37 concave lens ray diagram
Ray diagram for an object viewed through a concave lens. For an object viewed through a concave. lens, light rays from the top of the object will be refracted. and will diverge. on the other side ... A concave lens will always produce diminished, upright and virtual image of the object in front of it. But the nature of the image produced by a these lenses depends upon the position of the object. It can form both real and virtual images depending on where the light is coming from. Uses of convex lens . These are used for a variety of purposes in our day-to-day lives. For example, The lens ...
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object.
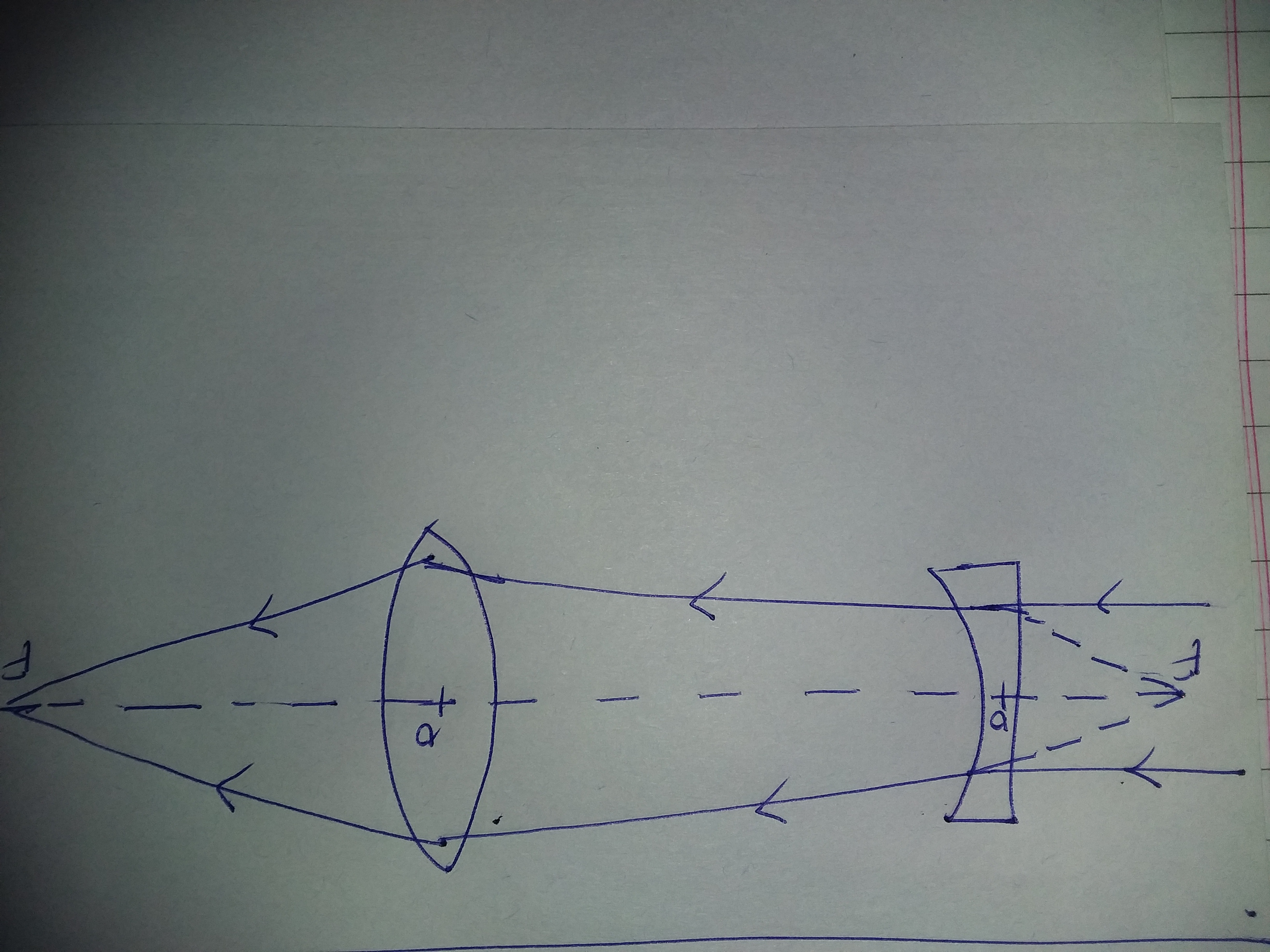
Concave lens ray diagram
The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ... A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as “the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses”. Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts NCERT Questions ...
Concave lens ray diagram. In figure the refracted ray parallel to the principal axis. So, the Incident ray must be appearing to meet at the principal focus of concave lens. To find the incident ray, F 2 is joined to Q and produced as shown in the figure. The ray diagram in Figure 13 shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as the object and, hence, cannot be projected—it is a virtual image. Note that the image is closer to the lens than the object. This is a case 3 image, formed for any object by a negative focal length or diverging lens. Figure 13. Ray tracing predicts the image location and size for a concave or diverging lens ... Best Explanation for Ray diagrams for the concave lens and Drawing concave lens with the help of a compass. For aconvex lens, we draw the ray diagram as follows: Draw a ray from the top of the object straight through the middle of the lens. Its direction is not changed. Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis. It is refracted by the lens to pass through the focal point. F From the diagram we see that the image in this example is inverted. This is also an example of a ...
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ A concave lens of focal length 15 cm form an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram also. The example "Ray tracing diagram for concave lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions. 26.04.2020 · Concave Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 26, 2020 by Teachoo. For a Concave lens, There are only 2 cases They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Infinity and Optical Center Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis Since ray parallel to ...
Concave lens ray diagram class 10 The light is reflected by a mirror. The light crosses, and is refracted by, a lens. The lenses have two focal points, one on both sides of the target. A concave mirror converges light at a focal point. For lenses, light converges to a point for a convex lens. A convex mirror diverges the light, as well as a ... Ray tracing diagram for concave lens. "In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces, complicating ... The example "Ray tracing diagram for concave lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from converging lens of focal length 10 cm . Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and nature of the image formed.
The students can use a convex lens diagram to understand the ray's path after passing through a convex lens. The students may create a convex ray diagram by hand, but the process is lengthy, and at the same time, complicated. If the students fail to place the paths of the light properly, they may end up with a faulty convex lens ray diagram.
So, the object is placed 30 cm away from the concave lens. Ray diagram: Was this answer helpful? 4.5 (146) (355) (41) Choose An Option That Best Describes Your Problem. Answer not in Detail. Incomplete Answer. Answer Incorrect. Others. Answer not in Detail. Incomplete Answer. Answer Incorrect. Others . Thank you. Your Feedback will Help us Serve you better. Related Questions & Answers: What Do ...
Shows how to draw the ray diagrams for locating the image produced by a concave lens and a convex mirror. You can see a listing of all my videos at my websit...
Double Concave Lens Ray Diagram. A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn. Because the rays always diverged by a concave lens, the emerging rays do not The concave lens image can still more be explained by a Concave Lens Ray ...
A ray diagrams helps you understand the chara... This video shows you a simple method for drawing a ray diagram for a concave lens given the location of object.
This is shown for two incident rays on the diagram below. Once the light ray refracts across the boundary and enters the lens, it travels in a straight line until it reaches the back face of the lens. At this boundary, each ray of light will refract away from the normal to the surface. Since the light ray is passing from a medium in which it travels slow (more optically dense) to a medium in ...
08.10.2021 · For a concave lens, we see that ray appears to pass through focus on left side Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis For a convex lens, we see that ray passing through focus on left becomes parallel to principal axis after refraction For a concave lens , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel ...
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens.
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction.A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis.Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape.
Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding...
With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens. Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
This video is created by http://www.course.onlinetuition.com.my/More videos and free notes are available at http://spmphysics.onlinetuition.com.my/
Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts NCERT Questions ...
A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as “the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses”.
The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ...





0 Response to "37 concave lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment