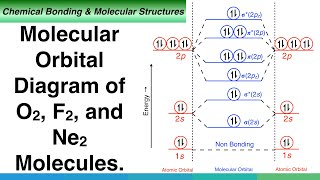
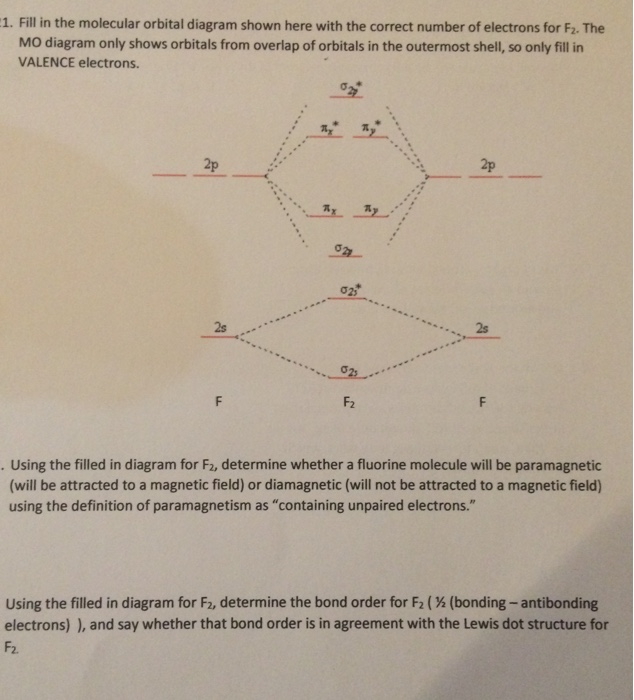
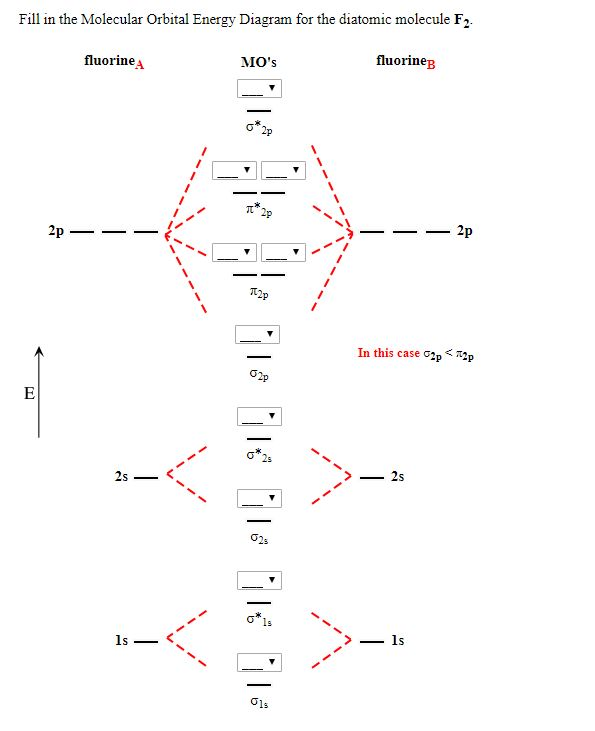
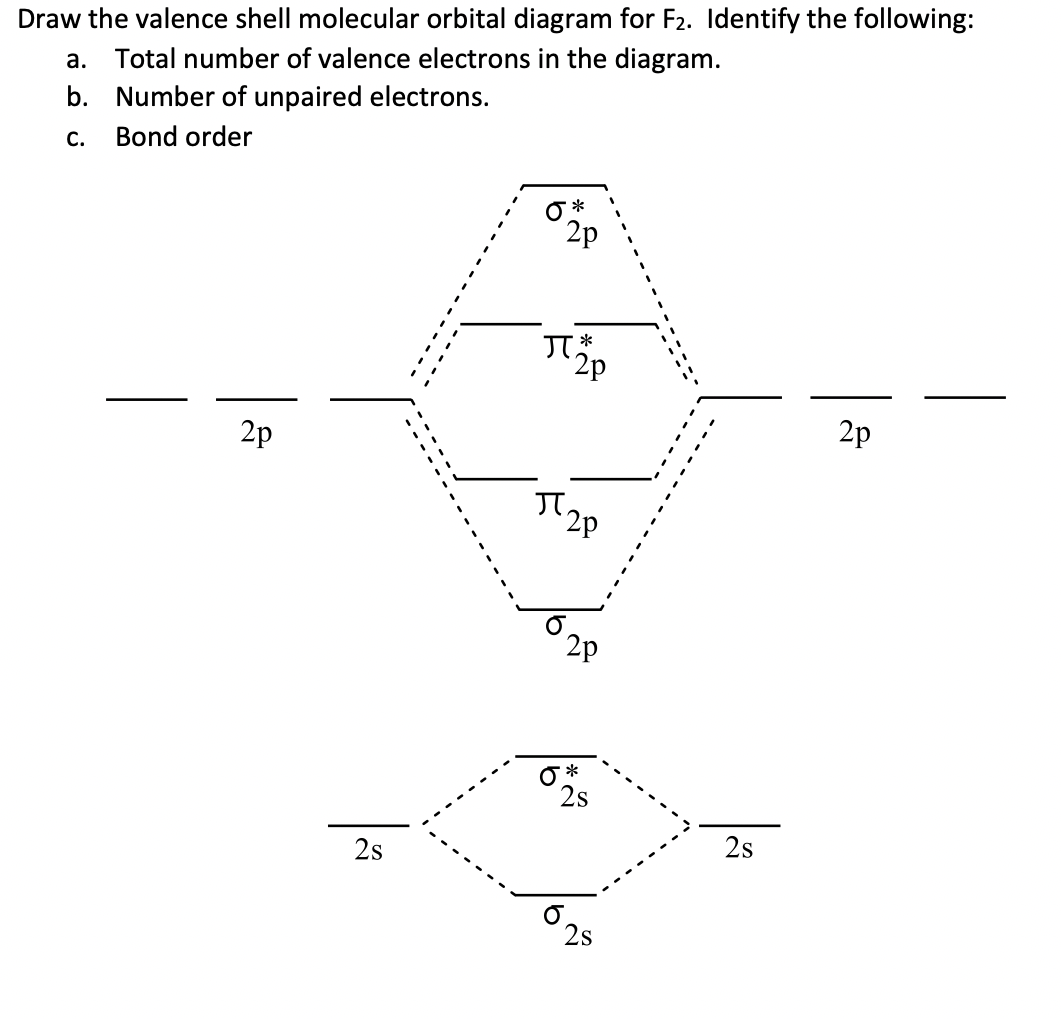
42 molecular orbital diagram f2
Molecular Orbital Theory: Explanation, Illustrations and... - Embibe Molecular Orbital Theory: To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Ans: The molecular orbital theory characterizes the electronic structure of molecules using In terms of the energy level diagram, it represents as. Give the molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. - Doubtnut Give the molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Updated On: 12-03-2022. camera. Get Answer to any question, just click a photo and upload the photo and ...1 answer · Top answer: Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams.
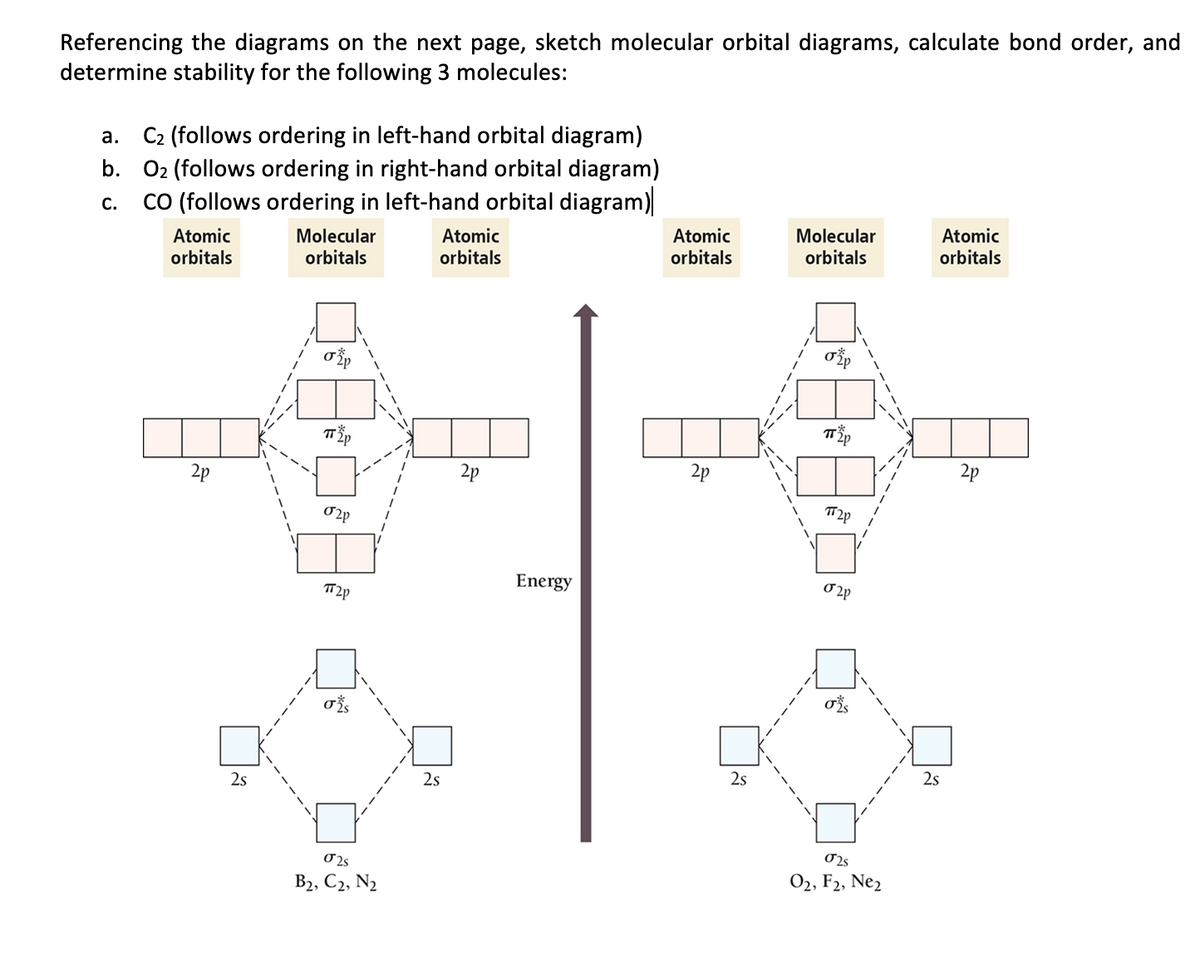
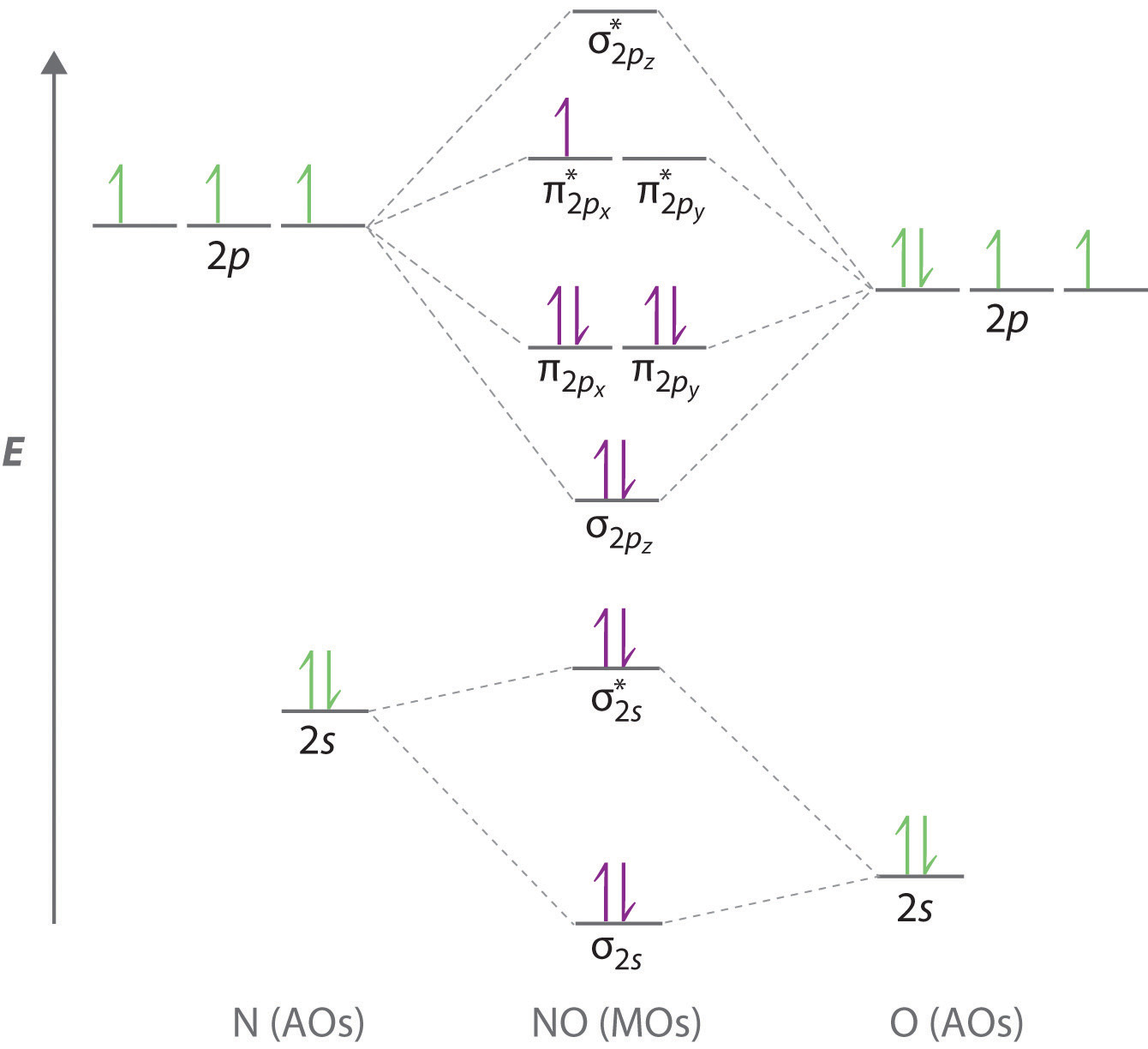
PDF Slide 1 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic. e.g. for CO - similar to N2 - but with different a.o. energies for C and O, i.e. O non-bonding electrons on F. Electronic configuration: [F2s22p4]σsp2σ*sp0. Diamagnetic. Bond order = 1. F2s non-bonding - too low in energy F2px,2py...
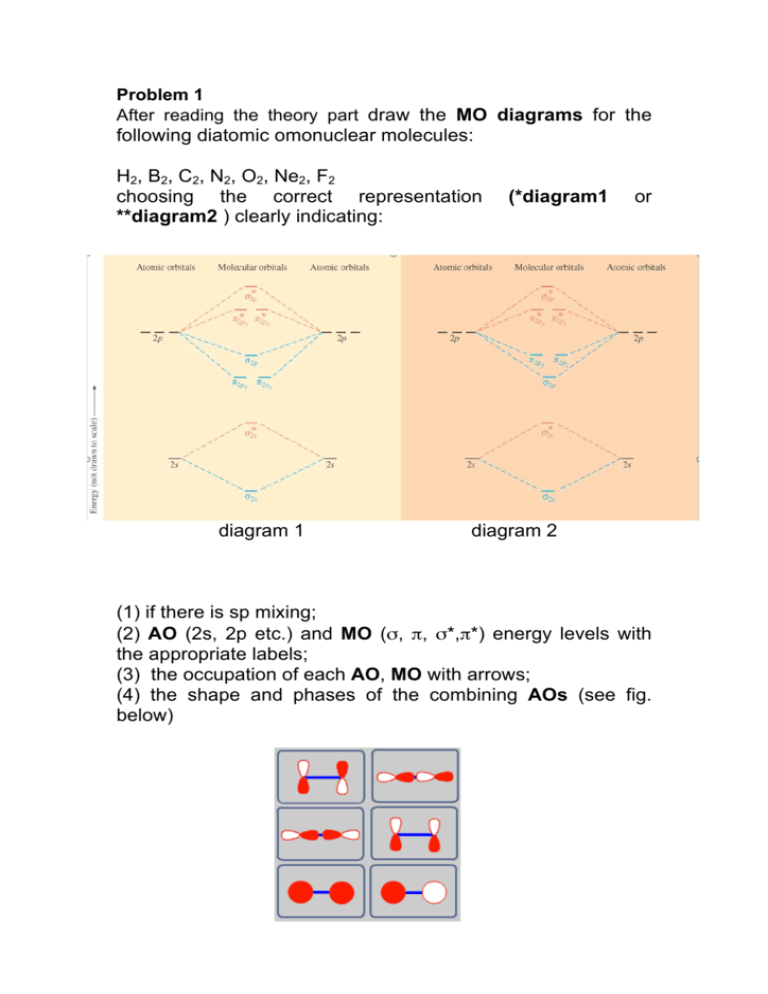
Molecular orbital diagram f2
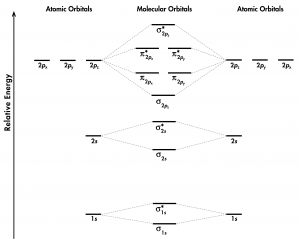
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Quora Originally Answered: Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O2 different from N2? Whilst this is the MO diagram for N₂: If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the Second Period (Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂, O₂, and F₂), the resulting pattern looks like this PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Molecular orbital calculations indicate, however, that for O2, F2, and hypothetical Ne2 molecules, the 2p orbital is lower in Diagrams such as these are used to describe the bonding in a molecule in MO terms. Electrons occupy MOs according to the same rules developed for atomic orbitals; they...
Molecular orbital diagram f2. PDF Molecular | 90" (porbitals). This dilemma has been resolved by orbital Molecular Orbital ~ a l c u l aitons. John D. Roberts. For practicing organic chemists the simple, linear-combination-of-atomic-orbitals (LCAO), molecular- orbital method p e r m i t s useful calculations of semi- empirical elec-tronic energies of unsaturated molecules with no m o r e than high school... Molecular orbital diagram - Infogalactic: the planetary knowledge core A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. PDF Lecture 1 Lecture 6: ML6 molecular orbital energy diagrams incorporating p-acceptor and p-donor ligands. Electron counting revisited and link to spectrochemical Using group theory it is possible to determine the symmetry of the orbitals involved. i) determine the point group of the molecule (in this case Oh)... What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Quora 12 Mar 2017 — The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine ...6 answers · 63 votes: Here is the solution, %3E * For O2 molecule, %3E * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.What is an (F2-) bond order? - Quora5 answers9 Feb 2016Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O₂ ...2 answers1 Aug 2019More results from
MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels. CHAPTER 5: MOLECULAR ORBITALS bond order = 1 (like F2) Cl2 has the weakest bond. ... molecular orbitals in the diagram ... of valence electrons as F2, would have a single bond.29 pages Molecular orbital diagram for BF3 - Chemistry Stack Exchange I'm trying to build a molecular orbital diagram for BF3 and I'm running into problems with irreducible representations on the F side. 2s for B has an irreducible I found the following diagram for BF3 online but it doesn't generate the E' anti bonding and also doesn't generate enough molecular orbitals.
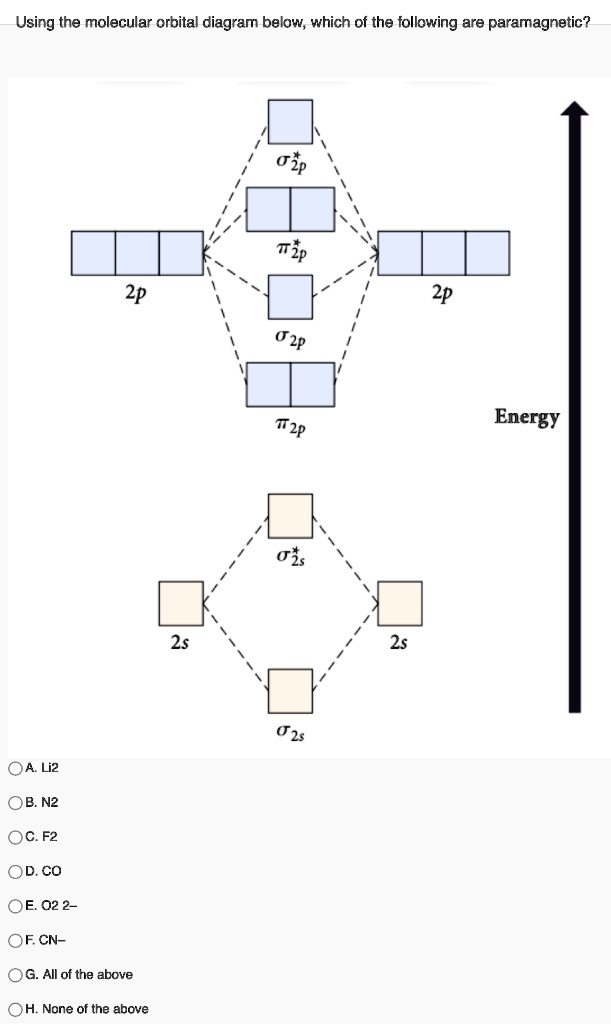
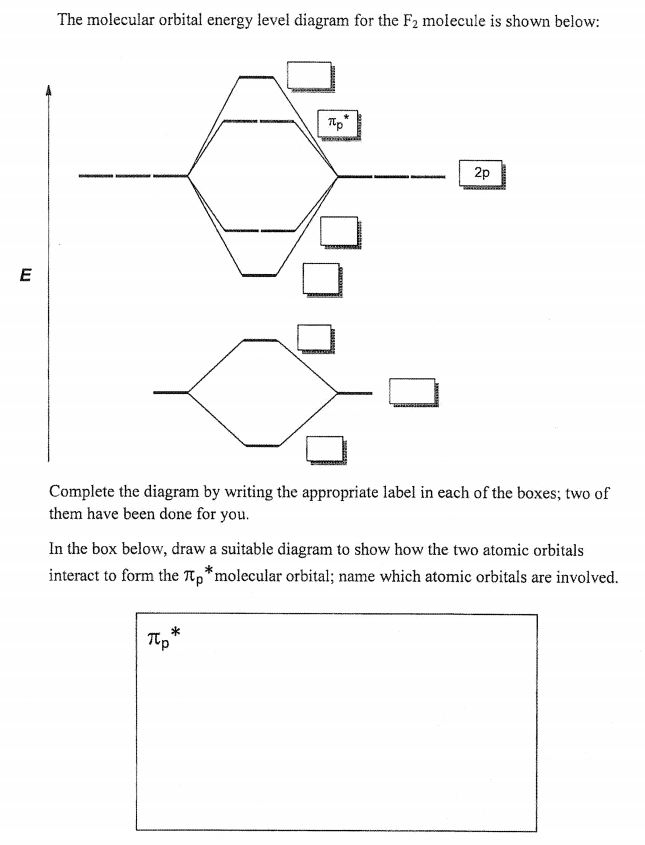
What is the molecular electron configuration of "F"_2? | Socratic 3 Jul 2017 — Notice how the σg(2p) , or the σ2pz molecular orbital, dips down below ... diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this:.1 answer · (σ2s)2(σ*2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π*2px)2(π*2py)2 Recall that there are orbital mixing effects for homonuclear diatomic molecules that decrease ... PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the... Asked for: "skewed" molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bonding... Figure 4.10.1: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules.(a) For F 2 , with 14 valence electrons (7 from each F atom), all To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O 2 , we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level... Molecular Orbital Theory: Types, Methods, Rules, Examples and... Molecular Orbital Theory. The Valence Bond Theory fails to answer certain questions like why He2 molecule does not exist and why O2 is paramagnetic. According to the Molecular Orbital Theory, individual atoms combine to form molecular orbitals. Thus the electrons of an atom are present in...
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram for F2(2+) - YouTube When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so...
Molecular Orbital Method - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Molecular orbital calculations on stable structures and on electronic and lithium-adsorption properties of several polyaromatic hydrocarbon sheets The method was applied to ab initio and empirically corrected calculations of LiF, F 2 , and F 2 − . The transformation of the matrix elements to the...
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry | Socratic Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure. It describes electrons as moving under the influence of the nucleus and not Molecular Orbital (MO) theory better explains the properties of more complex molecules. MO theory explains the partial bonds of NO₃⁻ without using...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified | by Megan A. Lim | Medium Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
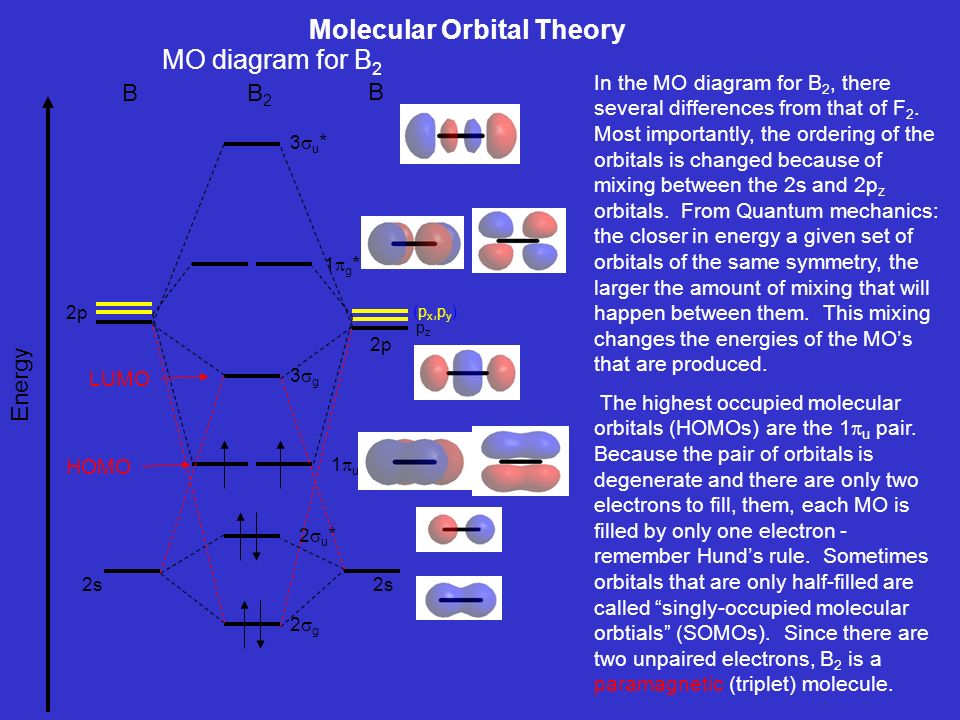
Molecular Orbital Theory The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p Experiments have shown that O2 and F2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B2, C2, and N2 are best...
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule Also class 11 ... Draw molecular orbital diagram for ${{F}_{2}}$ molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Verified. 101.4k+ views.1 answer · Top answer: Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT).The bond order calculations ...
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The diagram shows how the molecular orbitals in lithium hydride can be related to the atomic orbitals of the parent atoms. Notice that the relative energies of the 2p-derived σ and π bonding molecular orbitals are reversed in O2 and F2. This is attributed to interactions between the 2s orbital each atom...
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. Figure 8. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and find out the ... Molecular orbital diagram and bond order of fluorine molecule. Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons. These 18 electrons are filled in various molecular orbitals, in the increasing order of their...
PDF Microsoft Word - Handin8s2017ans.docx 1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. The XeF2 is an electron excess molecule. You can think of the molecule as the complex between Xe and F2, both of which are closed shell.
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory... Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. Molecular Orbital Theory - BH3. The BH3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Chemistry Study... | eMedicalPrep The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. This kind of mixing of orbitals or symmetry interaction is not applicable for O 2 and F 2 molecule formation because of larger energy gap between 2s and 2p orbitals for these atoms.
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... ...molecular orbitals (MOs) (σ, π and g, u) - Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams - mixing of different AO's - More complex molecules (CO, H2O ….) • It is a waste of both the lecturers and students time if the tutorial to ends up being a lecture covering questions. 5. An introduction to Molecular Orbital...
Molecular Orbital Theory - GeeksforGeeks The Molecular Orbital Theory is a chemical bonding theory developed at the turn of the twentieth century by F. R. Hund and R. S. Mulliken to explain the structure and properties of various molecules. The valence-bond theory failed to adequately explain how certain molecules, such as...
PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Molecular orbital calculations indicate, however, that for O2, F2, and hypothetical Ne2 molecules, the 2p orbital is lower in Diagrams such as these are used to describe the bonding in a molecule in MO terms. Electrons occupy MOs according to the same rules developed for atomic orbitals; they...
What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Quora Originally Answered: Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O2 different from N2? Whilst this is the MO diagram for N₂: If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the Second Period (Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂, O₂, and F₂), the resulting pattern looks like this
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
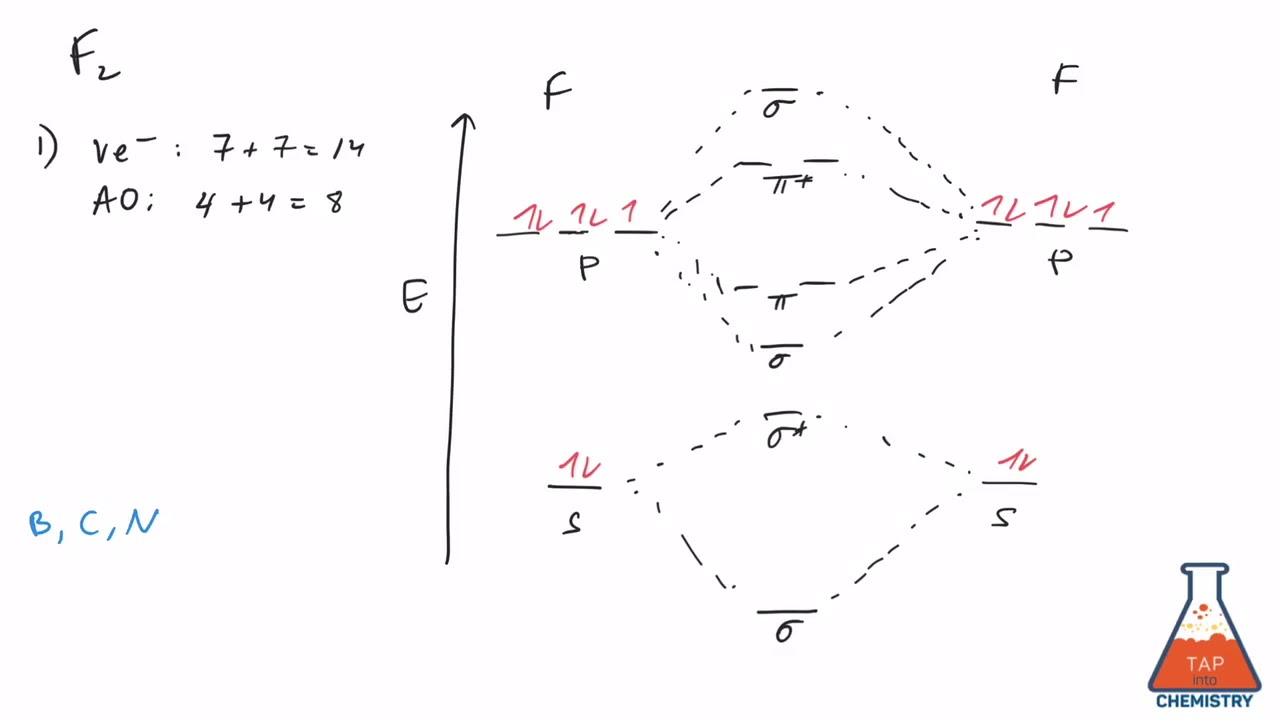





![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/dae/d7baa23a1d4a2ea2c90e0a703e2fd41d.jpg)

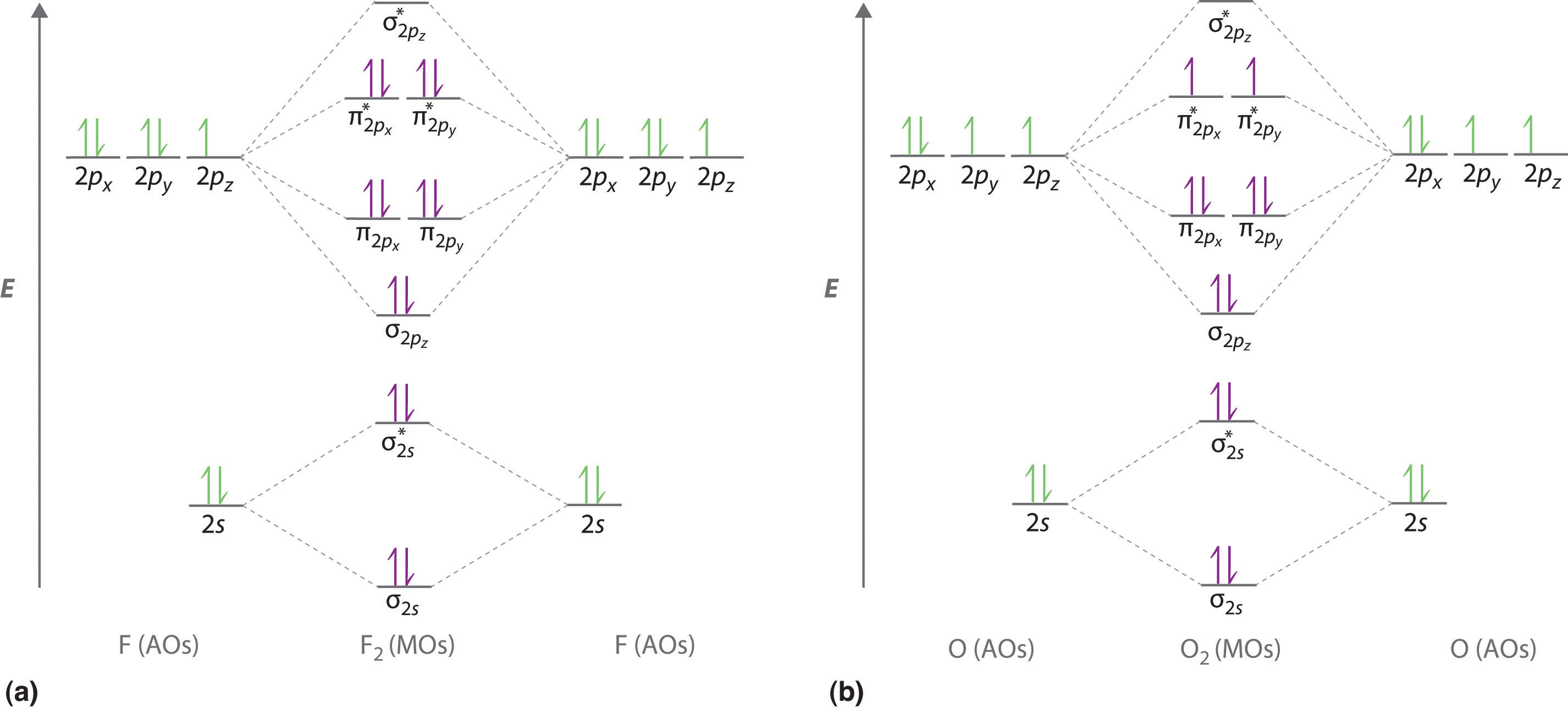












0 Response to "42 molecular orbital diagram f2"
Post a Comment