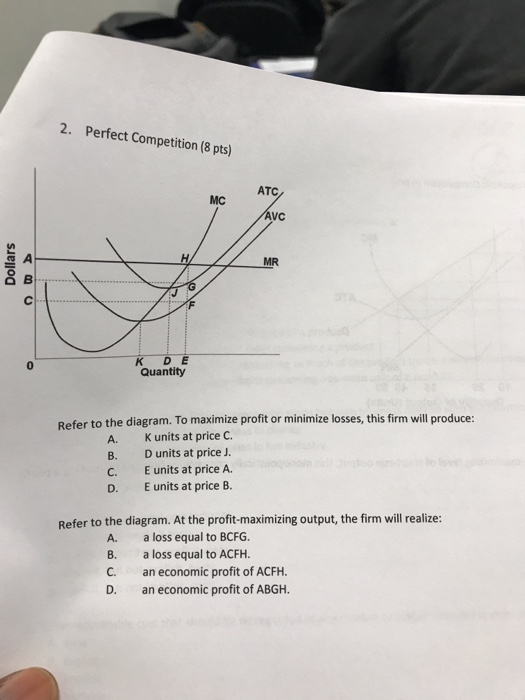
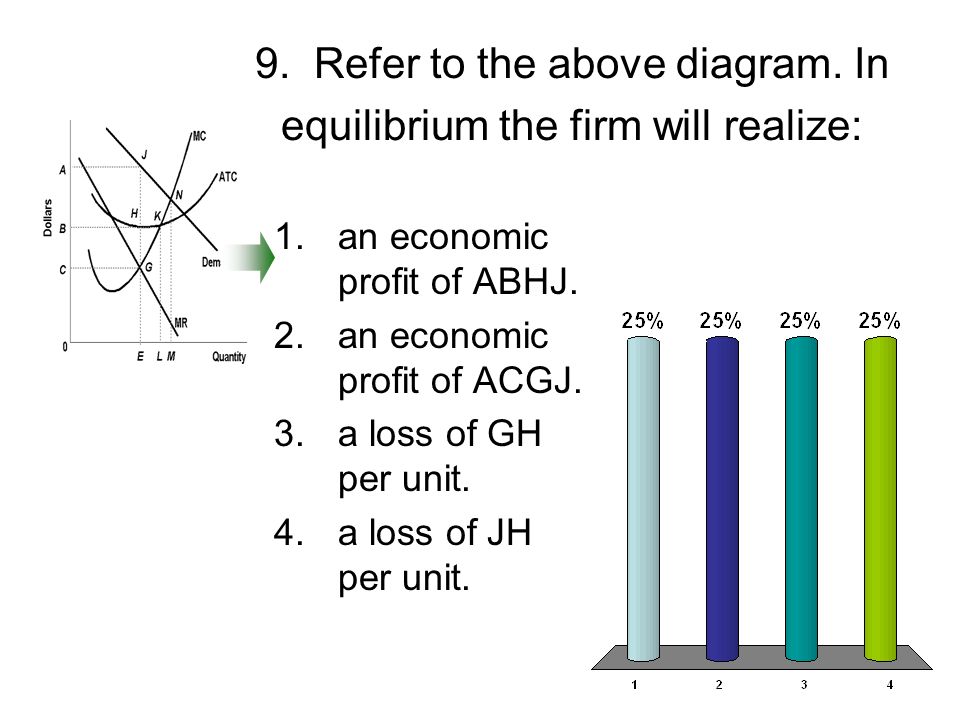
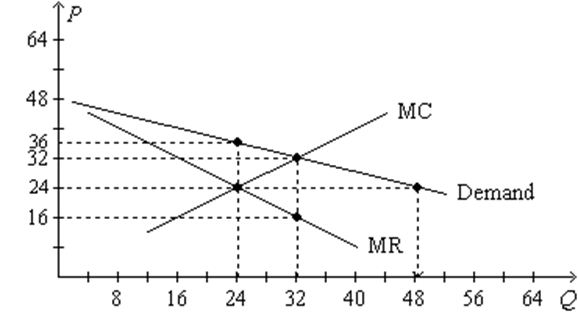
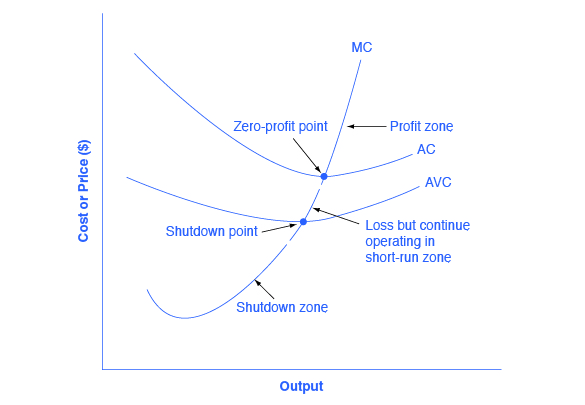
41 refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize:
Exams and Quiz Solutions. ACC 563 Quizzes and Exams – Perfect Score Guaranteed . Email us at ewood6449@gmail.com if you need help with your Quizzes, Exams, Writing Assignments, Homework Problems, Discussions, Term Papers etc. for your classes. Total profit is maximized when the firm produces OQ* units of output (as in Figure 7.1). Sales maximization, on the other hand, refers to maximization of total revenue ( = P x Q ), rather than maximization of Π (It is because if a firm quotes zero price it can sell an astronomical amount but its...
2. an economic profit of ACGJ. 3. a loss of JH per unit. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be

Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize:
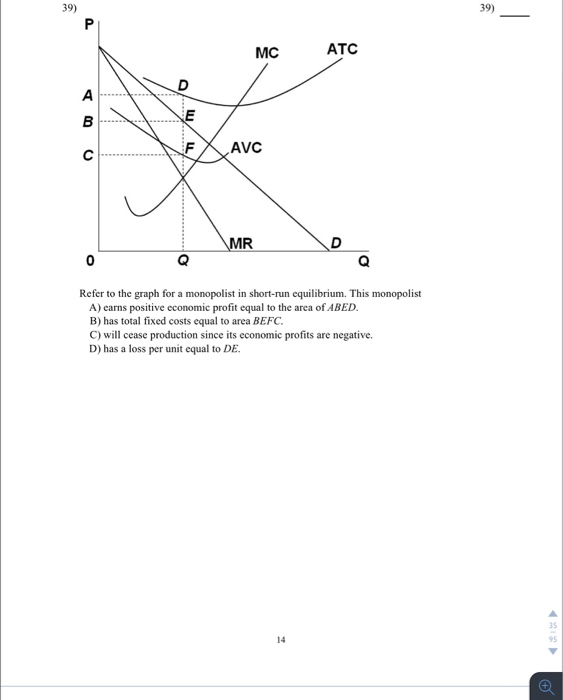
Profit maximizing-output: The optimal level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. It is the ascertained to be 4 under the first column above. Total revenue that maximized profit= profit-maximizing price × Profit maximizing-output. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A. a loss equal to BCFG. 6. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ.
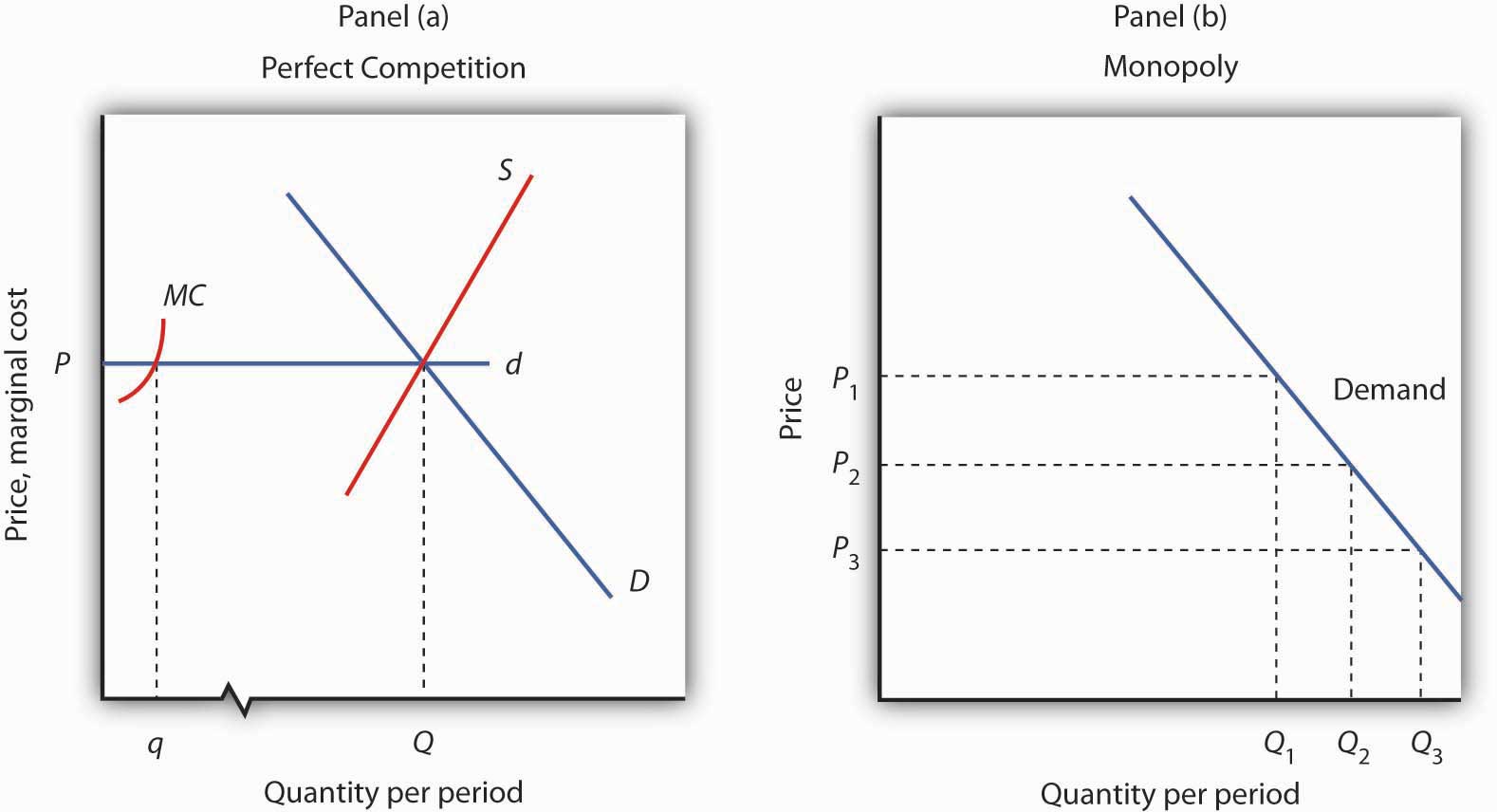
Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize:. Profits are maximized at the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. So profit maximization explains what the firm does when the price, when the market price, changes. So we want to show on the diagram how large your profits or how large your losses are when you... Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. The monopolist's profit maximizing level of output is found by equating its marginal revenue with its marginal cost, which is the same Monopolists will experience short‐run losses whenever average total costs exceed the price that the monopolist can charge at the profit maximizing level of output. The profit-maximizing output is found by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. To determine the profit-maximizing level of output with the tax, equate marginal revenue with If there is only one firm in the industry, then the firm will act like a monopolist and produce at the point...
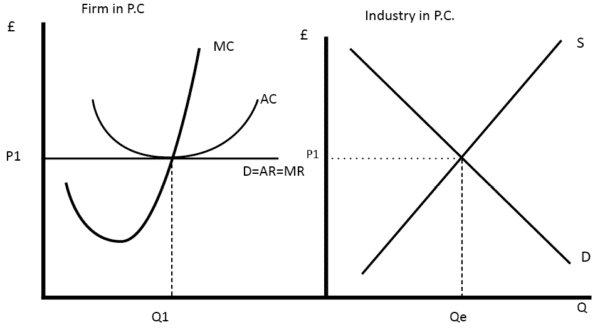
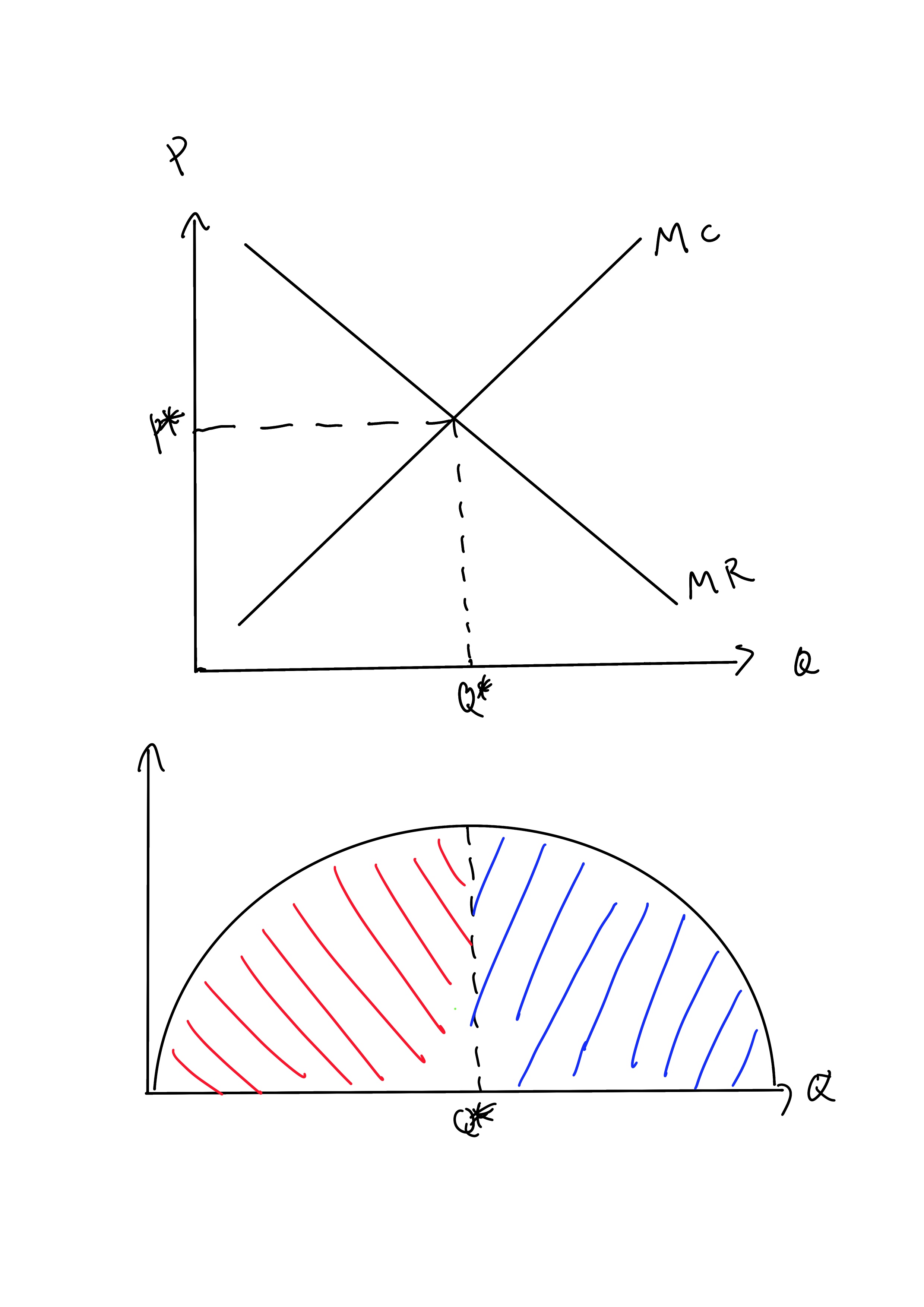
When the firm is producing at the profit maximizing output level, it chooses the combination of inputs that minimizes the cost of producing that output Therefore, profit is maximized and equilibrium is achieved at point E on producing Q2 level of output where MR = MC. Our focus remains to maximize... The same profit-maximization rule applies when positive profit is not possible. In the example above, a quantity of 3 is still the profit-maximizing quantity, since this quantity results in the largest amount of profit for the firm. When profit numbers are negative over all quantities of output, the... Instructor's Manual with Solutions Manual Principles of Microeconomics FOURTH EDITION PMG The firm wants to maximise profits, so it produces at the level of output where MC = MR. This occurs at point A. Drop a vertical line to find the firm's output (Q1). At Q1, AR > AC and the difference between average revenue and average cost is the distance AB. This is the profit per unit.
At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: 1. a loss equal to BCFG. 1. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: 1. loss of $320. • Profit maximization implies cost minimization. • The firm chooses the least cost combination of capital and. labour to achieve its profit-maximizing If the firm were to hold the initial cost outlay constant at C0 dollars, the isocost would rotate around C0 and the firm would move from point P to... a) Profit-maximizing firms generally allocate output among plants so as to keep marginal costs equal. But notice that MC2 < MC1 whenever 1 If consumers are less willing to change quantity as price increases toward the monopoly level, the firm will be able to extract more surplus from the market. To maximize profit, a firm chooses a quantity of output such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost. For example, hiring an extra unit of labor increases output and therefore increases revenue; the firm compares this additional revenue to the additional cost from the higher wage bill.
The Profit-Maximizing Price and Quantity A firm that sets both the price and quantity maximizes profits by producing a quantity at which the marginal The marginal cost is the increase in cost if a firm produces another unit of output. The firm charges what the market will bear at the profit...
Total output divided by a particular input, for example per worker (divided by the number of workers) or per worker per hour (total output divided by the total number of hours of labour put in). We can calculate Alexei’s average product of labour, as we did for the farmers in Unit 2. If he works for 4 hours per day, he achieves a grade of 50.
The profit-maximizing output for this firm is c. may realize either economic profit or losses in the long run. A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: a. will never produce in the output range where marginal revenue is positive.
At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A. a loss equal to BCFG . 76. Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market: Refer to the data.
The profit-maximizing output for this firm is. answer choices. above 440 units. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize.
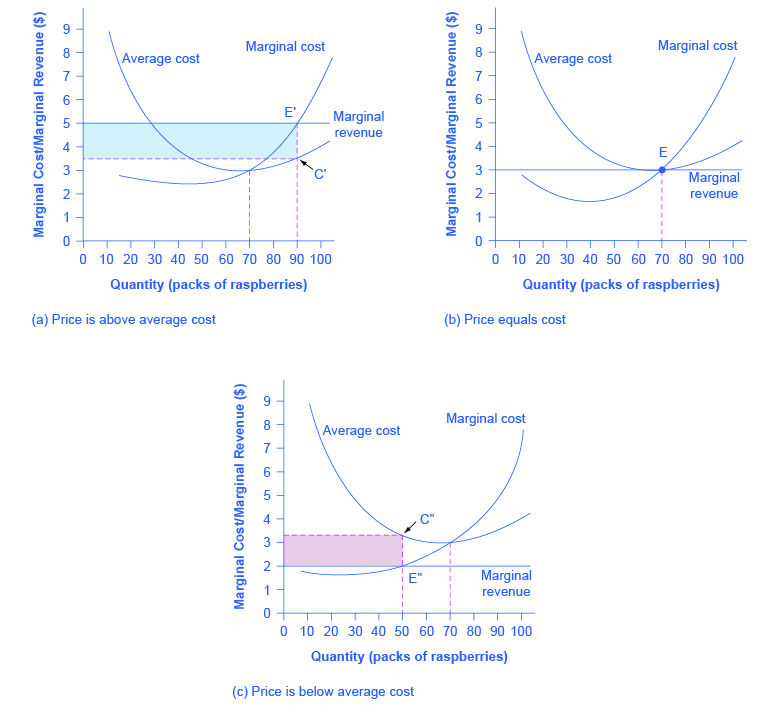
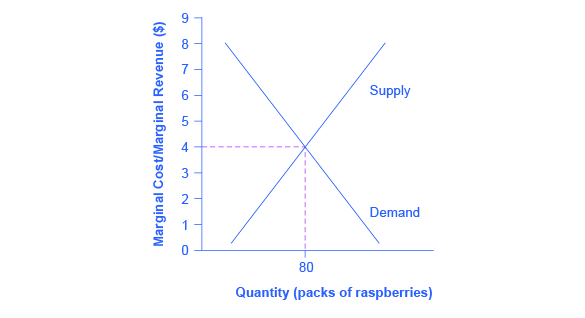
But a profit-maximizing firm will prefer the quantity of output where total revenues come closest to total costs and thus where the losses are smallest. This is referred to as duality. The profit-maximizing choice for a perfectly competitive firm will occur where marginal revenue is equal...
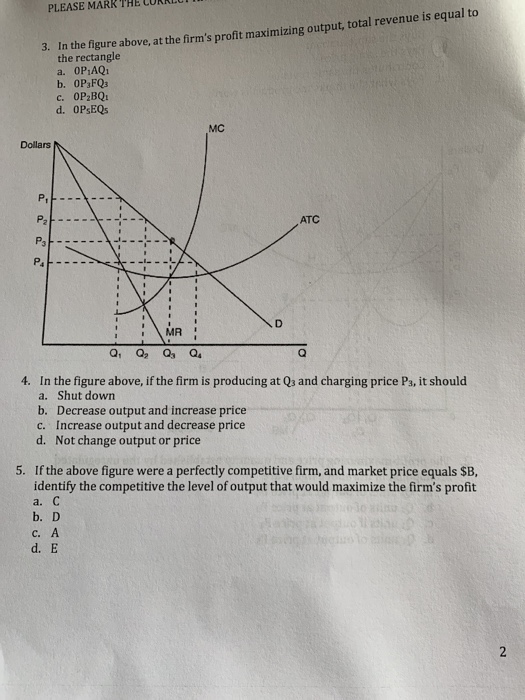
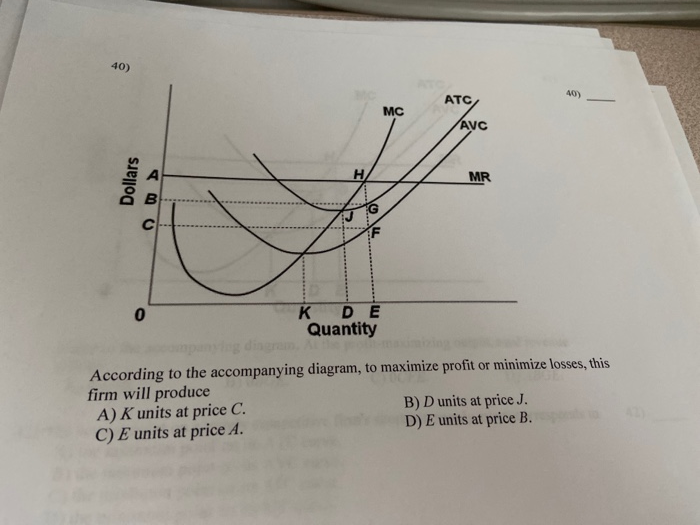
To maximize profit or minimize loses this firm will produce: a. C units at price G, and realize an economic profit of FG per unit. b. B units at Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: a. OF * NB b. OG* LD c. OG * KCthis is not the right answer because...
The profit-maximizing output is found by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. b. What are the firm's profit-maximizing output and price? Indicate the profit-maximizing output for each factory
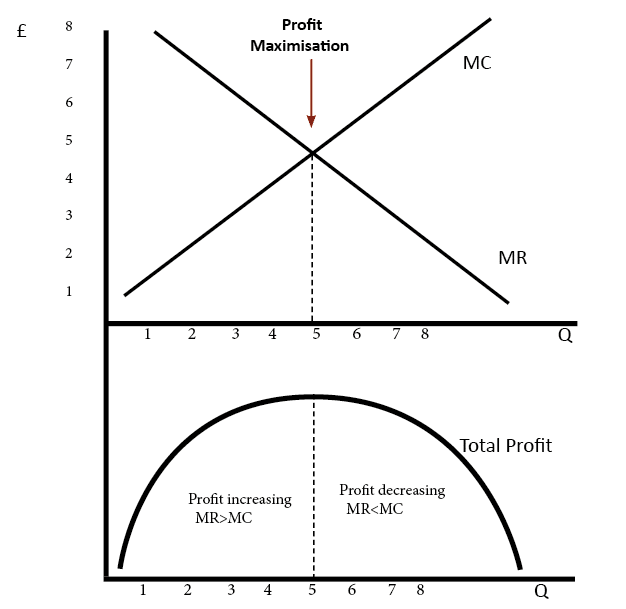
The profit-maximizing choice for a perfectly competitive firm will occur at the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost—that is, where MR = MC. This occurs at Q = 80 in the figure. Does Profit Maximization Occur at a Range of Output or a Specific Level of Output?
At the profit maximizing level of output the firm will realize. The profit maximizing output for this firm will be. Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Profit Maximising Behaviour Of A Firm With Diagram. Short Run Profit Max For A Perfectly Competitive Firm...
An explanation of profit maximisation with diagrams - Profit max occurs (MR=MC) implications for perfect competition/monopoly. Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal...
Profit maximization has been one the prime objectives of the private business enterprises. Later on, in recent times new theories of business firms have Minimum profits refer to the amount which is less than maximum profits. The minimum profits are determined on the basis of firm's need to maximize...
9 ) Refer to Figure 13-3. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units Should the firm represented in the diagram continue to stay in business despite its losses? price? c. At the profit-maximizing output level, how much profit will be realized? d. Does this graph...
• A profit-maximizing firm chooses both its inputs and its outputs with the goal of achieving maximum economic profits. • We can use the marginal cost curve to show how much the firm will produce at every possible market price.
Profit Maximizing Output Chapter 10 Proprofs Quiz Refer ... Produce 44 units and realize an economic profit. At the profit maximizing level of output the firm will realize. Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 4 units of output at 2 per unit and 5 units at 175 per unit.
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit.
At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ.
At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A. a loss equal to BCFG. 6. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3.
Profit maximizing-output: The optimal level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. It is the ascertained to be 4 under the first column above. Total revenue that maximized profit= profit-maximizing price × Profit maximizing-output.


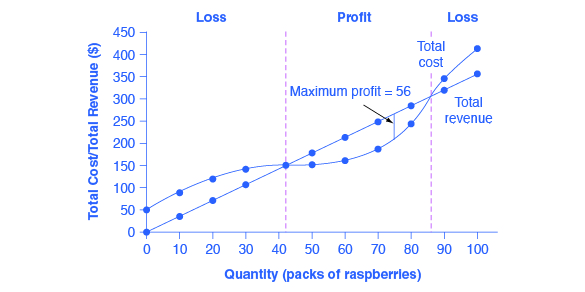
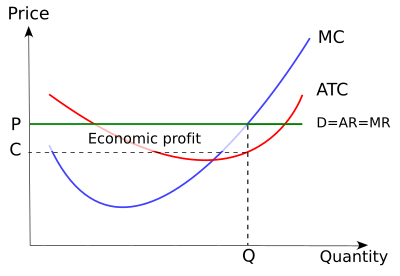

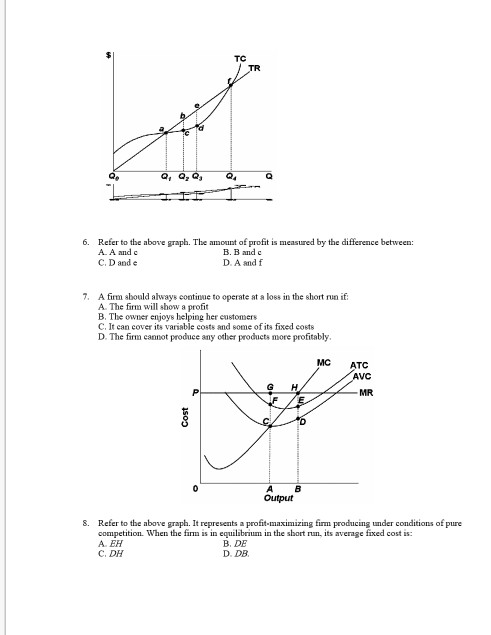


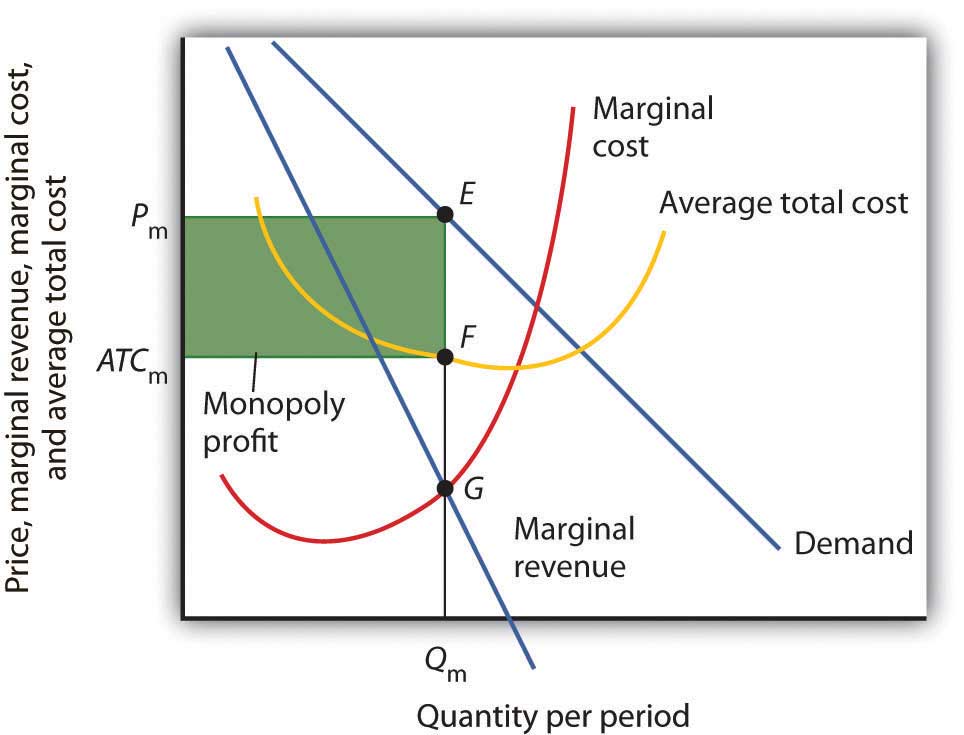










0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize:"
Post a Comment