42 the diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist.
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost ... Get the detailed answer: The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. a. Determine the profit-maximizing output Answered: The accompanying diagram shows the… | bartleby The accompanying diagram shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. (LO1, LO3, LO5) a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. b. What price and output would prevail if this firm's product were sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market? c. Calculate the deadweight loss of this monopoly.
Is the demand curve the same as the marginal revenue curve? - Similar ... Why is the marginal revenue curve below the demand curve in a monopoly? a. Because the monopolist must lower the price on all units in order to sell additional units, marginal revenue is less than price. Because marginal revenue is less than price, the marginal revenue curve will lie below the demand curve.
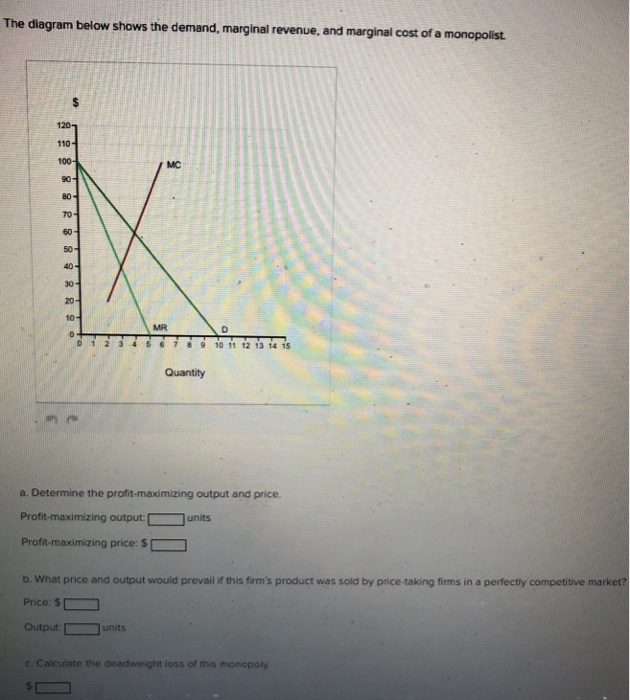
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist.
Monopoly Production and Pricing Decisions and Profit Outcome ... The key points of this diagram are fivefold. First, marginal revenue lies below the demand curve. This occurs because marginal revenue is the demand, p(q), plus a negative number. Second, the monopoly quantity equates marginal revenue and marginal cost, but the monopoly price is higher than the marginal cost. Answered: The diagram below shows a monopolist's… | bartleby The diagram below shows a monopolist's MC and ATC curves as well as the industry demand and MR curves. Diagram attached in images. What is the profit-maximizing price and level of output for the monopolist? Answer: 2. What are the total profits for the monopolist? Answer: 3. Price Discrimination under Monopoly | Microeconomics When the markets are segmented, the monopolist chooses to sell in each market that quantity at which the marginal revenue in that market equals his marginal cost. Thus we see from Fig. 10.27(a) and (b) that the monopolist decides to sell q d in the domestic market and q f in the foreign market.
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist.. [Solved] Please see an attachment for details | Course Hero The figure below shows the demand, marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost curves for a monopolist. 6) Pure Monopoly 450 400 MC 350 300 ATC 250 200 150 v ' 100 50 Price (dollars) D 25 50 75 100 125150 175 200 225 0 Quantity For this monopolist, the profit-maximizing quantity is Click to select v units and the profit-maximizing price is Click to select v . Demand, marginal revenue and cost curves - Grade Panda Demand, marginal revenue and cost curves. Just from $9/Page. Order Essay. Note: Make sure your name and student number are included on your assignment. Question 1. The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue and cost curves for Jingyi who owns the only golf course in her community. a. [Solved] The accompanying diagram shows the demand, marginal revenue ... A monopolist faces the demand marginal revenue and cost curves shown below The accompanying diagram shows the anticipated cash dividends for Delta Electronics over If Johns interest rate is known to be 8% compounded annually, what would be the desired (minimum) total selling price for the set of shares at the... Solved The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, | Chegg.com a) According to Profit Maximizing Condition of a monopoly : a monopolist Produces at that Point where MR = MC. We can see from above Graph that MR = MC when Quantity = 3 and when Qua …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist 1201 110 100 90 во 70 ...
Perfect competition - Wikipedia Such markets are allocatively efficient, as output will always occur where marginal cost is equal to average revenue i.e. price (MC = AR). In perfect competition, any profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that a factor's price equals the factor's marginal revenue product. Solved The graph below shows the demand, marginal revenue, | Chegg.com The graph below shows the demand, marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost curves for a single price monopolist. If the firm chooses their optimal quantity what price will they charge consumers? $ 11 101 9 8 ON Mc ATC 6 5 4 2 1 0 0 -MR 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60 66 Q The diagram below shows a natural monopoly. ECON563 Module 6 Assignment 3-1.pdf - 2/16/2020 Module 6 Assignment ... View ECON563 Module 6 Assignment 3-1.pdf from ECON 1002 at Baruch College, CUNY. 2/16/2020 Module 6 Assignment Module 6 Assignment 3 Submitted The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost For a Monopolist - Nigerian Scholars As a result, the marginal cost of the second unit will be: MC = $1800-$1500 1 = $300 MC = $ 1800 - $ 1500 1 = $ 300. Step 3. Remember that, similarly, marginal revenue is the change in total revenue from selling a small amount of additional output. MR = change in total revenue change in quantity sold MR = change in total revenue change in ...
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, | Chegg.com The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. "The horizontal axis labeled quantity ranges from 0 to 15 in increments of 1. The vertical axis labeled dollar ranges from 0 to 120 in increments of 10. A line labeled M R begins at the point (0, 100) goes down to the right and ends at the point (5, 0). AP Microeconomics 2017 Free-Response Questions (MPC), marginal social benefit (MSB), demand (D), and marginal revenue (MR) curves for a monopoly. (a) Identify the monopolist’s (i) profit-maximizing quantity (ii) profit-maximizing price (b) What information in the graph indicates that there is a negative externality? (c) Identify the socially optimal quantity. Solved The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, | Chegg.com The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. How much consumer surplus is lost, as compared to the outcome that would occur if this industry were in perfect competition (or if the monopolist were forced to set price at the socially optimal level)? Econ Working Quiz 6 Flashcards | Quizlet For a monopolist, marginal revenue is A.unable to be determined. B.less than the price of the product. C.greater than the price of the product. D.equal to the price of the product. Using the line drawing tool , show a possible marginal revenue curve for this monopolist on the graph to the right. Label it 'MR'.
[Solved] The diagram below shows the demand curve, marginal revenue ... The diagram below shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and cost curves for a monopolist that owns the only golf course on Eagle Island. The monopolist's product is 18-hole golf games. a. What is the profit-maximizing price and output (number of rounds of golf per week) for the monopolist? Provide the reasoning behind your answer.
Monopoly in a Perfectly Competitive Market (With Diagram) The average revenge curve of the monopolist is just the market demand. To get the relationship among total, average and marginal revenue, consider a firm facing the following demand curve P = 6 – Q. Table 9.1 shows the relation of total, average and marginal revenues. Note that revenue is zero when the price is £6, because, at this price ...
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS QUIZ-2 - The accompanying diagram shows the demand ... The accompanying diagram shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. a) Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. b) What price and output would prevail if this firm's product was sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market? c) Calculate the deadweight loss of this monopoly. To find the profit maximizing output and price, MR=MC, Hence, the ...
Marginal Revenue and the Demand Curve - ThoughtCo In this case, marginal revenue is equal to price as opposed to being strictly less than price and, as a result, the marginal revenue curve is the same as the demand curve. This situation still follows the rule that the marginal revenue curve is twice as steep as the demand curve since twice a slope of zero is still a slope of zero. Beggs, Jodi.
microeconomics ch3 Flashcards - Quizlet The following equations describe the monopolist’s demand, marginal revenue, total cost, and marginal cost: Demand: P = 10 - Q, Marginal Revenue: MR = 10 - 2Q, Total Cost: $$ TC = 3 + Q + 0.5Q^2 $$ , Marginal Cost: MC = 1 + Q where Q is quantity and P is the price measured in Wiknamian dollars. a.
Profit Maximization: Definition, Equation & Theory - Video ... Sep 22, 2021 · A monopolist's demand function is shown below. P= 29 - 0.5Q The fixed costs of production are 8 and the variable costs are Q + 2 per unit. Use the equation MR= MC to determine the value of Q which max
Solved The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue ... - Chegg The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. Profit-maximizing output: units. Profit-maximizing price: $ b. What price and output would prevail if this firm's product was sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market? Price: $
The diagram below shows the demand.docx - The diagram below shows the ... The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. Profit-maximizing output: 3 Numeric Response 1.Edit Unavailable. 3 correct.units Profit-maximizing price: $ 70 Numeric Response 2.Edit Unavailable. 70 correct.
[Solved] The diagram below shows the demand, marginal cost, and ... The diagram below shows the demand, marginal cost, and marginal revenue curves for a monopolist. Redraw the diagram for yourself to be able to answer the following questions. a. If the monopolist charges its single profit-maximizing price, show what areas are consumer surplus and producer surplus. ... The diagram below shows the demand ...
[Solved] Please see attachments for details | Course Hero 1 The graph below shows the demand and marginal cost curves for the monopolist Mr. Peanut. a. Draw the marginal revenue curve. Plot only the endpoints of the graph below. 10 CD points D 44 E Tools 40 Pflnt // References 36 marginal revel 32 28 24 20 1 6 12 eBook Costs and revenues C 816 24 32 4o 48 56 64 72 80 Quantity per period
(Solved) - The diagram below shows the demand, marginal cost, and ... The diagram below shows the demand, marginal cost, and marginal revenue curves for a monopolist. Redraw the diagram for yourself to be able to answer the following questions. a. If the monopolist charges its single profit-maximizing price, show what areas are consumer surplus and producer surplus. b.
Price Discrimination under Monopoly | Microeconomics When the markets are segmented, the monopolist chooses to sell in each market that quantity at which the marginal revenue in that market equals his marginal cost. Thus we see from Fig. 10.27(a) and (b) that the monopolist decides to sell q d in the domestic market and q f in the foreign market.
Answered: The diagram below shows a monopolist's… | bartleby The diagram below shows a monopolist's MC and ATC curves as well as the industry demand and MR curves. Diagram attached in images. What is the profit-maximizing price and level of output for the monopolist? Answer: 2. What are the total profits for the monopolist? Answer: 3.
Monopoly Production and Pricing Decisions and Profit Outcome ... The key points of this diagram are fivefold. First, marginal revenue lies below the demand curve. This occurs because marginal revenue is the demand, p(q), plus a negative number. Second, the monopoly quantity equates marginal revenue and marginal cost, but the monopoly price is higher than the marginal cost.

0 Response to "42 the diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist."
Post a Comment