42 pacemaker cell action potential diagram
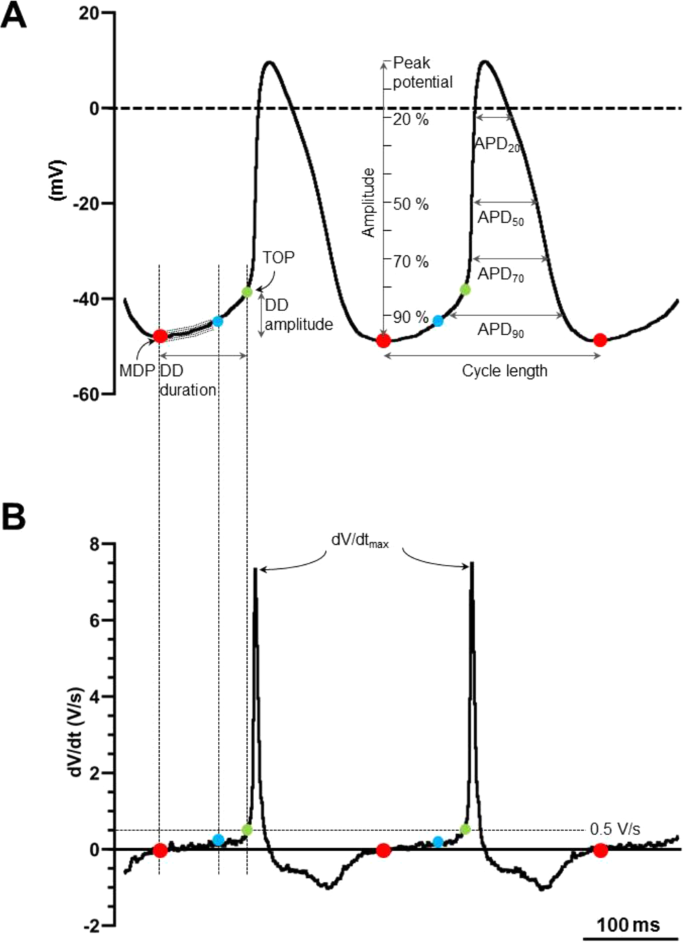
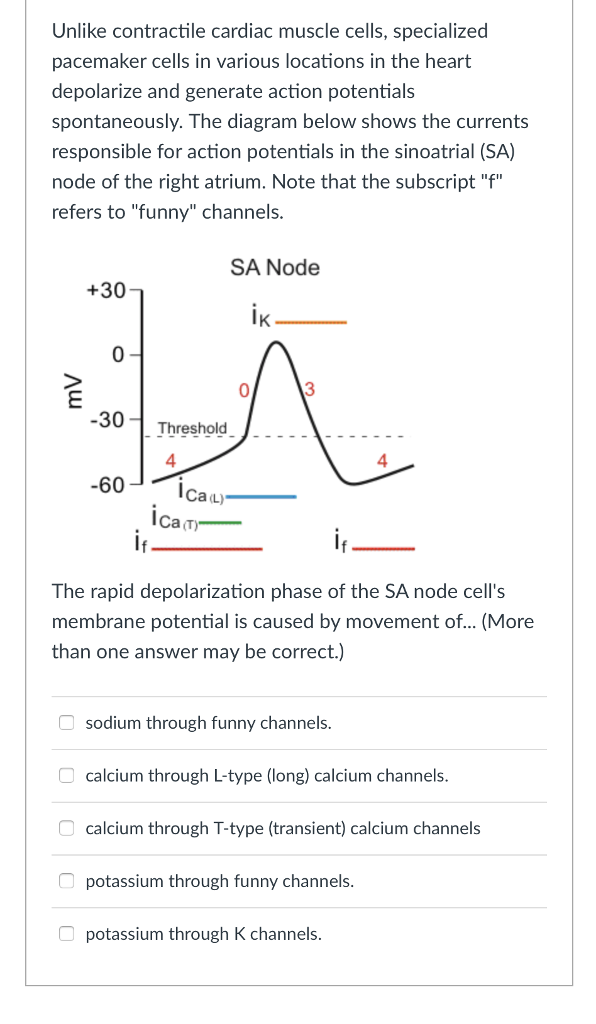
Factors Controlling Pacemaker Action in Cells of the ... length) A and B. In C recording is from a Intent or subsidiary pacemaker cell (upper) and true pacemaker (lower), rate of drive 300/min or 200 msec cycle length. Note the decrease in amplitude of pacemaker cell spike and the greater than normal duration of pacemaker cell action potentials after drive. Cardiac action potential - All About Cardiovascular System ... Action potential of ventricular myocardial cell. Action potential of pacemaker cells. Action potential of the pacemaker cell is different from that of ventricular myocardial cell. It is characterized by lower slope of phase 0 (lower Vmax) and the presence of diastolic depolarization mediated by the funny current (I f), also known as pacemaker ...
› forum › topicCorrection, Corrective Action and Preventive Action - We ask ... Oct 04, 2017 · Preventive Action: Preventive action is a proactive action taken to eliminate the cause of a potential non-conformity or other undesirable potential situation so as to prevent nonconformities from occurrence. For example, we may come to know that motherboard of a particular brand has been found to be of sub-standard quality.
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram
teachmephysiology.com › biochemistry › proteinTranscription of DNA - Stages - TeachMePhysiology Sep 20, 2021 · DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase. This mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression.In this article we will look at the process of DNA ... Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential • LITFL • BSCC Examination Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential. This diagram is a diagram of a cardiac myocyte - a ventricular muscle cell as apposed to a cardiac pacemaker cell. The resting membrane potential (RMP) is -90mv. A membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and the exterior of the cell membrane. Cardiac cell action potentials are short-lived ... (a) The cardiac pacemaker cell action potential represents the transmembrane voltage, as a function of time, in a pacemaker cell. Phase 4, the so-called pacemaker potential, corresponds to ...
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Action_potentialAction potential - Wikipedia The action potential in a normal skeletal muscle cell is similar to the action potential in neurons. Action potentials result from the depolarization of the cell membrane (the sarcolemma ), which opens voltage-sensitive sodium channels; these become inactivated and the membrane is repolarized through the outward current of potassium ions. The membrane action potential of pacemaker cells and the ... The particularity of these cells is their spontaneous depolarization during Phase 4 of the action potential. This diastolic depolarization slowly increases the membrane potential to a threshold... File:Pacemaker potential.svg - Wikipedia Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. Licensing. I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license: Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no ... Action Potentials Made Easy: Cardiac Myocyte ... - EZmed An action potential is a change in voltage across a cell membrane, specifically a rise in voltage followed by a fall. Action potentials are used to send information throughout the body, and they are also necessary for some types of cells to function as they trigger intracellular processes (such as contraction of muscle cells).
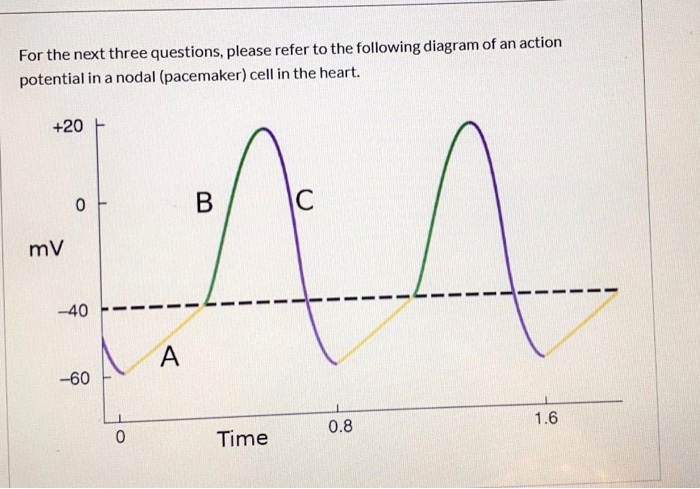
Conduction System of the Heart: Step-By-Step ... - EZmed The pacemaker cells have the capability of generating spontaneous action potentials. They are located in the SA node, AV node, bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, and the Purkinje fibers. They make up the conduction system of the heart. The contractile cells are the muscle cells that lead to contraction of the heart once depolarized. Answered: 1) Diagram and explain the mechanisms… | bartleby 1) Diagram and explain the mechanisms of a pacemaker potential for a nodal cell. 2) Diagram and explain the mechanisms of a ventricular myocardial cell action potential. Cardiac Electrophysiology Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations ... Figure 17.2 Graph depicting the action potential of a pacemaker cell. ACTION POTENTIALS IN MYOCYTES osms.it/myocyte-action-potentials Myocytes Receive signal from from pacemaker cells causing them to contract Able to depolarize, spread action potentials Action potential phases: Phase 0 (depolarization phase): rapid influx of sodium into cell (inward current); responsible for rapid ... Action Potential - The Resting Membrane Potential ... An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs.
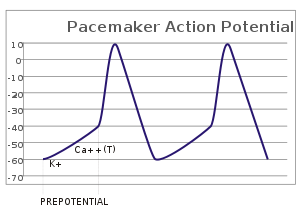
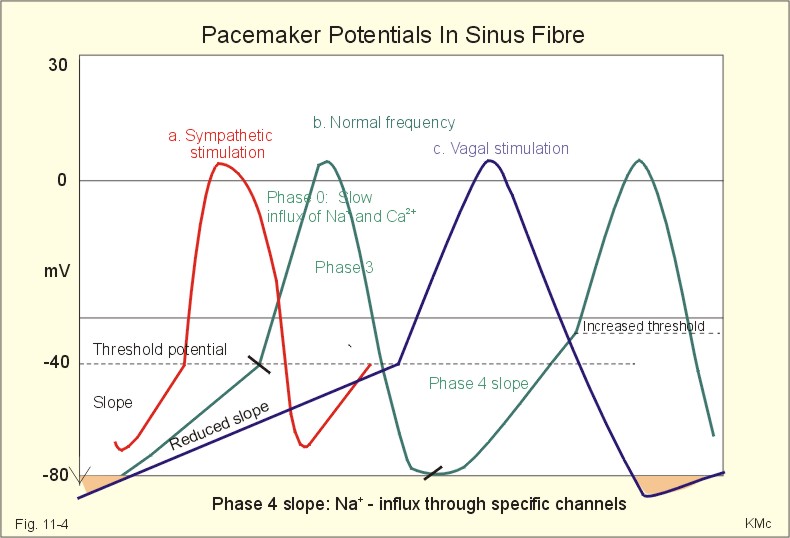
38 pacemaker cell action potential diagram - Wiring ... This diagram illustrates the action potential profile of a nodal cell within the heart, with time plotted against membrane potential. From this diagram, several characteristics of a nodal cell can be noted. ... Pacemaker cells do not compete, they go at the fastest rate. In a healthy human, this is the SA node. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Resting_potentialResting potential - Wikipedia The resting potential of a cell can be most thoroughly understood by thinking of it in terms of equilibrium potentials. In the example diagram here, the model cell was given only one permeant ion (potassium). In this case, the resting potential of this cell would be the same as the equilibrium potential for potassium. Phases of the Cardiac Action Potential - Sciencing The cardiac cell action potential, like action potentials in nerves, is divided into five phases, numbered 0 through 4. Two of these, phase 2 (the plateau phase) and phase 4 (the diastolic interval) are marked by little to no change in voltage. Sodium, potassium and calcium are the primary ions. Pacemaker potential - Wikipedia In the pacemaking cells of the heart (e.g., the sinoatrial node ), the pacemaker potential (also called the pacemaker current) is the slow, positive increase in voltage across the cell 's membrane (the membrane potential) that occurs between the end of one action potential and the beginning of the next action potential.
Action Potential in Cardiac Pacemaker Cells ... Fig 2 - Diagram showing the action potential in cardiac pacemaker cells and the main ion movements at each stage. Control by the Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system (ANS) alters the slope of the pacemaker potential, in order to alter heart rate.
(PDF) Numerical Bifurcation Analysis of Pacemaker Dynamics ... Numerical Bifurcation Analysis of Pacemaker Dynamics in a Model of Smooth Muscle Cells arXiv:2004.00343v1 [math.DS] 1 Apr 2020 Hammed O. Fatoyinbo,∗ Richard G. Brown, David J. W. Simpson, and Bruce van Brunt School of Fundamental Sciences, Massey University, New Zealand E-mail: h.fatoyinbo@massey.ac.nz Abstract Evidence from experimental studies shows that oscillations due to electro ...
› doi › 10Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct ... Feb 22, 2022 · In metazoan organisms, circadian (∼24 h) rhythms are regulated by pacemaker neurons organized in a master–slave hierarchy. Although it is widely accepted that master pacemakers and slave oscillators generate rhythms via an identical negative feedback loop of transcription factor CLOCK (CLK) and repressor PERIOD (PER), their different roles imply heterogeneity in their molecular clockworks.
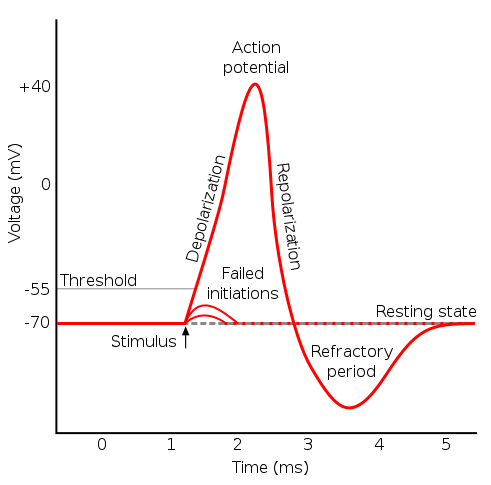
Normal processes of cardiac ... - Deranged Physiology Ends in an "overshoot" action potential (around +20 to +50 mV) After opening, the sodium channels close and become inactive (absolute refractory period) Phase 1: Early repolarisation A rapid repolarisation back to a membrane potential close to 0 mV Mediated by opening of potassium channels, which permit the transient outward potassium current (Ito)
Action potentials in pacemaker cells | Circulatory system ... Find out how the pacemaker cells use the movement of sodium, calcium, and potassium to get your heart beating! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physic...
Potassium channels in the sinoatrial node and their role ... The pacemaker action potential has a characteristic morphology with a diastolic depolarization before a threshold is reached with a consequent action potential. Figure 1shows this in single mouse SAN cells studied in the current clamp mode of the patch clamp. Exactly how the intrinsic pacemaker clock is generated is controversial.
Cardiac Action Potential, Animation. - YouTube (USMLE topics, cardiology) Cardiac action potential in pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes, electrophysiology of a heartbeat. Purchase PDF (script of th...
Cardiac action potential | Psychology Wiki | Fandom The cardiac action potential has five phases. The standard model used to understand the cardiac action potential is the action potential of the ventricular myocyte. The action potential has 5 phases (numbered 0-4). Phase 4 is the resting membrane potential, and describes the membrane potential when the cell is not being stimulated.
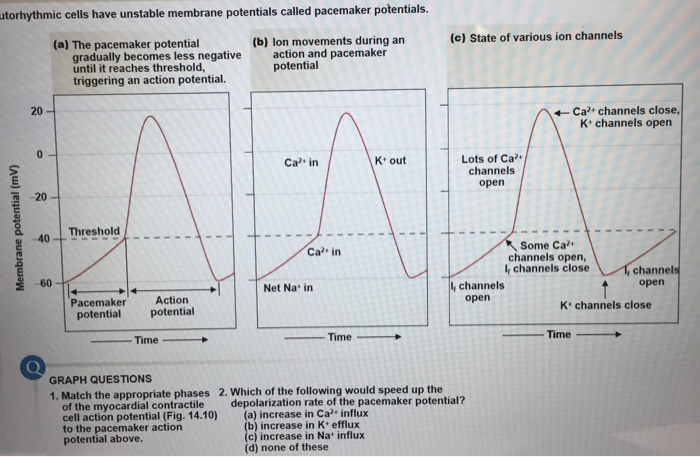
BIO 2982 Action Potentials of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells ... BIO 2982 Action Potentials of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match Created by mkrach7694 PLUS Terms in this set (6) Pacemaker potential--due to slow influx of Na+ and closing of K+ channels. ... Depolarization--point at which action potential begins, as it reaches threshold; due to influx of Ca++ ...
Cardiac Pacemaker Cells and Action potential • LITFL Pacemaker cells are found in the (SA) sinoatrial, the atrioventricular (AV) nodes and a third group is found in the bundles of HIS and purkinje fibres.Pacemaker cells have automaticity; they don't require adjacent cells to fire in order to activate them. Pacemaker cells have a prepotential or pacemaker potential that is never resting.
Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac ... Start studying Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac Pacemaker Cells. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
PDF Cardiac Action Potential - interactivephysiology.com 1. Pacemaker Potential • An autorhythmic cell has the unique ability to depolarize spontaneously, resulting in a pacemaker potential. 2. Depolarization and Reversal of the Membrane Potential • Once threshold is reached, an action potential is initiated, which begins with further depolarization and leads to reversal of the membrane potential ...
Cardiac electrophysiology: action potential, automaticity ... The action potential in the sinoatrial node and in contractile myocardial cells. Phase 4 of the action potential in the sinoatrial node is called 'pacemaker potential', because it is responsible for the spontaneous repetitive depolarization. The depolarization spreads from the sinoatrial node to the atrial and ventricular myocardium.
Action Potential of a Pacemaker Cell Quiz - PurposeGames.com This is an online quiz called Action Potential of a Pacemaker Cell. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Your Skills & Rank. Total Points. 0. Get started! Today's Rank--0. Today 's Points. One of us! Game Points. 8.
Sinoatrial Node Action Potentials - CV Physiology SA nodal action potentials are divided into three phases. Phase 4 is the spontaneous depolarization (pacemaker potential) that triggers the action potential once the membrane potential reaches threshold between -40 and -30 mV). Phase 0 is the depolarization phase of the action potential. This is followed by phase 3 repolarization.
teachmephysiology.com › biochemistry › atpAnaerobic Respiration - Process - TeachMePhysiology Mar 28, 2022 · Anaerobic respiration is the process of creating energy without the presence of oxygen. Sometimes the body cannot supply the muscles with the oxygen it needs to create energy, for example during intense exercise. Without the process of anaerobic respiration, there would be no energy supplied to muscles in these times of high demand.This article will consider the process of anaerobic ...
Cardiac cell action potentials are short-lived ... (a) The cardiac pacemaker cell action potential represents the transmembrane voltage, as a function of time, in a pacemaker cell. Phase 4, the so-called pacemaker potential, corresponds to ...
Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential • LITFL • BSCC Examination Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential. This diagram is a diagram of a cardiac myocyte - a ventricular muscle cell as apposed to a cardiac pacemaker cell. The resting membrane potential (RMP) is -90mv. A membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and the exterior of the cell membrane.
teachmephysiology.com › biochemistry › proteinTranscription of DNA - Stages - TeachMePhysiology Sep 20, 2021 · DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase. This mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression.In this article we will look at the process of DNA ...






























0 Response to "42 pacemaker cell action potential diagram"
Post a Comment