38 newton's third law diagram
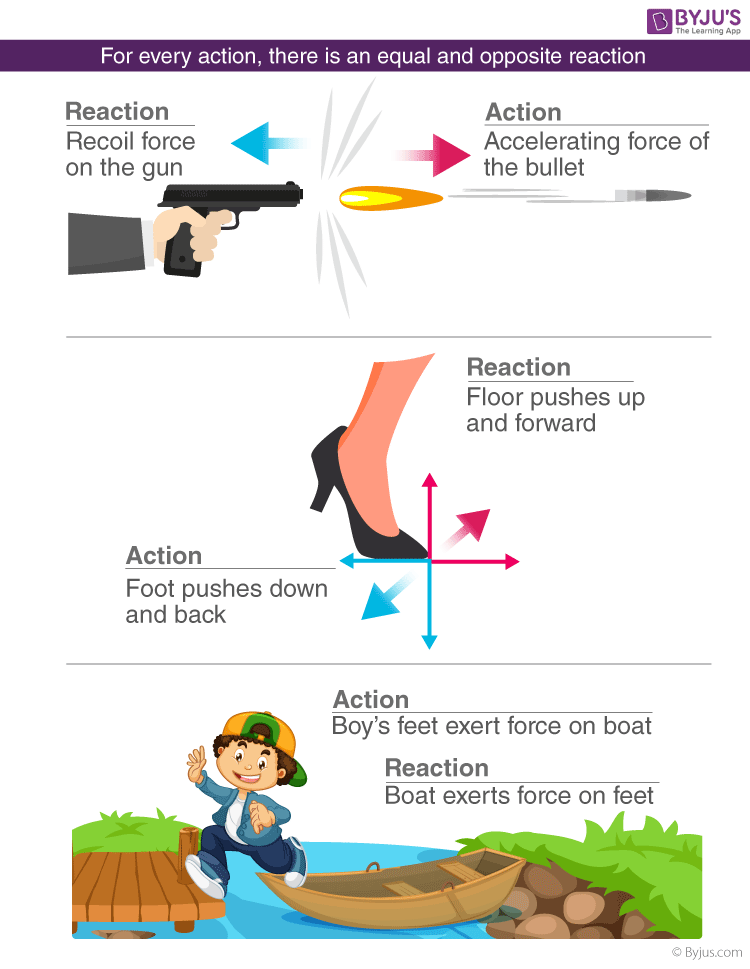
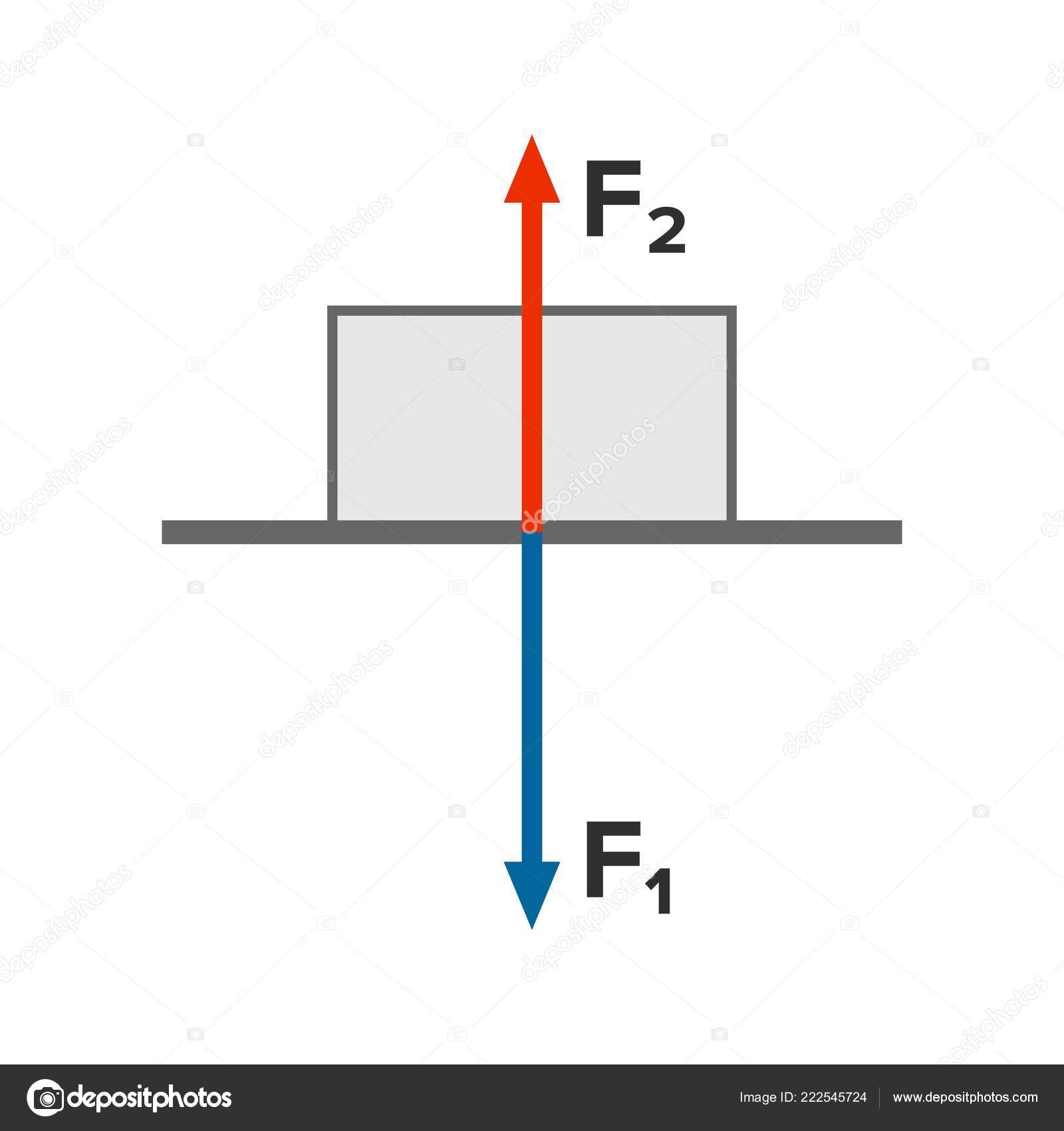
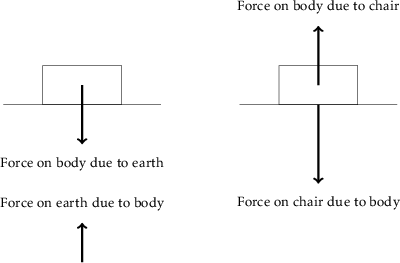
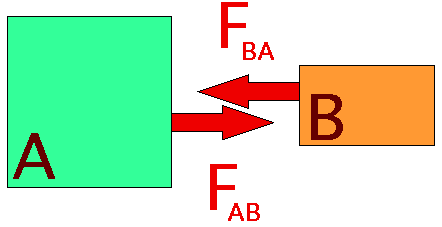
What is Newton's Third Law of Motion - PEDIAA The free body diagram for the apple and the table would be as follows: In the above diagram, you can identify one Newton's third law pair. The apple pushes down on the table (), and the table pushes back up on the apple (). The apple is at rest, so the forces on the apple are balanced (according to Newton's first law). 4.4 Newton's Third Law of Motion - Physics | OpenStax Newton's third law of motion tells us that forces always occur in pairs, and one object cannot exert a force on another without experiencing the same strength force in return. We sometimes refer to these force pairs as action-reaction pairs, where the force exerted is the action, and the force experienced in return is the reaction (although ...
Force diagrams - Newton's 3rd law - ExamSolutions In this video I show you how to draw some common force diagrams and introduce you to Newton's 3rd Law. (Hope you like the sledge part!)
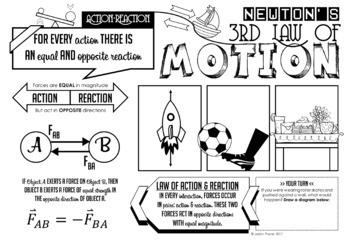
Newton's third law diagram
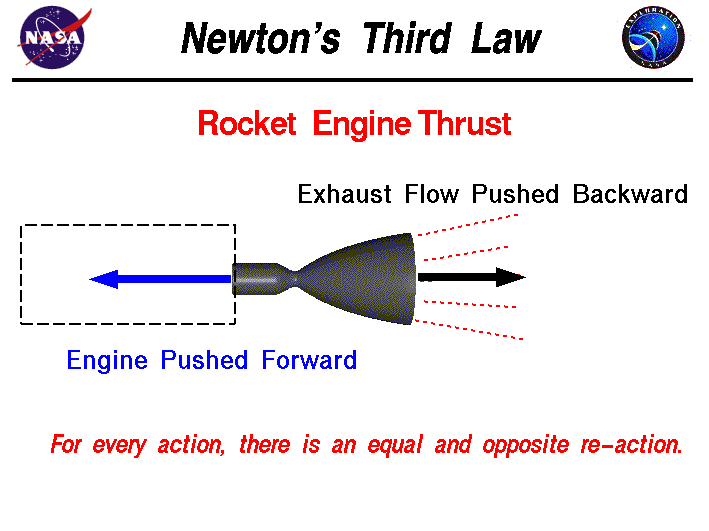
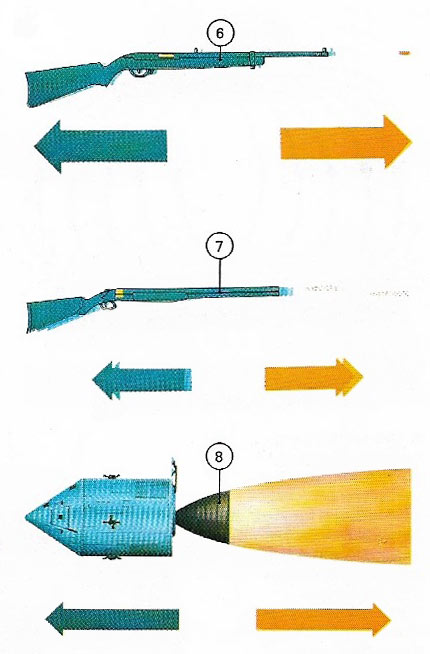
Newtons third law, elevator question (free body diagram ... Newton's third law and free body diagrams. Last Post; May 27, 2009; Replies 1 Views 3K. D. Free-Body Diagrams: Several Objects and Newton's Third Law. Last Post; Feb 23, 2010; Replies 2 Views 2K. S. Free body diagram and applying newtons law. Last Post; Nov 18, 2014; Replies 4 Views 1K. Free body diagrams and Newton's Law. PDF 3: Newton's Third Law of Motion Concepts to know for Newton's Laws Test: Study Note Packet! - Who Sir Isaac Newton was - Newton's Three Laws of Motion - what they are and how they work - All the equations we have used - Speed, distance, time - Velocity - Acceleration - Force - Gravity - Friction - Mass - Action Force - Reaction Force Newton's Third Law of Motion - NASA Newton's third law explains the generation of thrust by a rocket engine. In a rocket engine, hot exhaust gas is produced through the combustion of a fuel with an oxidizer. The hot exhaust gas flows through the rocket nozzle and is accelerated to the rear of the rocket. In re-action, a thrusting force is produced on the engine mount.
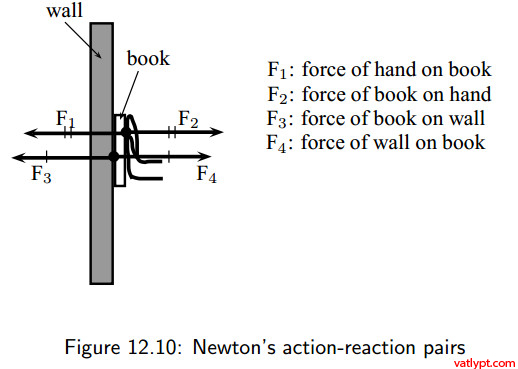
Newton's third law diagram. PDF Physics Secondary 5 3. Newton's Laws d. Describes qualitatively the law of action-reaction (Newton's Third Law). 7 Dynamics 5. Centripetal force a. Explains qualitatively the effect of centripetal force on a body in motion. 8 Dynamics 7. Equilibrium and resultant of several forces b. Determines the magnitude and direction of the vector associated with the Freebody Diagrams and Newton's Third Law Freebody Diagrams and Newton's Third Law Freebody diagrams often help you to figure out what happens in a dynamics problem. Simply draw the object in question and all the forces on it. Remember to add forces properly as vectors. It usually helps to split them up into "x" and "y" components before adding. PDF ENERGY FUNDAMENTALS - LESSON PLAN 1.4 Newton's Third Law ... Newton's Third Law of Motion explains the action - reaction force pairs. (Teachers can write the question on the board and discuss with the class.) UNDERSTAND : Explain Newton's Third Law of Motion in your own words. (Class discussion) ANALYZE. Compare and contrast all three of Newton's Laws of Motion using a Venn diagram. Newton's third law & interaction diagrams | IOPSpark Newton's third law & interaction diagrams. for Talking sense about force-pairs. Drawing an interaction diagram provides a way to generate a representation of all the interacting objects in a process, connected as interacting pairs. Each interaction results in a force acting on each of the pairs of objects.
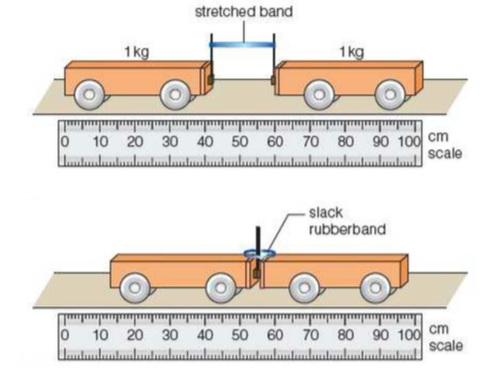
Newton's Third Law of Motion | Digestible Notes ⇒ By drawing a free body diagram for Alan (mass 80kg), the rope (mass 2kg) and Ben (mass 60kg), we can analyse the forces acting on each person ⇒ For each body the resultant force caused an acceleration of 2 ms-2. These calculations use Newton's second law. Newton's third law pairs ⇒ The Earth pushes Alan with 400N to the left. Alan ... What Is Newton's Third Law? - Lesson - TeachEngineering Students are introduced to Newton's third law of motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. They practice identifying action-reaction force pairs for a variety of real-world examples, and draw and explain simplified free-body diagram vectors (arrows) of force, velocity and acceleration for them. They also learn that engineers apply Newton's third law and an ... Newton's Third Law of Motion - Explanation, Interaction ... Newton's third law of motion states that to every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law implies a certain symmetry in nature. Visit BYJU'S to know more about Newton's 3rd law. Newton's Third Law of Motion - Physics Classroom Newton's third law of motion describes the nature of a force as the result of a mutual and simultaneous interaction between an object and a second object in its surroundings. This interaction results in a simultaneously exerted push or pull upon both objects involved in the interaction.
PDF How a Vanier College Instructor Connects Real Life With ... a Visual Classrooms activity focused on Newton's Third Law and the forces arising between pairs of interacting objects. As homework, Rhys asked students to take or find a sequence of photos of two interacting objects, before, during and after the interaction and post it to Visual Classrooms. In class, Newton's third law and free-body diagrams (practice ... Practice: Newton's third law and free-body diagrams. This is the currently selected item. Newton's third law of motion. More on Newton's third law. Next lesson. Newton's second law. Newton's third law of motion. Up Next. Newton's third law of motion. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. 4.2 Newton's Third Law | Week 2: Newton's Laws | Classical ... But Newton's third law tells us that there is a tiny acceleration on the Earth due to the person. That is the third law pair for gravity. mg downward exerted by the Earth on the person is paired with mg upward on the Earth exerted by the person. Now, for the normal force acting on the person, that force is exerted by the ground. Lesson Explainer: Newton's Third Law of Motion | Nagwa Newton's third law of motion describes the forces involved in these interactions. Sometimes this law of motion is stated this way: "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.". Here, "action" and "reaction" refer to the forces that arise whenever two objects interact. Considering the cases listed above, we can say ...
Newton's 3 Laws of Motion | The Science Cube Free body diagrams Tension in a string Static and dynamic friction Weight in an elevator. What are Newton's laws of motion? To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, states Newton's 3rd law of motion. If Newton's third law is true then how does a horse pull a cart.
5.5 Newton's Third Law - University Physics Volume 1 ... 5.10. Newton's third law represents a certain symmetry in nature: Forces always occur in pairs, and one body cannot exert a force on another without experiencing a force itself. We sometimes refer to this law loosely as "action-reaction," where the force exerted is the action and the force experienced as a consequence is the reaction.
PDF Newtons' Third Law - Montana State University the opposing force according to Newton's Third Law. A d The horizontal static friction force from the dashboard on the can. B The centrifugal force toward the curve's center on the can. C The horizontal static friction force from the can on the dashboard. D The downward gravity force from the Earth on the can. E The downward normal force
Same case of Newton's third law | Physics Forums Same case of Newton's third law. Thread 'Car's maximum acceleration on a road is proportional to what?'. I think both are same cases of Newton's third law. Both require applications of a force which generates static friction on rope and road and this force helps accelerate the monkey and the car up the rope and down the road. Right?
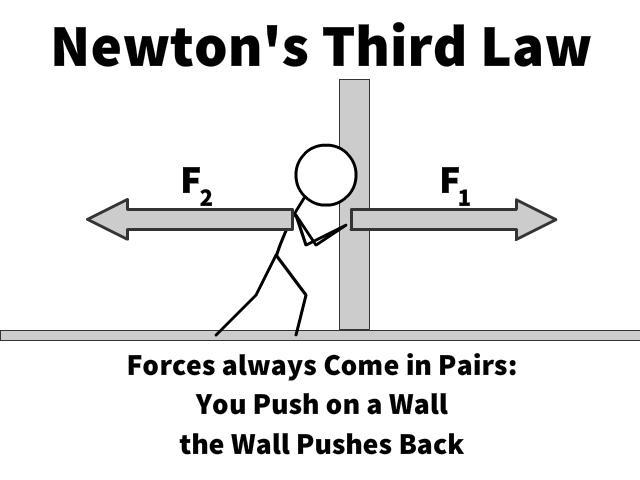
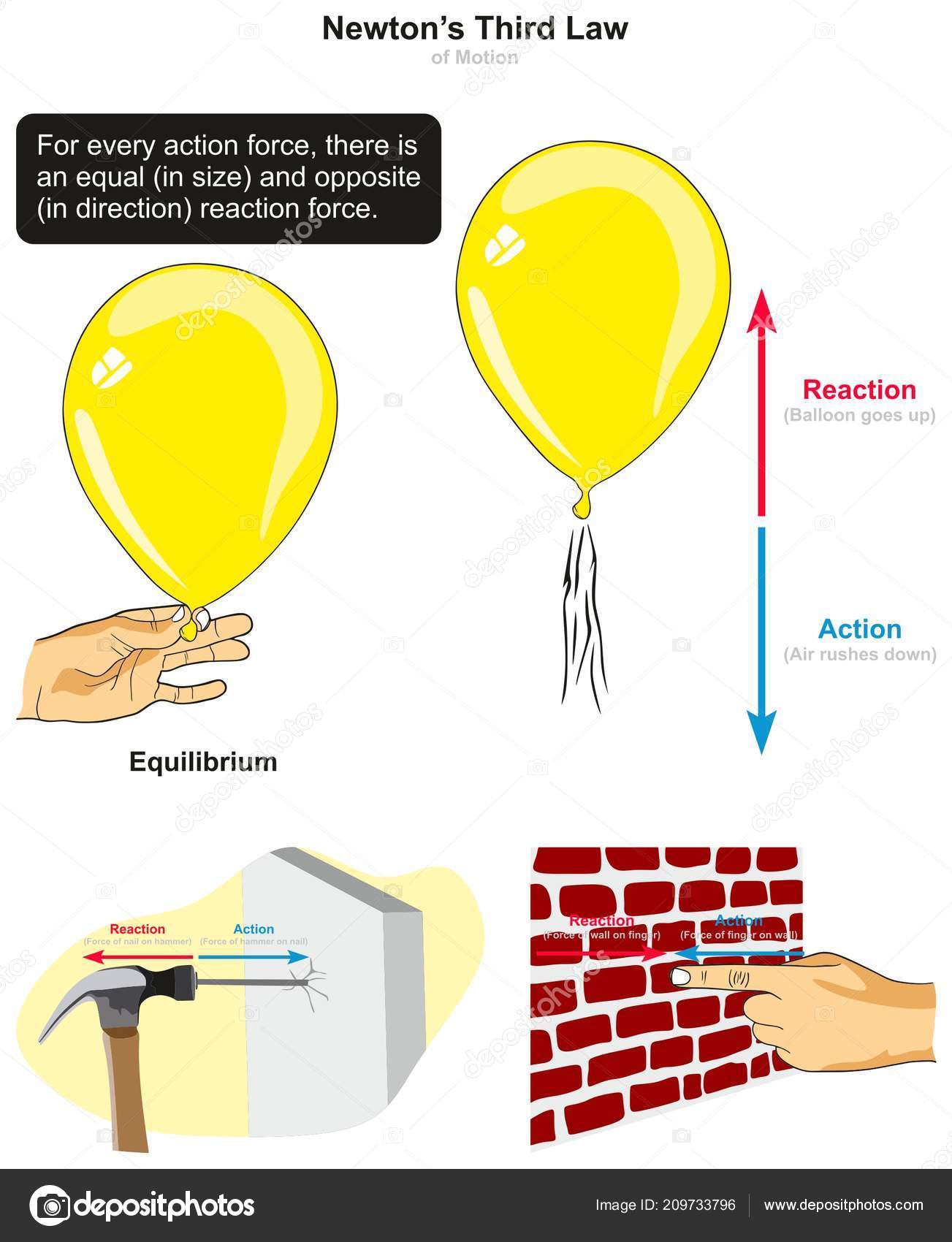
Newton's Laws Study Guide - CK-12 Foundation Newton's Third Law. This law states that for any force exerted by one object on another, the other object exerts an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. For example, if a person is pushing on a wall, the wall is also pushing back on them with an equal force in the opposite direction.
Newton's Three Laws Diagram - SmartDraw Newton's Three Laws of Motion. 3. To every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction. 2. The force exerted on a body equals the resulting change in the body's momentum divided by the time elapsed in the process. 1. Law of Inertia: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same ...
Newton's Laws of Motion - Three Laws of Motion Explanation ... Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's third law of motion describes what happens to the body when it exerts a force on another body. Newton's 3rd law states that there is an equal and opposite reaction for every action. When two bodies interact, they apply forces on each other that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Module 3 -- The Two-body Rule and Newton's Third Law - PER ... Free Body Diagrams and Newton's Laws. When constructing each free body diagram, think carefully about how the forces acting on it must be consistent with Newton's second and third laws: For every force in the diagram, you must be able to identify both the type of interaction that causes it and the other object involved in this interaction.
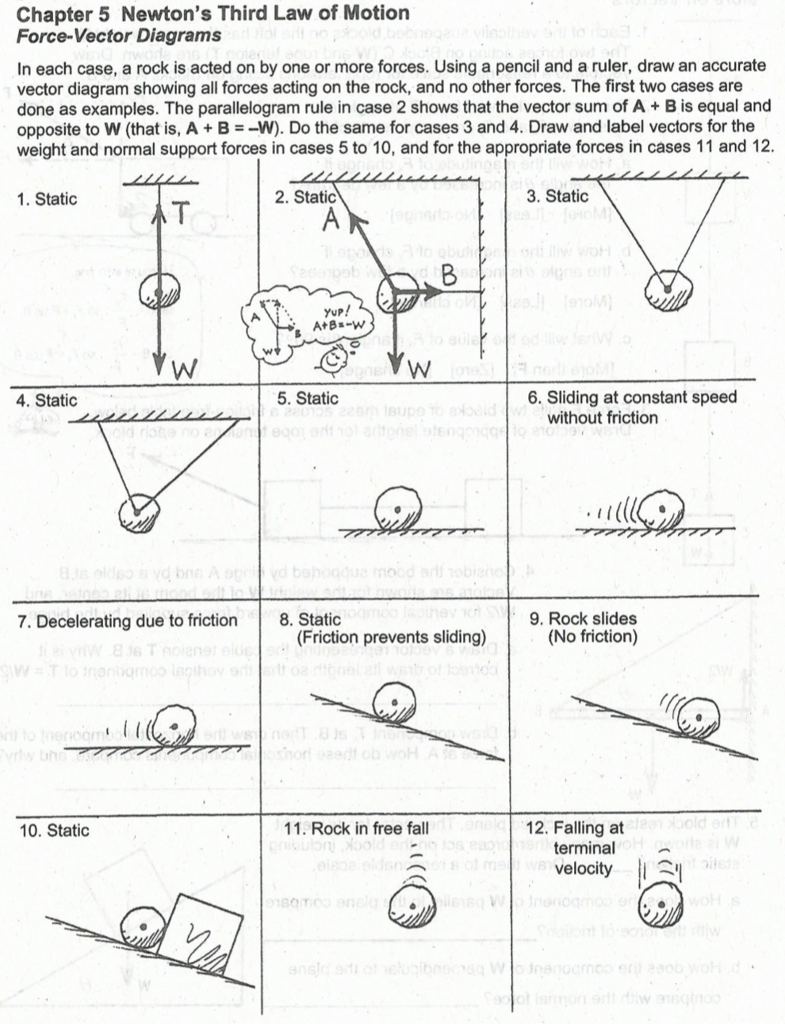
PDF NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION - University of Houston 5-3 Newton s Second Law of Motion • Free-body diagrams: A free-body diagram shows every force acting on an object. 1) Sketch the forces 2) Isolate the object of interest 3) Choose a convenient coordinate system 4) Resolve the forces into components 5) Apply Newton's second law to each coordinate direction
PDF Newton's third law - files.gabbart.com Newton's third law • Calculate the effect of forces on objects, including the nature of force pairs between objects. • Explain why action and reaction forces do not cancel each other out. • Correctly draw reaction (or action) forces on free-body diagrams. Objectives 1.
Newton's laws of motion - David Darling Newton's first law of motion describes inertial effects. An object resists being from rest by toppling backwards (1), although moving steadily it is undisturbed, as if at rest (2). When stopped it resists slowing and tends to continue moving (3). Fig 3. Newton's third law states there is an equal and opposite reaction to every force.
Newton's Third Law of Motion - NASA Newton's third law explains the generation of thrust by a rocket engine. In a rocket engine, hot exhaust gas is produced through the combustion of a fuel with an oxidizer. The hot exhaust gas flows through the rocket nozzle and is accelerated to the rear of the rocket. In re-action, a thrusting force is produced on the engine mount.
PDF 3: Newton's Third Law of Motion Concepts to know for Newton's Laws Test: Study Note Packet! - Who Sir Isaac Newton was - Newton's Three Laws of Motion - what they are and how they work - All the equations we have used - Speed, distance, time - Velocity - Acceleration - Force - Gravity - Friction - Mass - Action Force - Reaction Force
Newtons third law, elevator question (free body diagram ... Newton's third law and free body diagrams. Last Post; May 27, 2009; Replies 1 Views 3K. D. Free-Body Diagrams: Several Objects and Newton's Third Law. Last Post; Feb 23, 2010; Replies 2 Views 2K. S. Free body diagram and applying newtons law. Last Post; Nov 18, 2014; Replies 4 Views 1K. Free body diagrams and Newton's Law.
















0 Response to "38 newton's third law diagram"
Post a Comment