9 adiabatic expansion pv diagram
So on a PV diagram, an isothermal process is gonna look something like this, it's gonna curve like 1/x and it can be an isothermal expansion if volume increases or an isothermal compression if volume decreases. So the actual shape of the line drawn on a PV diagram for an isothermal process is sometimes called an isotherm and they look like that. The paths look somewhat similar on the P-V diagram, but you should notice clear differences. Note that an isothermal process has no change in temperature, so the change in internal energy is zero, but in an adiabatic process the heat transferred is zero. Note that for each press of a button, the volume will change by 1 liter, unless that ...
Fig. 3.2 a) illustrates a Carnot cycle. This is a combination of reversible isothermal and adiabatic expansion and compression of a perfect gas: A ...
Adiabatic expansion pv diagram
Visit us (http://www.khanacademy.org/science/healthcare-and-medicine) for health and medicine content or (http://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat) for MCAT... Adiabatic Expansion - Adiabatic Compression. See also: What is an Ideal Gas In an ideal gas, molecules have no volume and do not interact.According to the ideal gas law, pressure varies linearly with temperature and quantity, and inversely with volume.. pV = nRT. where: p is the absolute pressure of the gas; n is the amount of substance; T is the absolute temperature Adiabatic expansion is defined as an ideal behaviour for a closed system, in which the pressure is constant and the temperature is decreasing. What is Adiabatic Compression? Adiabatic compression of the air is defined as the compression in which no heat is added or subtracted from the air and the internal energy of the air is increased which is ...
Adiabatic expansion pv diagram. 21.02.2021 · Adiabatic Process Thermodynamics | Work done Adiabaticaly | Adiabatic Expansion & Contraction | PV Diagram in Hindi / UrduAn adiabatic process is a thermodyn... PV diagram is a "steep hyperbola" Q = 0 ⇒ ∆ U = W PVγ = constant Superman saves the day with adiabatic cooling. The rapid expansion of the gas expelled from Superman's lungs cooled the overheating truck, thwarting the evil General Zod's attempt to explode its fuel tank. Thank you Superman. … and the rest liquids solids The most extreme form of an irreversible isothermal expansion is the adiabatic isothermal expansion of an ideal gas into vacuum. In this case no pressure-volume work is done, so in the PV diagram pressure first drops to zero, then volume increases to the final volume, and the pressure increases to the final value. The area under the curve is zero. 1. This question does not show any research effort; it is unclear or not useful. Bookmark this question. Show activity on this post. In non isolated systems where there is no adiabatic process, P V is constant. But the graph gets steeper in adiabatic process because of the γ over the V. Why is it there in adiabatic processes and why only over ...
Adiabatic is a Greek word in which 'a' means 'not', 'dia' means 'through' and 'bait' means 'hot'.So in short adiabatic is a system that does not allow heat to pass through it. Definition : It is the thermodynamic process in which there is a change in pressure, volume, and temperature of the system, but there is no ... The Rankine cycle is often plotted on a pressure volume diagram (pV diagram) and on a temperature-entropy diagram (Ts diagram). When plotted on a pressure volume diagram , the isobaric processes follow the isobaric lines for the gas (the horizontal lines), adiabatic processes move between these horizontal lines and the area bounded by the ... A reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas is represented on the pV diagram of (Figure). The slope of the curve at any point is Quasi-static adiabatic and isothermal expansions of an ideal gas. The dashed curve shown on this pV diagram represents an isothermal expansion where T (and therefore pV) is constant. Expansion: work on piston positive, work on gas negative Compression: work on piston negative, work on gas positive . Work during a volume change ⇒=∫ = = = 2 1.. V V W pdV pdV p Adx dW F dx. Work in pV diagrams Work done equals area under curve in pV diagram Careful with the signs… 1st Law of Thermodynamics ∆U =Q −W Conservation of energy Heat is positive when …
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... through adiabatic expansion and ends at a temperature of 300 K, determine how much work the gas did. The PV diagram we would get for this adiabatic process is shown here. Notice how we started on the 525 K isotherm, but ended on the 300 K isotherm. The temperature did not stay constant, so this process must be adiabatic. Thermodynamics (Adiabatic PV Diagram) Thread starter alexgmcm; Start date Apr 8, 2010; Apr 8, 2010 #1 alexgmcm. 77 0. Homework Statement Give a definition of an adiabatic process. Derive an expression for the work performed by n mol of an ideal gas undergoing an adiabatic expansion in terms of the initial and the final temperature of the gas ... The mathematical equation for an ideal gas undergoing a reversible (i.e., no entropy generation) adiabatic process can be represented by the polytropic process equation =, where P is pressure, V is volume, and for this case n = γ, where = = +, C P being the specific heat for constant pressure, C V being the specific heat for constant volume, γ is the adiabatic index, and f is the number of ...
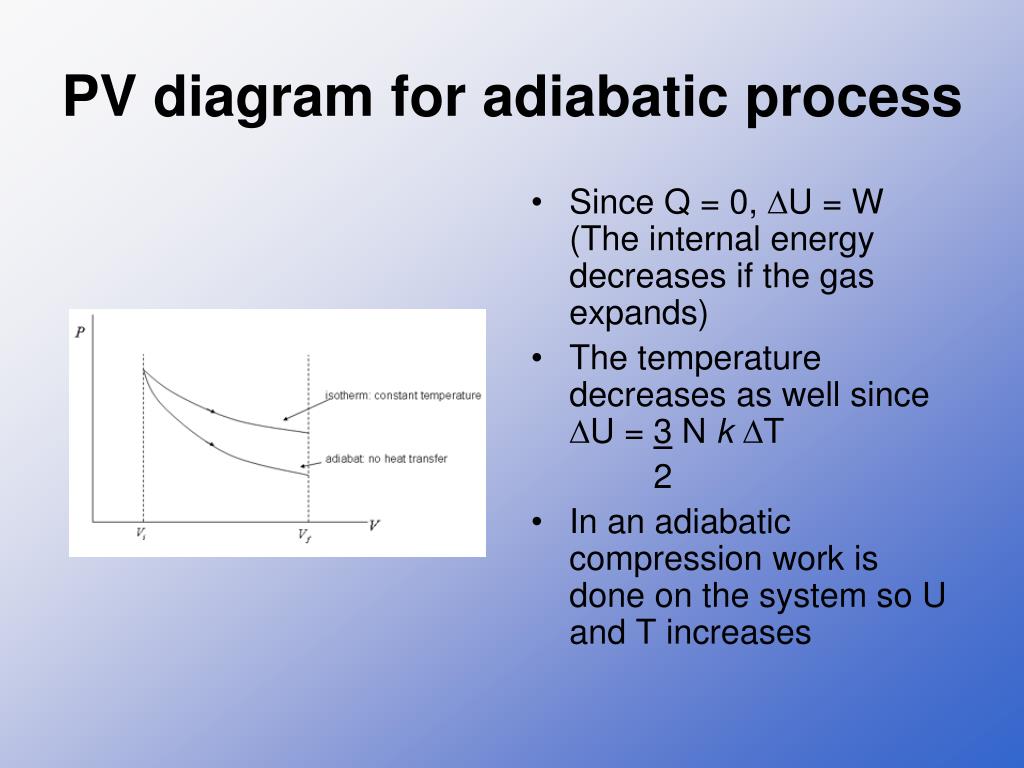
09.09.2018 · The PV diagram of an adiabatic expansion and adiabatic compression process are shown in Figure 8.30. The PV diagram for an adiabatic process is also called adiabat Note that the PV diagram for isothermal (Figure 8.25) and adiabatic (Figure 8.30) processes look similar. But actually the adiabatic curve is steeper than isothermal curve.
Adiabatic vs Isothermal PV diagram. A PV diagram is most widely used in thermodynamics to describe corresponding changes in pressure and volume in a system. Each point on the diagram represents different state of a gas. PV diagram of Isothermal Process and Adiabatic Process is similar but Isothermal graph is more tilted.
An adiabatic process is one in which no heat is gained or lost by the system. The first law of thermodynamics with Q=0 shows that all the change in internal ...
A reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas is represented on the pV diagram of Figure 3.15. The slope of the curve at any point is The slope of the curve at any point is d p d V = d d V ( constant V γ ) = − γ p V . d p d V = d d V ( constant V γ ) = − γ p V .
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect: A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries. Students (upto class 10+2) preparing for All Government Exams, CBSE Board Exam, ICSE Board Exam, State Board Exam, JEE (Mains+Advance) and NEET can ask questions from any subject and get quick answers by subject teachers/ experts/mentors/students.
Adiabatic Expansion (DQ = 0) Occurs if: • change is made sufficiently quickly • and/or with good thermal isolation. Governing formula: PV g = constant where g = CP/CV Because PV/T is constant (ideal gas): V g-1 T = constant (for adiabatic) P V Adiabat Isotherms. Proof of PV g =constant (for adiabatic process)
When an ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion or compression, the adiabatic equation can be used: $$ pV^{\gamma} = \text{constant} $$ Where $\gamma$ is the adiabatic constant which depends on the molecular structure of the gas. Typical values include $\gamma = 1.67$ for a monatomic gas and $\gamma = 1.40$ for a diatomic gas.
Adiabatic expansion is defined as an ideal behaviour for a closed system, in which the pressure is constant and the temperature is decreasing. What is Adiabatic Compression? Adiabatic compression of the air is defined as the compression in which no heat is added or subtracted from the air and the internal energy of the air is increased which is ...
Adiabatic Expansion - Adiabatic Compression. See also: What is an Ideal Gas In an ideal gas, molecules have no volume and do not interact.According to the ideal gas law, pressure varies linearly with temperature and quantity, and inversely with volume.. pV = nRT. where: p is the absolute pressure of the gas; n is the amount of substance; T is the absolute temperature
Visit us (http://www.khanacademy.org/science/healthcare-and-medicine) for health and medicine content or (http://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat) for MCAT...





0 Response to "9 adiabatic expansion pv diagram"
Post a Comment