or diagram, but it symbolically represents any of the real life levers mentioned above. The lever pivots at a point called a fulcrum represented by the black triangle (in real life, this could be the screw holding the two blades of a scissors together). The diagram above shows a stone being shifted. Force is applied at one end of the bar in order to exert an upward force on the stone. The down ward force is called effort and the weight of the stone is called load. ... Mechanical Advantage of a Lever.
Torques are involved in levers, since there is rotation about a pivot point. Distances from the physical pivot of the lever are crucial, and we can obtain a useful expression for the MA in terms of these distances. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): A nail puller is a lever with a large mechanical advantage.
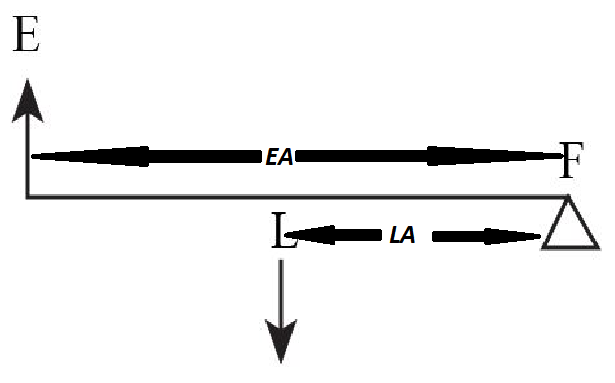
The diagram shows a lever. the mechanical advantage of the lever is
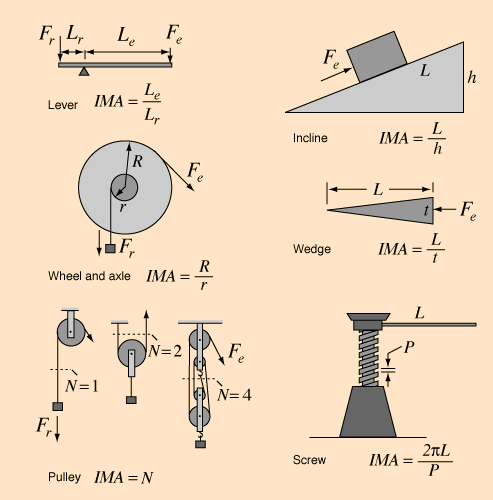
Mechanical Advantage Formula. The mechanical advantage for a simple machine such as a lever is: Mechanical Advantage= Load / Effort . We can assume that when the mechanical advantage is >1, the ... These two parts act as one simple machine. Check also: mechanical and understand more manual guide in mechanical advantage of a lever worksheet with answers Weight 90 N. The mechanical advantage of a lever is given as. Spayn 35 7 months ago. Diagram Of Three Classes Of Levers Basic Math Skills Science Lessons Fun Science Input or effort is applied on the right end of the pulley lever. The load is suspended halfway between the fulcrum and the input end of the lever. Hence, the effort arm is twice the load arm. Each Newton of input will support two newtons of load, so the mechanical advantage is 2. mechanical advantage of a pulley & the distances moved
The diagram shows a lever. the mechanical advantage of the lever is. 1 Answer. We know that, in the third class lever, an effort lies between a load and a fulcrum. So, effort distance (ED) is never greater than load distance (LD) and so the velocity ratio (VR) is less than one since VR = ideal MA. So, mechanical advantage (MA) in the third class lever is also less than one and it can never magnify the applied force. The total mechanical advantage of the system is the product of all three multiplied together: The first factor is the brake lever itself. The lever's mechanical advantage is determined by the distance from the lever's pivot to the cable end, and by the effective length of the brake lever from its pivot to where the rider's fingers grip it. preferably use a lever of class II. This is because the mechanical advantage of levers of class II, is always greater than one. A simple diagram of a lever of class II is shown alongside. The wheel barrow, the bottle opener and the mango cutter are some of the practical forms of lever of class II. Question 7: The diagram below shows a lever in use. The ratio of output to input force magnitudes for any simple machine is called its mechanical advantage (MA). (5.4.1) M A = F o F i. One of the simplest machines is the lever, which is a rigid bar pivoted at a fixed place called the fulcrum. Torques are involved in levers, since there is rotation about a pivot point.
The mechanical advantage of a wheel and axle is the radius of the wheel divided by the radius of the axle. On wheel and axle A, the wheel and axle are very close in size. On wheel and axle B, the radius of the wheel is much greater than the radius of the axle. This is because the mechanical advantage of levers of class II, is always greater than one. A simple diagram of a lever of class II is shown alongside. The wheel barrow, the bottle opener and the mango cutter are some of the practical forms of lever of class II. Question 7: The diagram below shows a lever in use. Weegy: The mechanical advantage of a wheel and axle is the radius of the wheel divided by the radius of the axle. On wheel and axle A, the wheel and axle are very close in size. [ On wheel and axle B, the radius of the wheel is much greater than the radius of the axle. Wheel and axle B has greater mechanical advantage. Question: The diagram below shows a lever in use. (i) To which class of lever done it belong? (ii) If FA = 40 cm. AB = 60 cm, then find the mechanical advantage of the lever. Answer: (i) Class II lever (iii) We know that Load × Load arm = Effort × Effort Arm. Mechanical advantage =Load X EEffort arm = ffort X Load arm =100 / 40 2.5
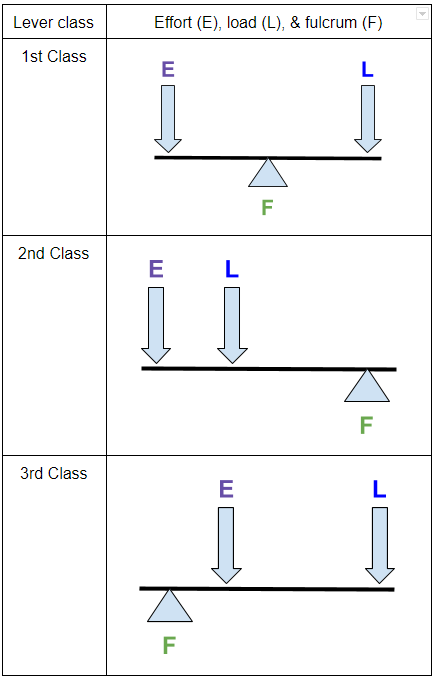
Mechanical advantage is a term used to describe the ratio of an output force to the input force. In other words, the amount of output with a given effort. Using physics and "leverages" certain mechanical features can be constructed to output a larger force that was input. In the case of a lever, the mechanical advantage is directly related ... The mechanical advantage of a lever is equal to the ratio of the effort arm to the load arm, i.e. Mechanical advantage of a lever = Effort arm / Load arm ... The diagram given below shows the three kinds of levers. Name the class of each lever and give one example of each class. Answer: Examples : The examples of class I levers are : a see saw ... This system can be thought of as a simple machine (lever), since force is multiplied.The mechanical advantage can be found by rearranging terms in the above equation to. Mechanical Advantage(IMA) = D1/D2 = A2/A1. For the sample problem above, the IMA would be 10:1 (10 inches/ 1 inch or 10 square inches / 1 square inch). The diagram above shows a stone being shifted. Force is applied at one end of the bar in order to exert an upward force on the stone. The down ward force is called effort and the weight of the stone is called load. ... Mechanical Advantage of a Lever.
This is where the mechanical advantage of a lever and fulcrum comes from. Imagine gripping a nail with a hammer's claw and resting the hammer's head against the wall to use it as a fulcrum. The closer the fulcrum is to the nail, the farther you'll have to move the handle to extract the nail.
What is the mechanical advantage of the lever? O 2 03 3 m 6 m mi 0 9 - 20919491 vivianagonzalez1231 vivianagonzalez1231 01/25/2021 Chemistry College answered ASAP I WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST The diagram shows a lever. What is the mechanical advantage of the lever? O 2 03 3 m 6 m mi 0 9 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement taylorvierthaler ...
If a lever operates at a mechanical advantage, it means that the _____. Group of choices lever system is; Triangle knm is isosceles, where angle n is the vertex. What is the measure of angle k? 11º 25º 50º; According to the textbook, the experience of fear can be described as a(n): Group of choices immediate emotional reaction; Categories ...
A man lifts various loads with the same lever. The distance of the applied force from the fulcrum is 2.00 m and the distance from the fulcrum to the load is 0.500 m. A graph of resistance force vs. effort force is shown. What is the mechanical advantage of the lever? What is the ideal mechanical advantage of the lever?
Mechanical advantage is equal to the product of velocity ratio and efficiency. For a machine of a given design, the velocity ratio does not change. Question 13. Derive the relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of a machine. Answer 13. Let a machine overcome a load L by the application of an effort E.
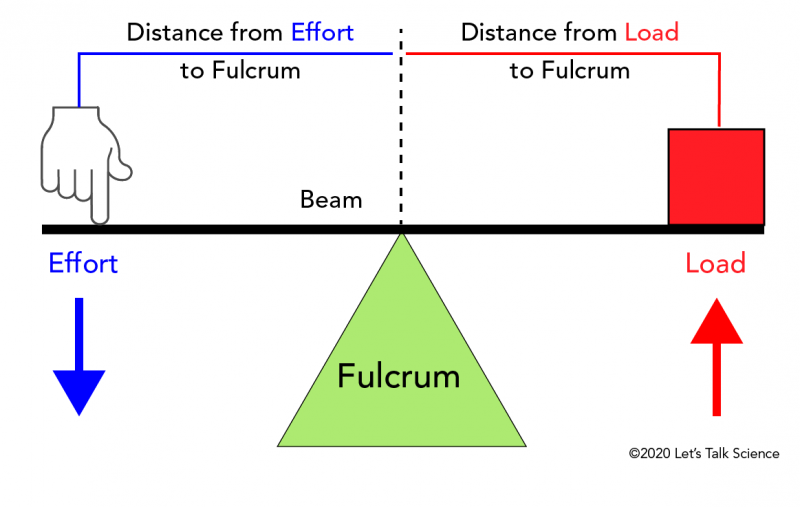
Mechanical Advantage. Lever. The advantage of levers, which relates effort and load (or input and output force), depends on how far away each are from the fulcrum. The mechanical advantage of a lever is increased when either the effort is moved further away from the fulcrum or the load is shifted closer to the fulcrum, or both.
lever: A simple machine that increases or decreases the force to lift something. Usually a bar pivoted on a fixed point (fulcrum) to which force is applied to do work. mechanical advantage : An advantage gained by using simple machines to accomplish work with less effort. Making the task easier (which means it requires less force), but may ...
Draw a diagram of a lever which is always used as a force multiplier. How is the effort arm related to the load arm in such a lever? Answer 25. Diagram: The effort arm is longer than load arm in such a lever. Question 26. Explain why the mechanical advantage of a class II type of lever is always more than 1. Answer 26
Jul 12, 2017 — Explanation: A lever is usually defined as a long and hard rod, with a fulcrum that is needed to place near the object in order to lift it.2 answers · 37 votes: The mechanical advantage of the lever shown in the diagram is 2
levers - mechanical advantage: simple quantitative ... Individual learners draw free-hand sketches to show two different design ideas in 3D for a cell phone tower to be ... Circuit diagram: Each learner draw a circuit diagram using the correct symbols for components.
We are all familiar with the concept that Mechanical advantage is the force multiplication technique. It is the relation which tells us what is the value of the ...
Dec 7, 2018 · 1 answer(i) Sum of the clockwise moments about the fulcrum is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments about the fulcrum. (ii) Lever of class ...
Mechanical advantage of a lever of first order. In case of First order lever Mechanical advantage can be equal to 1 or greater than or less than 1.It depends on the position of the fulcrum between effort arm and load arm. In case of levers of first order, we try to keep the load arm smaller than the effort arm i.e., effort arm > load arm.
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ The diagram shows a lever in use.Without changing the dimensions of the lever, if the load is shifted ...1 answer · Top answer: When the load is shifted towards the fulcrum, then less effort is required to lift the load and thus mechanical advantage of the lever increases.
(b) The mechanical advantage of the lever increases when load is shifted towards the fulcrum, as less effort is required to lift the load. Answered By.
2) Without changing the dimensions of the lever, if the load is shifted towards the fulcrum what happens to the mechanical advantage of the lever?
Learn about different types of simple machines such as the lever, inclined plane, and pulley, and determine the formula for their mechanical advantage. Updated: 10/28/2021 Create an account
Input or effort is applied on the right end of the pulley lever. The load is suspended halfway between the fulcrum and the input end of the lever. Hence, the effort arm is twice the load arm. Each Newton of input will support two newtons of load, so the mechanical advantage is 2. mechanical advantage of a pulley & the distances moved
These two parts act as one simple machine. Check also: mechanical and understand more manual guide in mechanical advantage of a lever worksheet with answers Weight 90 N. The mechanical advantage of a lever is given as. Spayn 35 7 months ago. Diagram Of Three Classes Of Levers Basic Math Skills Science Lessons Fun Science
Mechanical Advantage Formula. The mechanical advantage for a simple machine such as a lever is: Mechanical Advantage= Load / Effort . We can assume that when the mechanical advantage is >1, the ...
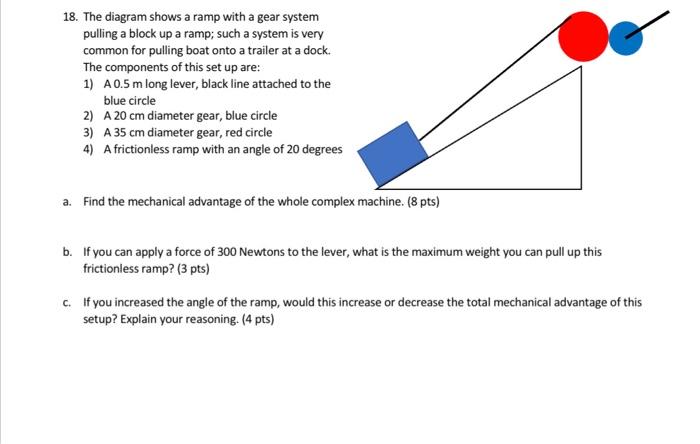




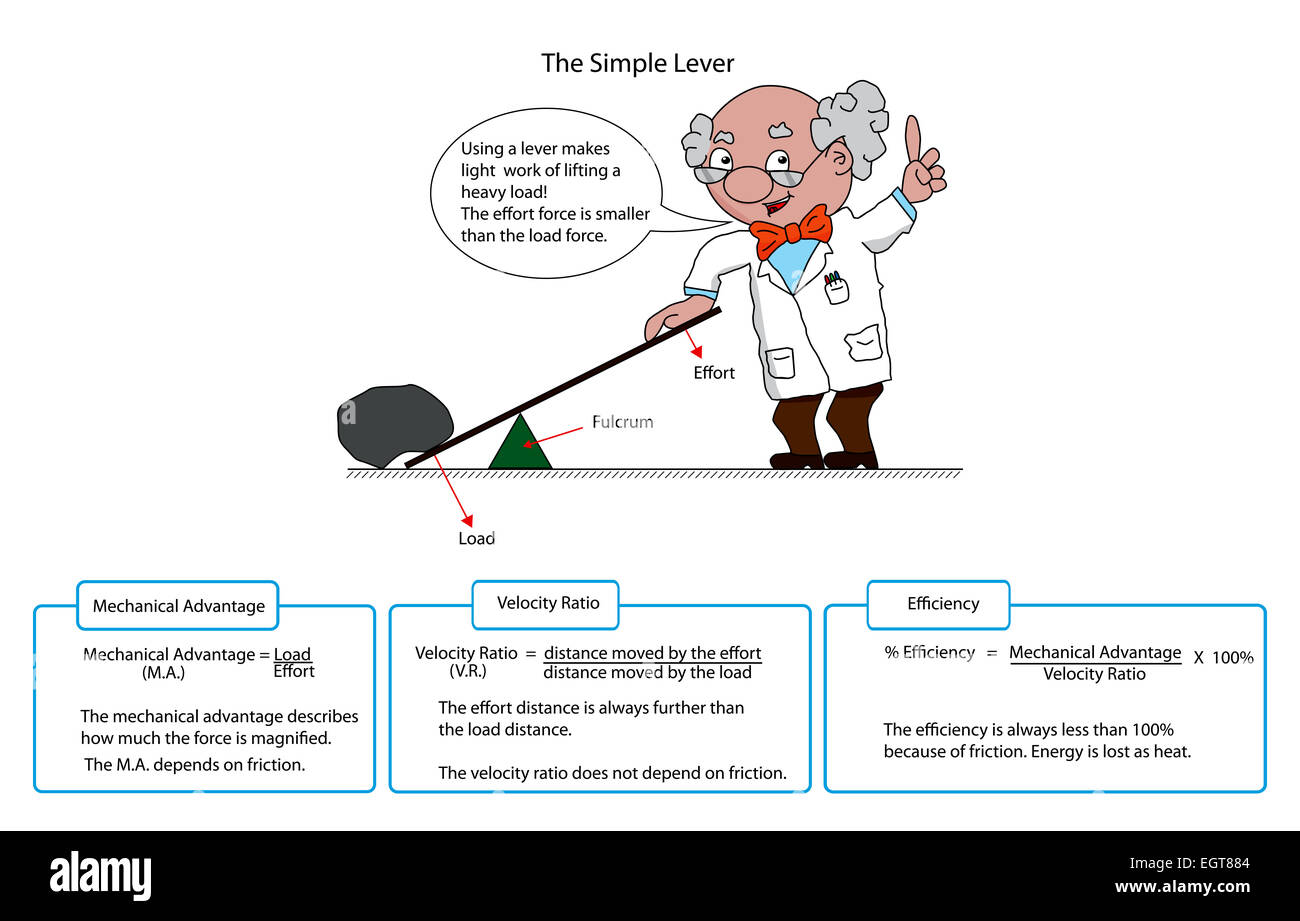

















0 Response to "41 the diagram shows a lever. the mechanical advantage of the lever is"
Post a Comment