37 Centripetal Acceleration Free Body Diagram
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Circular_motionCircular motion - Wikipedia The only acceleration responsible for keeping an object moving in a circle is the radial acceleration. Since the sum of all forces is the centripetal force, drawing centripetal force into a free body diagram is not necessary and usually not recommended. Amusement Park Physics - Physics Classroom The free-body diagrams for these two positions are shown in the diagrams at the right. The magnitude of the force of gravity acting upon the passenger (or car) can easily be found using the equation Fgrav = m•g where g = acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s 2 ).
physics.bu.edu › ~erikl › Subject_ForcesSubject: Forces (Free Body Diagrams; F = ma) acceleration with which the blocks move. Assume there is no friction. The problem asks for the acceleration, and therefore “Forces” is the best way to approach this problem (because if we find the net force, we’ve found the acceleration – via ΣF = ma .). 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object.
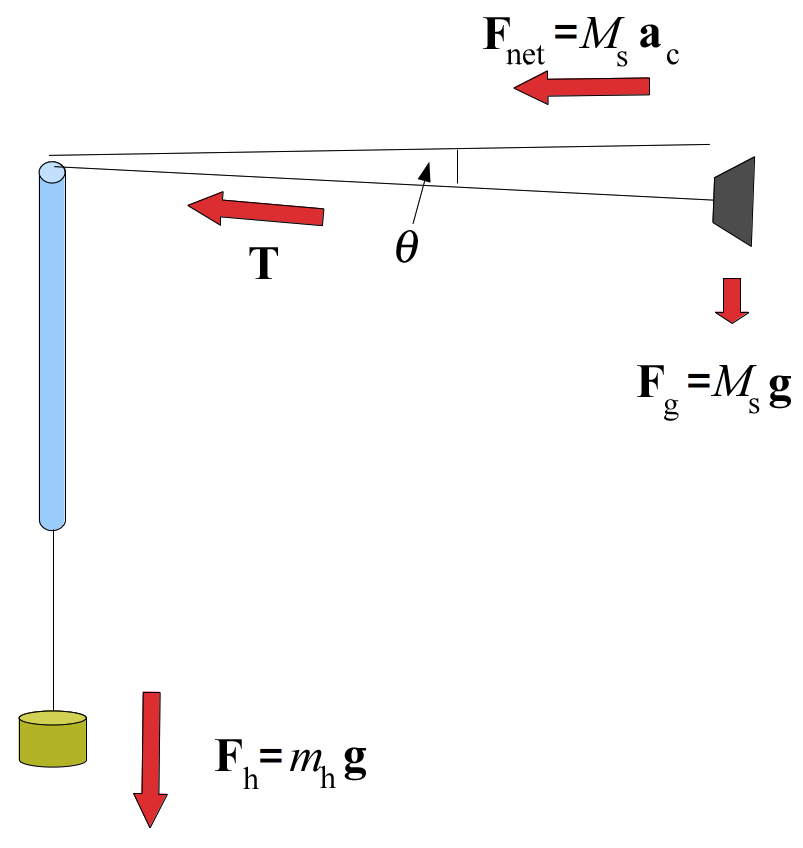
Centripetal acceleration free body diagram
Circular Motion Problems ANSWERS Dec 11, 2012 · 2/r Tension provides net force, acceleration is centripetal F tension =m(4 2r/T2) Speed equals circumference divided by period F tension =1.7 N Substitute values and calculate 2. A 15 g stopper is swung in a horizontal circle with a radius of 0.80 meters. The tension in the string is 1.5 Newtons. 251 | Physics | NDSU 251 Topics Detail Measurement [typically includes: definition of physics; SI system, units, & unit conversions; significant figures]; One-Dimensional Motion [typically includes: displacement, speed, velocity, & acceleration; motion with constant acceleration & free-fall]; Vectors [typically includes: vector vs. scalar quantities; addition & subtraction; components; unit vector notation; vector ... Centripetal Acceleration - Slidelegend.com Now draw below a free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper. From Newton's second law and the free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper, the horizontal component of the string's tension on the revolving rubber stopper must be ms a = FT cos θ (4) Substitute equation (2) for centripetal acceleration into (4). ms (4π2r/T2)= FT cos θ (5)
Centripetal acceleration free body diagram. acceleration and force Physics Free Body Diagrams a Explanation Physics : acceleration and force Free Body Diagram • A free body diagram is a picture representation of all forces acting on an object. • We use arrows to represent the forces and indicate their direction and magnitude. • Magnitude expressed by number and arrow size. 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... Centripetal Acceleration - Introduction, Example, Formula ... A centripetal acceleration example can be that of taking a sharp turn in a vehicle. If a person is holding the wheel constant while taking a turn, he/she is in a uniform circular motion. Derivation Of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. The following diagram represents a body moving in a circular pathway at a persistent speed. Here, centripetal ... homework and exercises - The centripetal force direction ... In your example, the centripetal force is the consequence. If you define the positive direction for the vertical ($\hat{\jmath}$) axis to be upwards (away from the Earth's center), then the free-body diagram would show $$\vec{n} + \vec{w} = \vec{F}_\text{net} \quad \rightarrow \quad N \hat{\jmath} - W \hat{\jmath} = \vec{F}_\text{net}$$
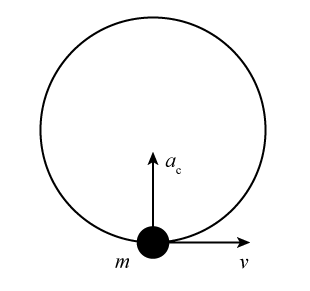
courses.lumenlearning.com › physics › chapterCentripetal Acceleration | Physics - Lumen Learning (b) What is the centripetal acceleration at the bottom of the arc? (c) Draw a free body diagram of the forces acting on a rider at the bottom of the arc. (d) Find the force exerted by the ride on a 60.0 kg rider and compare it to her weight. (e) Discuss whether the answer seems reasonable. Unreasonable Results. PDF Carl Lundstedt's EDU Problems Tests: Newton's 2nd law, free body diagrams, moments of inertia, torque. Type: Numeric Random Variables supplied to the problem: v0, theta Student is asked for: range ... Tests: centripetal acceleration, friction, free body diagrams. Type: Inline Random Variables supplied to the problem: x1, x2, x3, m, Mp Physics Help: Centripetal Force Free Body Diagrams Part 7 ... simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website. Free Body Diagram Centripetal Force - schematron.org The correct free-body diagram is diagram 3, which shows only the force of gravity applied by the Sun on the Earth. The word "centripetal" means "directed toward the center." When an object experiences uniform circular motion, the object has a centripetal acceleration directed toward the center of the circle.
Newest 'centripetal-force' Questions - Physics Stack Exchange homework-and-exercises newtonian-mechanics acceleration free-body-diagram centripetal-force. Mina. 147; asked Jan 18 at 15:33. 0 votes. 0 answers. 11 views. What is the relationship between the number of turns of an unwinding pendulum and its radius of motion? How to Draw a Free Body Diagram: 10 Steps (with Pictures) A free-body diagram can be drawn very simply, with squares and arrows, or you can make it much more complex. The only requirement is that you or someone else looking at it should be able to understand what the diagram is telling. A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it. PDF Physics Kinematics, Projectile Motion, Free-Body Diagrams ... Free-Body Diagram Example Problem 2 A car with a mass of 1050 [kg] travels around a curve of radius 300 [m] banked at a 14˚ angle. Find the maximum speed the car can take this curve without assistance from friction. Find the centripetal force on the car. The Physics Classroom 2009 Answer Key Free Body Diagrams ... A free body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams. Net Force Worksheet Answers New Free Body Diagrams In 2020 Body Diagram Diagram Design Diagram. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. Presence of a centrifugal force on your body. Click on the Physics Tutorial link.
Free Body Diagram Centripetal Force - UNTPIKAPPS Free Body Diagram Centripetal force. physics help centripetal force free body diagrams part 7 free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website centripetal force and free body diagram 1 the problem statement all variables and given known data a draw a free body diagram for mass mb while in motion fig 2a identify the centripetal
PDF General Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Forces, Circular ... in the fishing line is 3.0 times its weight. Draw the forces acting on the fish (free body diagram) and find the acceleration of the fish (magnitude and direction). 12. (14) A space station is a hollow cylinder of radius 440 m, that rotates to simulate gravity by its centripetal acceleration. The astronauts live at the radius 440 m from
Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion ... Let's practice with free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion by drawing one for each position of the roller coaster. Remember, in this instance, there is only centripetal acceleration, no tangential acceleration. If there is a centripetal force causing centripetal acceleration, it must point to the center.
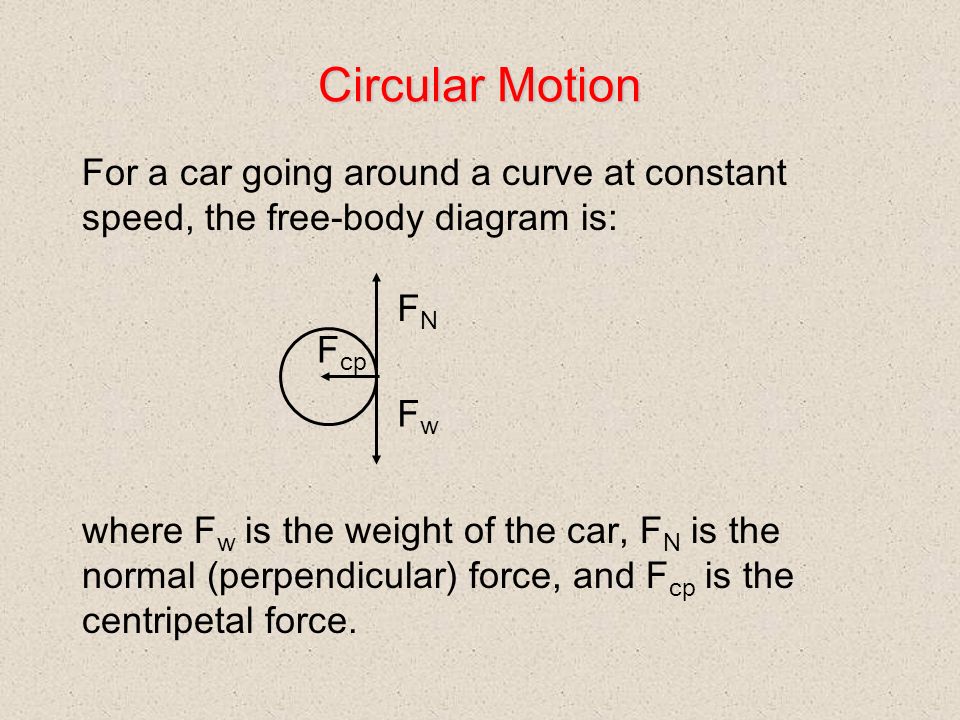
Centripetal and Centrifugal Acceleration and Force Centripetal and Centrifugal Force are the action-reaction force pair associated with circular motion. Centripetal Acceleration. Velocity is a vector - specifying how fast (or slow) a distance is covered and the direction of the movement. Since the velocity vector (the direction) of a body changes when moved in a circle - there is an acceleration.
Free Body Diagrams - BrainMass Use the Free-body diagrams to answer the following: 1. You are driving along the highway, when the car in front of you makes a right-hand turn. ... centripetal acceleration is a= v^2/R, so F= M v^2/R = 6667 nt. Question #3: B The normal force equals the weight; N= Mg since vertical acceleration is... Solution Summary.
courses.lumenlearning.com › 6-3-centripetal-forceCentripetal Force | Physics - Lumen Learning At what angle θ below the horizontal will the cage hang when the centripetal acceleration is 10 g? (Hint: The arm supplies centripetal force and supports the weight of the cage. Draw a free body diagram of the forces to see what the angle θ should be.)
PDF Circular Motion and Universal Law of Gravitation acceleration • Free Body Diagram for all forces ... centripetal acceleration of the moving puck? 1. less than g 2. g 3. greater than g 4. zero 5. insufficient information . Universal Law of Gravitation • The force on body 1 due to the gravitational interaction between two bodies of masses m 1 and m
PDF Physics - SC1117 Scope and Sequence - Edgenuity Interpret position-time graphs for motion with constant acceleration. Free Fall Define acceleration due to gravity. ... Interpret and construct free-body diagrams. ©Edgenuity Inc. Confidential Page 2 of 11. Physics - SC1117 Scope and Sequence ... Solve problems involving centripetal accelerations.
Why do athletic runners lean forward (Newtonian ... - Quora Answer (1 of 3): The answer is similar for both sprints and distance running, although different factors are more or less critical between them. From a Newtonian mechanics standpoint, it amounts to a few different factors: A first observation is that one wants to ALWAYS have foot placement behi...
Centrodyne Z059 Wiring Diagram centripetal force free body diagrams,centripetal force in space diagram,centripetal force lab diagram,centripetal force pendulum diagram,centripetal force vector diagram,centripetal free body diagram,centripetal pump diagram rebuild,centripital acceleration free body diagram,centripital force free body diagram,centripro ses duplex control ...
force acceleration - Homework Help Videos - Brightstorm Understanding and applying the Law of Force and Acceleration. newton's second law motion acceleration force. Force ... Recognizing the differences between centripetal and centrifugal force. centrifugal force centripetal force ... Drawing and interpreting free-body force diagrams. free body force diagrams net force normal force. Electric Force ...
› accelaration-gravityAcceleration of Gravity and Newton's Second Law An object dropped in free air accelerates to speed 9.81 m/s (32.174 ft/s) in one - 1 - second. a heavy and a light body near the earth will fall to the earth with the same acceleration (when neglecting the air resistance) Acceleration of Gravity in SI Units. 1 a g = 1 g = 9.81 m/s 2 = 35.30394 (km/h)/s. Acceleration of Gravity in Imperial Units
Free Body Diagrams - What are They and How are They Used ... A Free Body Diagram is an engineering tool that simplifies a component or system of components to the loads, moments and applied to it in space. ... Consider weird loads like centripetal acceleration. Once you have all these things, you can move to the next step. 3. Draw the Forces on the Diagram. Start drawing these forces on the diagram. Most ...
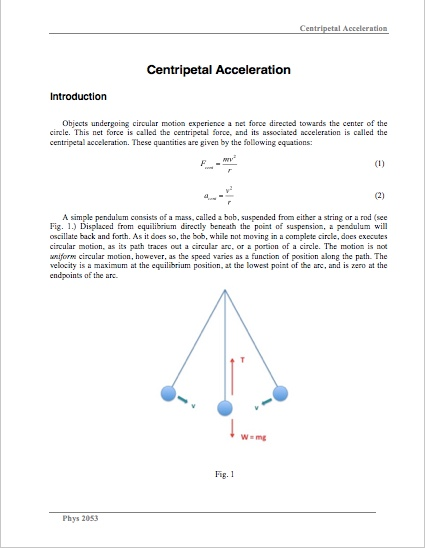
What Are Centripetal Acceleration And Centrifugal Force ... The diagram below illustrates this, and it is this diagram that we will use to derive the expression for centripetal acceleration. The circle represents the circular trajectory of a body, which at point P has a linear velocity v, and later, at point P' , has a linear velocity v' .
Determine the Centripetal Acceleration and Force Centripetal Acceleration Free Body Diagrams Centripetal acceleration of earth revolving around the sun circuile motion and work-enegy theorem Angular speed of race car, tangential speed, loop-the-loop Newton's law of gravitation Rotational Motion: Angular and Centripetal Force. View More.
Satellite Orbits and Energy - University Physics Volume 1 It has centripetal acceleration directed toward the center of Earth. Earth's gravity is the only force acting, so Newton's second law gives ... To start from first principles, draw a free-body diagram and apply Newton's law of gravitation and Newton's second law.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom It is generally customary in a free-body diagram to represent the object by a box and to draw the force arrow from the center of the box outward in the direction that the force is acting. An example of a free-body diagram is shown at the right T he free-body diagram above depicts four forces acting upon the object.
Centripetal Acceleration: Formula, Equation and Derivation 22.12.2021 · Centripetal Force. Centripetal acceleration refers to the rate of change of tangential velocity. It is the net force that leads to the centripetal acceleration of an object in a circular motion. The centripetal force is directed towards the centre, which is perpendicular to the body's motion. Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal motion - swinging a bucket full of water ... A free body diagram will help here too. Draw one for the position of the bucket at the top of the vertical circle, (that would be the same as you used in A), and a second one for the bucket at the bottom of the circle. If you do this, you will see that there are more forces pulling on your hand at the bottom then there are at the top.
Centripetal Acceleration - Slidelegend.com Now draw below a free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper. From Newton's second law and the free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper, the horizontal component of the string's tension on the revolving rubber stopper must be ms a = FT cos θ (4) Substitute equation (2) for centripetal acceleration into (4). ms (4π2r/T2)= FT cos θ (5)
251 | Physics | NDSU 251 Topics Detail Measurement [typically includes: definition of physics; SI system, units, & unit conversions; significant figures]; One-Dimensional Motion [typically includes: displacement, speed, velocity, & acceleration; motion with constant acceleration & free-fall]; Vectors [typically includes: vector vs. scalar quantities; addition & subtraction; components; unit vector notation; vector ...
Circular Motion Problems ANSWERS Dec 11, 2012 · 2/r Tension provides net force, acceleration is centripetal F tension =m(4 2r/T2) Speed equals circumference divided by period F tension =1.7 N Substitute values and calculate 2. A 15 g stopper is swung in a horizontal circle with a radius of 0.80 meters. The tension in the string is 1.5 Newtons.






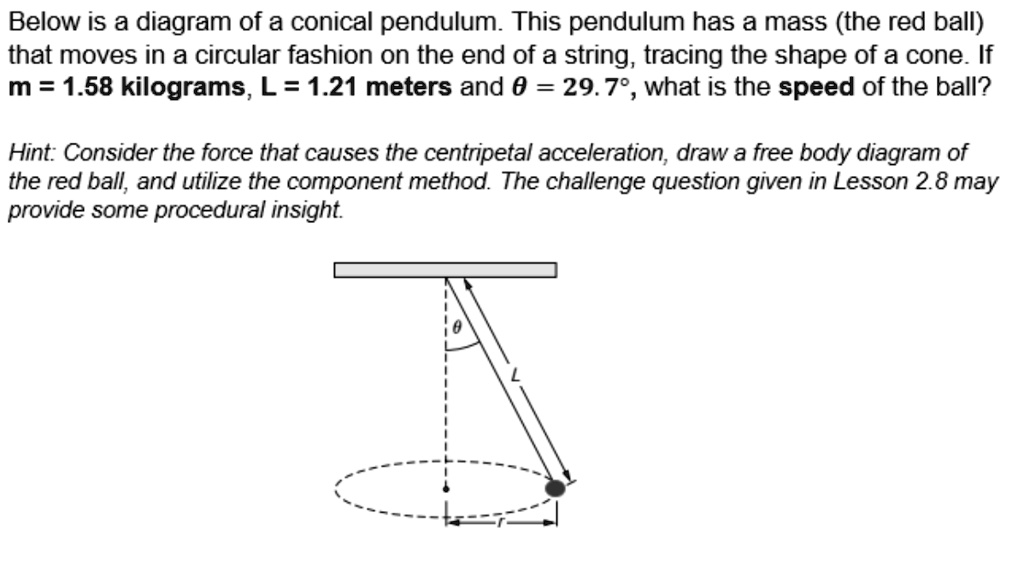



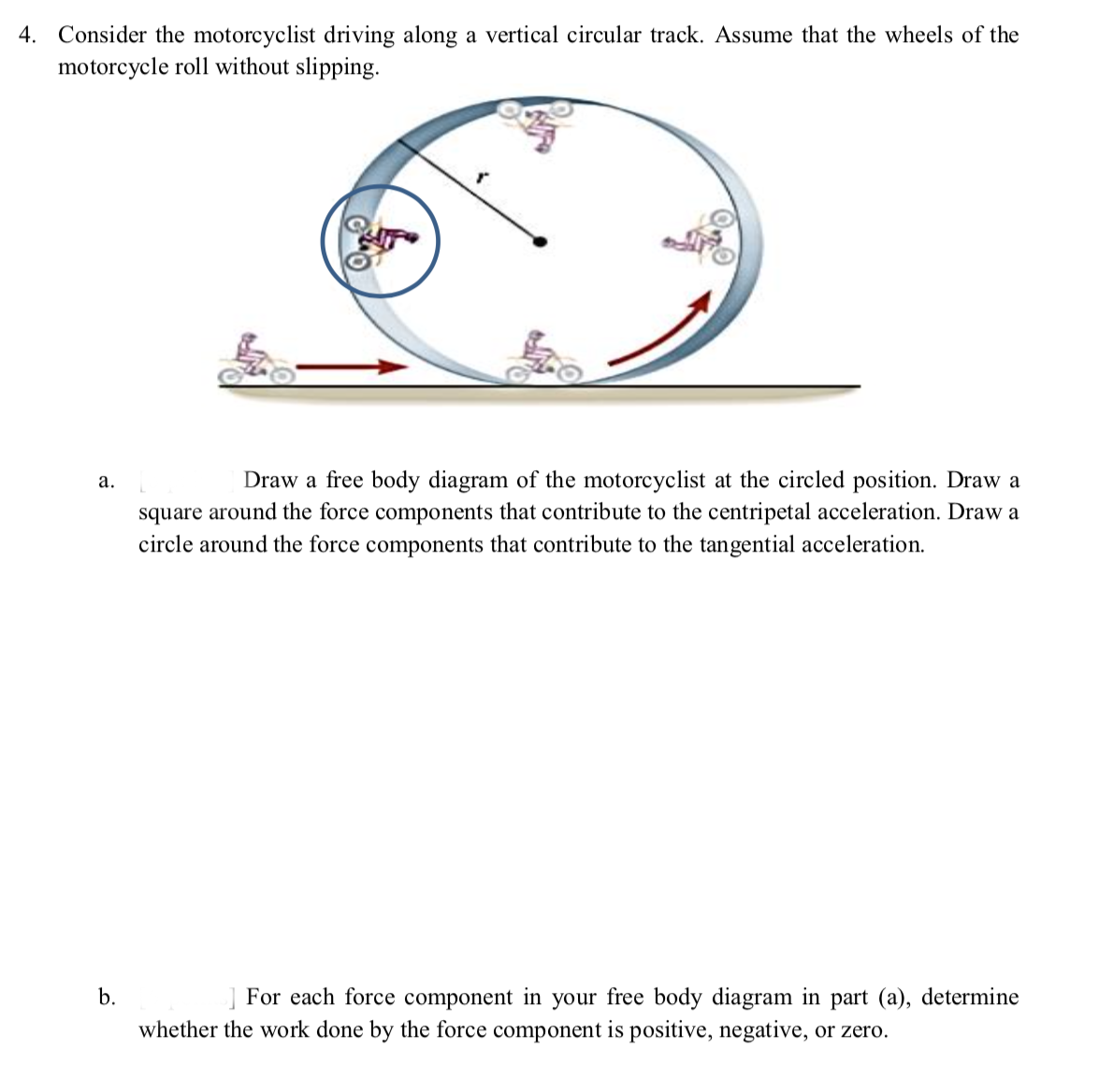


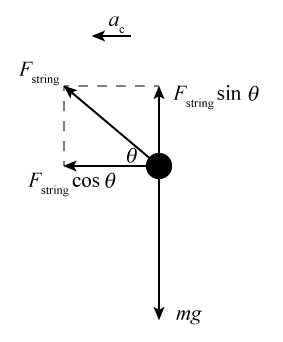






0 Response to "37 Centripetal Acceleration Free Body Diagram"
Post a Comment