41 Newton's Second Law Diagram
Newton's Laws of Motion - Three Laws of Motion Explanation ... Newton's 2nd law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the object's mass. Newton's second law describes precisely how much an object will accelerate for a given net force. How to Solve Problems using Newton's Second Law - CPP Step 2: Select a "system" to which you intend to apply Newton's Second Law. In some problems there may be more than one candidate for the "system." You may not choose the best one the first time. No problem; just choose another one and do it again.
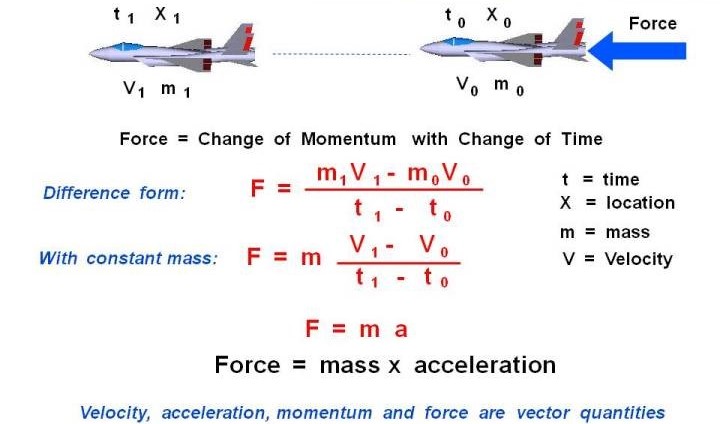
PDF Newton'S Laws of Motion, Equations of Motion, & Equations ... NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION (continued) The first and third laws were used in developing the concepts of statics. Newton's second law forms the basis of the study of dynamics. Mathematically, Newton's second law of motion can be written F = ma where F is the resultant unbalanced force acting on the particle, and a is the acceleration of the ...

Newton's second law diagram
Newton's Second Law - Revisited - Physics Classroom Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The law is often expressed in the form of the following two equations. Newton's Second Law and a Force Analysis. In Unit 2 of The Physics Classroom, Newton's second law was used to analyze a variety of physical ... Newton's 2nd Law (15 of 21) Free Body Diagrams, One ... Shows how to draw free body diagrams for simple one dimensional motion. Free-body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upo... Newton's laws of motion - Boston University In applying Newton's second law to a problem, the net force, which is the sum of all the forces, often has to be determined so the acceleration can be found. A good way to work out the net force is to draw what's called a free-body diagram, in which all the forces acting on an object are shown.
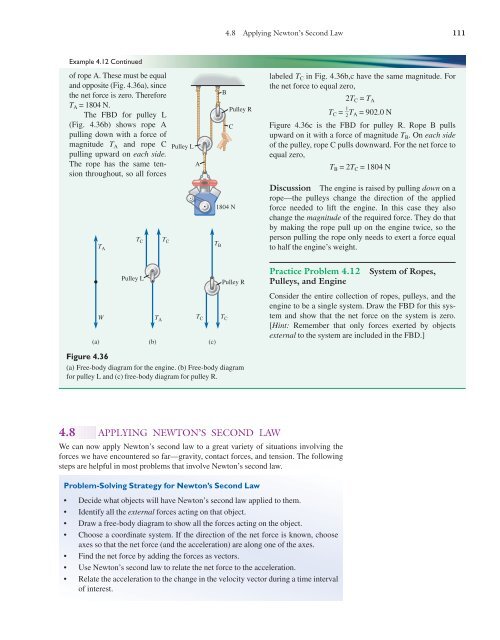
Newton's second law diagram. Newton's Laws of Motion - Eastern Illinois University We can apply Newton's Second Law to the y-component forces and find that n 1 = w 1 1. But now there is an additional and unknown force in the x-component of Newton's Second Law, F 1,net = F - P' = m 1 a. We need more information so we turn to the other mass, m 2. The first mass m1 exerts a force P on this mass, m2. PDF Experiment 5: Newton's Second Law 28 Experiment 5: Newton's Second Law FREE-BODY DIAGRAM SOLUTION METHOD: INSTRUCTIONS Step 1: Sketch the problem/situation and specify the coordinate system for each object in your system. Step2: Draw all forces (arrows that represent these vectors) acting on each object in the system you are investigating. PDF Newton's Second Law - Michigan State University Newton's Second Law Figure 4.2: Diagram of the apparatus 4.7 Procedure 1. Set up the air track as shown in Figure4.2. With the hanging mass disconnected from the glider and the air supply on, level the air track by carefully adjusting the air track leveling feet. The glider should sit PDF Newton's Second Law Lab - people.springfield.k12.or.us Newton's Second Law Lab Newton's second law of motion explains the relationship among force, mass, and acceleration. In this activity, you will study the relationship between acceleration and mass, while keeping force constant. A car carrying different masses will be pulled across a table by a hanging weight—the constant force.
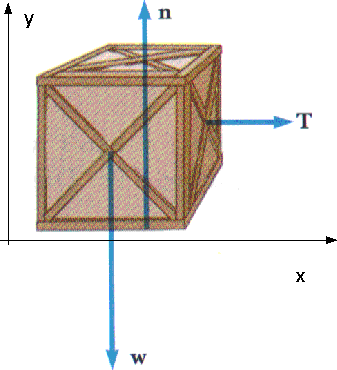
PDF Newton's Second Law Newton's Second Law 3 Figure 2: Free-Body Diagram of Forces on Cart and Hanging Mass Since force is a vector quantity, it is necessary to decide what are the positive and negative directions so that each force can be labelled as being either positive or negative. A useful rule is to say that the direction of motion is the positive direction. Newton's Second Law Of Motion - Derivation, Applications ... Newton's second law can be formally stated as, The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This statement is expressed in equation form as, a = F ne Dynamics (Force or Newtons 2nd Law) Problems - Physics ... Because Newton’s Second Law is a vector equation, you will need to divide all forces into their x- and y- components in order to work with the equation. Math is always easiest if you pick one axis to be along the direction of acceleration. That way, one component of a will be zero and you will have fewer linked equations. 3. Select the Relation PDF Newton's Second Law - Physics Department Newton's Second Law Objective The Newton's Second Law experiment provides the student a hands on demonstration of "forces in motion". A formulated analysis of forces acting on a ... Free-body diagrams of the forces on the cart and hanging mass are shown in Figure 4. Figure 3: Inclined Track with Hanging Mass .
Newton's Second Law for Rotation - Boston University Physics As usual, start with a free-body diagram, and then apply Newton's Second Law for Rotation. Στ = I α. The only torque we care about comes from the tension in the string. With torque given by τ = r × F, in this case the torque is: τ = rT There's a 90 degree angle between r and T. Solving Newton's Second Law for α: α = rT/I PDF Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion To study and apply Newton's first law. To study and apply Newton's second law. To study and apply Newton's third law & identify action-reaction force pairs. To draw a free-body diagram representing the forces acting on an object. To differentiate between mass and weight. Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion Courtesy of Wenhao Wu 6.1 Solving Problems with Newton's Laws - University ... Once a free-body diagram is drawn, we apply Newton's second law. This is done in Figure(d) for a particular situation. In general, once external forces are clearly identified in free-body diagrams, it should be a straightforward task to put them into equation form and solve for the unknown, as done in all previous examples. PDF 3.B) Newton's Second Law of Motion - Dr. Nada H. Saab-Ismail Figure (b): a free-body diagram that shows the horizontal forces acting on the car. In the diagram, the car is represented as a black dot, and its motion is along the +x axis. The free - body diagram is very helpful when applying Newton's second law and to determine the net force (F net). 17
5.4: Applying Newton's Laws - Physics LibreTexts To apply Newton's Second Law using the free-body diagram and coordinate system from Figure 5.4.10, we first write out all of the vector and then identify their x and y components.
Inertia and Mass - Physics Classroom Newton's conception of inertia stood in direct opposition to more popular conceptions about motion. The dominant thought prior to Newton's day was that it was the natural tendency of objects to come to a rest position. Moving objects, so it was believed, would eventually stop moving; a force was necessary to keep an object moving.
Speed versus Velocity - Physics Classroom Newton's Laws. Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces; Change of State; Fnet = m•a; Force and Motion; Mass and Weight; Match That Free-Body Diagram; Net Force (and Acceleration) Ranking Tasks; Newton's Second Law; Normal Force Card Sort; Recognizing Forces; Air Resistance and Skydiving; Solve It! with Newton's Second Law; Which One Doesn't Belong ...
6.1 Solving Problems with Newton's Laws - University ... Once a free-body diagram is drawn, we apply Newton's second law. This is done in Figure 6.2(d) for a particular situation. In general, once external forces are clearly identified in free-body diagrams, it should be a straightforward task to put them into equation form and solve for the unknown, as done in all previous examples.
Newton's second law - Newton's laws - Edexcel - GCSE ... Newton's second law Force, mass and acceleration. Newton's second law of motion can be described by this equation: resultant force = mass × acceleration
Entropy as Time's Arrow - Georgia State University The diagram at left depicts a more random or disordered configuration, but the key point is that there is a vast number of ways that such configurations could be achieved. So multiplicity is the key concept - molecular ensembles will spontaneously tend to evolve from configurations of lower multiplicity to configurations of greater multiplicity.
Newton's Second Law of Motion: Statement, Applications ... Newton's Second Law of Motion is one of the three laws of motion given by Sir Isaac Newton. Newton's Laws of Motion deal with force and its effects. Newton's Second Law of Motion is going to help us with the calculation of the net force on an object and its acceleration. The formula of Newton's Second Law of Motion is F = m × a.
10 Examples of Newton's Second Law of Motion in Everyday ... Newton's second law of motion can be observed by comparing the acceleration produced in a car and a truck after applying an equal magnitude of force to both. It is easy to notice that after pushing a car and a truck with the same intensity, the car accelerates more than the truck. This is because the mass of the car is less than the mass of ...
14A: Newton's Laws #1: Using Free Body Diagrams - Physics ... The key to the successful solution of a Newton's 2 nd Law problem is to draw a good free body diagram of the object whose motion is under study and then to use that free body diagram to expand Newton's 2 nd Law, that is, to replace the Σ F → with an the actual term-by-term sum of the forces. Note that Newton's 2 nd Law (14A.2) a → = 1 m ∑ F →
Lab 3 - Newton's Second Law - WebAssign In the horizontal direction, the tension in the string acts in the + x direction on the cart while the friction force between the cart's tires and the surface of the track acts in the − x direction. Newton's second law, in the x and y directions, respectively, are ( 7 ) Fnet,2x = T − f = m2a ( 8 ) Fnet,2y = FN − m2g = 0
Freebody Diagrams and Newton's Third Law Freebody Diagrams and Newton's Third Law Freebody diagrams often help you to figure out what happens in a dynamics problem. Simply draw the object in question and all the forces on it. Remember to add forces properly as vectors. It usually helps to split them up into "x" and "y" components before adding.
Newton's Laws of Motion & Force: Overview & Examples ... Newton's second law is as known as the law of force and acceleration. It is a math equation stating: f = m x a, where f is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration. Register to view this lesson
PDF LESSON PLAN 1.3 Newton's Second Law of Motion Create an experiment that proves Newton's Second Law as true. Teachers can ask students to brainstorm ideas and teachers write them on the board. Students can conduct the experiments if materials are available. Complete a Venn diagram comparing Newton's First Law of Motion and Newton's Second Law.
Isaac Newton - Wikipedia Isaac Newton was born (according to the Julian calendar in use in England at the time) on Christmas Day, 25 December 1642 (NS 4 January 1643), "an hour or two after midnight", at Woolsthorpe Manor in Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, a hamlet in the county of Lincolnshire.
Newton's Second Law of Motion - Physics Classroom Newton's second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object.
PDF PHYS 101 Lecture 5 Dynamics: Forces & Newton's Laws PHYS 101: Lecture 5 Applying Newton's Second Law: The Free-Body Diagram (FBD) A free-body diagram (great tool for identifying forces): isolates the object being analyzed has labeled arrows (vectors) for each individual force acting on the object. The vector length is the magnitude of the force The vector direction is the direction in which the force acts
Newton's laws of motion - Boston University In applying Newton's second law to a problem, the net force, which is the sum of all the forces, often has to be determined so the acceleration can be found. A good way to work out the net force is to draw what's called a free-body diagram, in which all the forces acting on an object are shown.
Newton's 2nd Law (15 of 21) Free Body Diagrams, One ... Shows how to draw free body diagrams for simple one dimensional motion. Free-body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upo...
Newton's Second Law - Revisited - Physics Classroom Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The law is often expressed in the form of the following two equations. Newton's Second Law and a Force Analysis. In Unit 2 of The Physics Classroom, Newton's second law was used to analyze a variety of physical ...







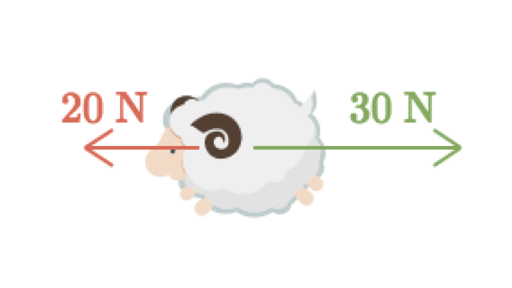



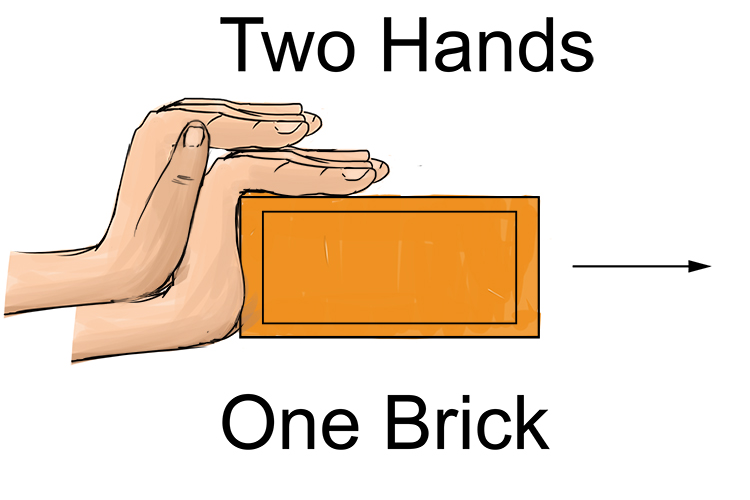












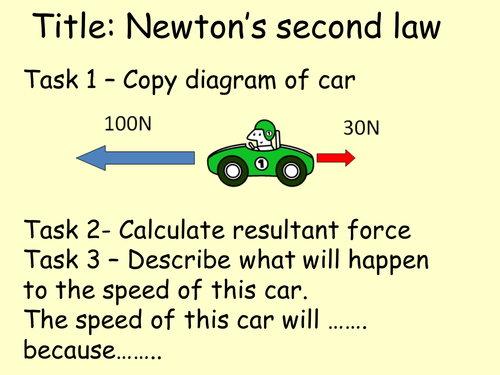

![PDF] Problem Solving of Newton's Second Law through a System ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/bcd6718c9916476104d4e09db0b8307d7689d8d7/3-Figure1-1.png)


0 Response to "41 Newton's Second Law Diagram"
Post a Comment