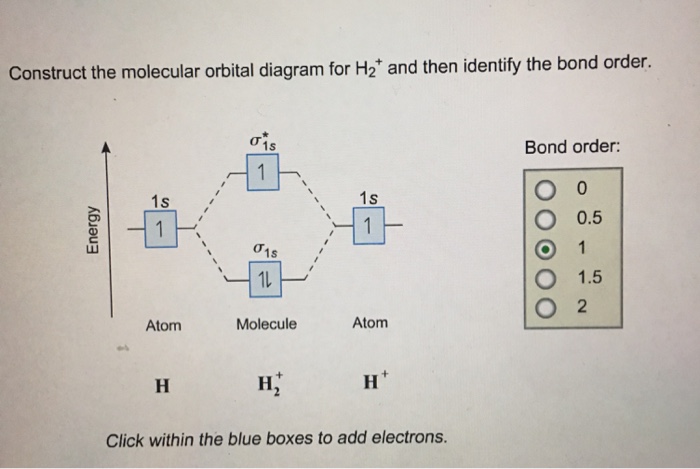
37 molecular orbital diagram for h2- and bond order
Mo · Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. chemical bonding molecular orbitals of h2 and he2 as before the greater the number of these nodal planes the more the electrons that occupy the orbitals are excluded from the region between the nuclei and hence the higher the energy the resulting molecular ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
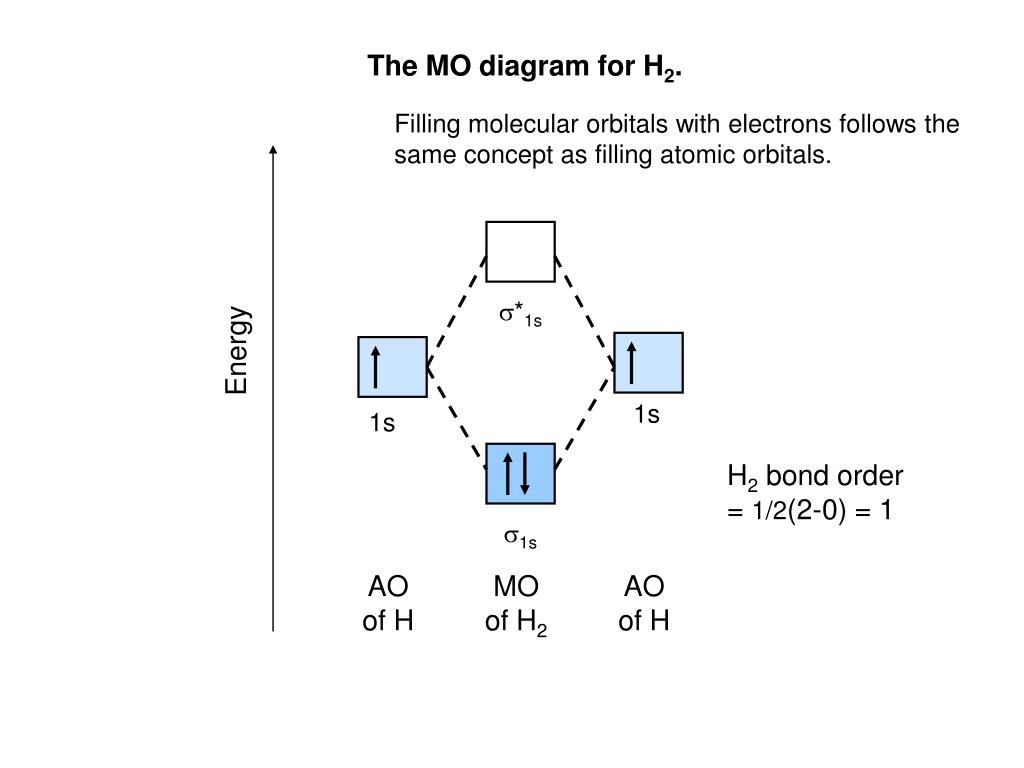
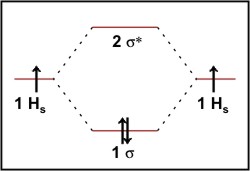
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ...
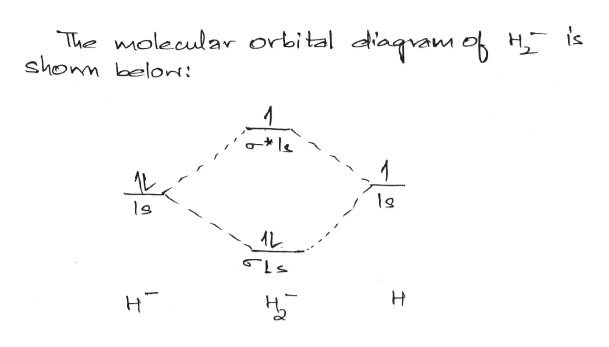
Molecular orbital diagram for h2- and bond order
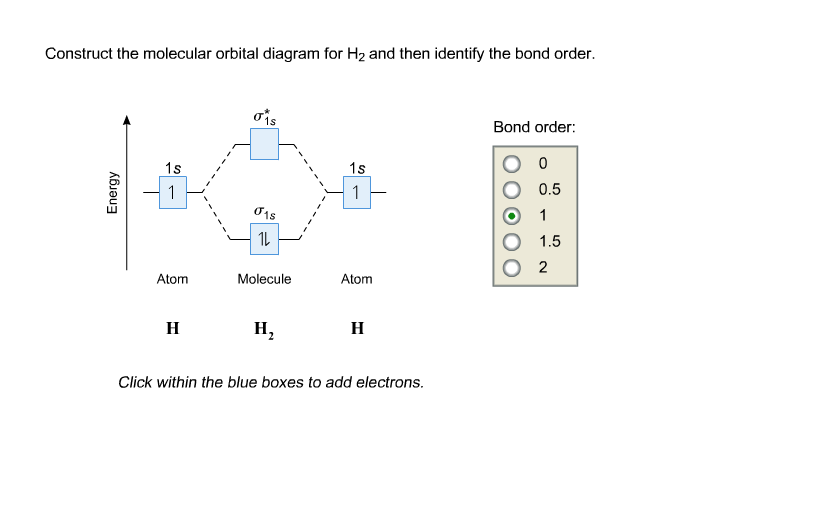
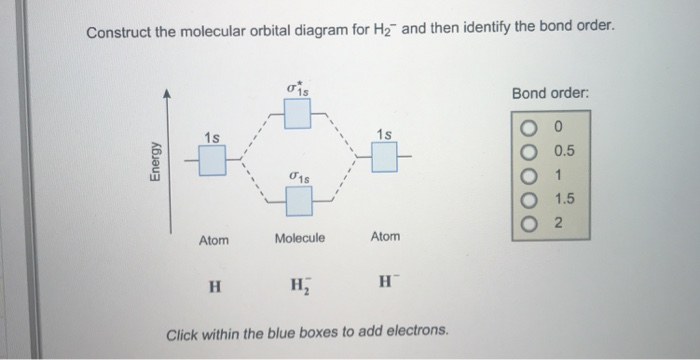
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here. Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can ... Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Testin g qualitative MO theory prediction of Bond Order with experiment for homonuclear diatomics made from elements in the 1st row of the Periodic Table (using the "Molecular Orbital Aufbau" principle): BondOrder [# ' # ' ]/2≡−bondinge s antibondinge s [D.A. McQuarrie, Quantum Chemistry]
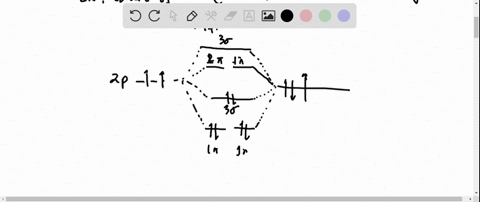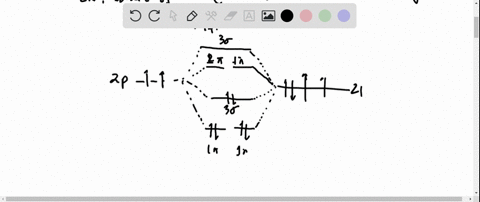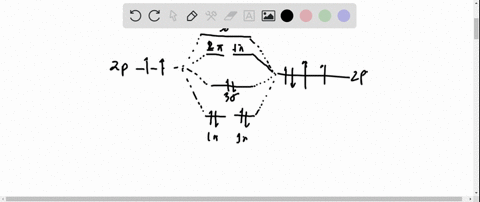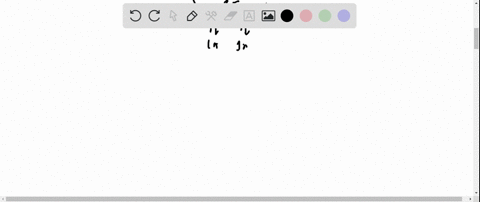
Molecular orbital diagram for h2- and bond order. LCAO MO Energy Diagram for H2 Energy H-H ∆E1 ∆E2 • ∆E2> ∆E1, so the antibonding orbital is always more anti-bonding than the bonding orbital is bonding H2molecule: two 1s atomic orbitals combine to make one bonding and one antibonding molecular orbital. Ha Hb This question deals with the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of the simple diatomic hydrogen molecule. VSEPR theory describes this as two hydrogen atoms forming a single covalent bond. N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
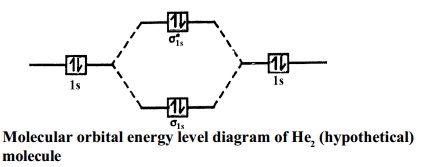
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 . Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. In fact they do. πε and jr k r mr lr defined explicitly in atkins. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the same thing two electrons fill a single bonding molecular orbital. The procedure can be introduced by considering the h2 molecule.
LUMO = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital HOMO = highest occupied molecular orbital Similar phase of electron density (no node) adds together constructively. energy of isolated atoms bond order (H2 molecule) = (2) - (0) 2 = 1 bond 1sb H H H H σ∗ = 1s H H a - 1sb = antibonding MO = LCAO = linear combination of atomic orbitals node = zero ... Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals. Now we can add electrons to the diagram. Each hydrogen atom has 1 electron. These 2 electrons go to fill the lowest energy molecular orbital, the sigma bonding orbital. The electrons are more stable, lower energy, in the molecular orbital than they were in the separated atomic orbitals. In other words, when the H-H bond forms, each atom loses ... Bond Order in Molecular Orbital Theory. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the same result. ... In the second diagram, one of the bonding electrons in H2 is "promoted" by adding energy and ...
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
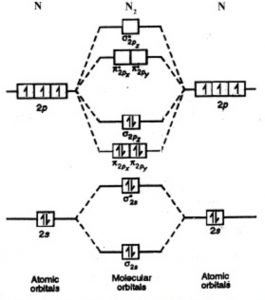
Based on molecular orbital theory, what is the bond order of the H 2 molecule? a) 1 b) 2 c) 0 d) 1/2 e) 1.3. The bond order of N22+is 2.5 2 1.5 3. Given the molecular orbital diagram below, determine the bond order for nitrogen gas, N2 A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 E. 4. One of the excited states of a C2 molecule has the electron configuration: (σ1s)2 ...
Fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable. The stability of a molecule is measured by its bond dissociation energy.
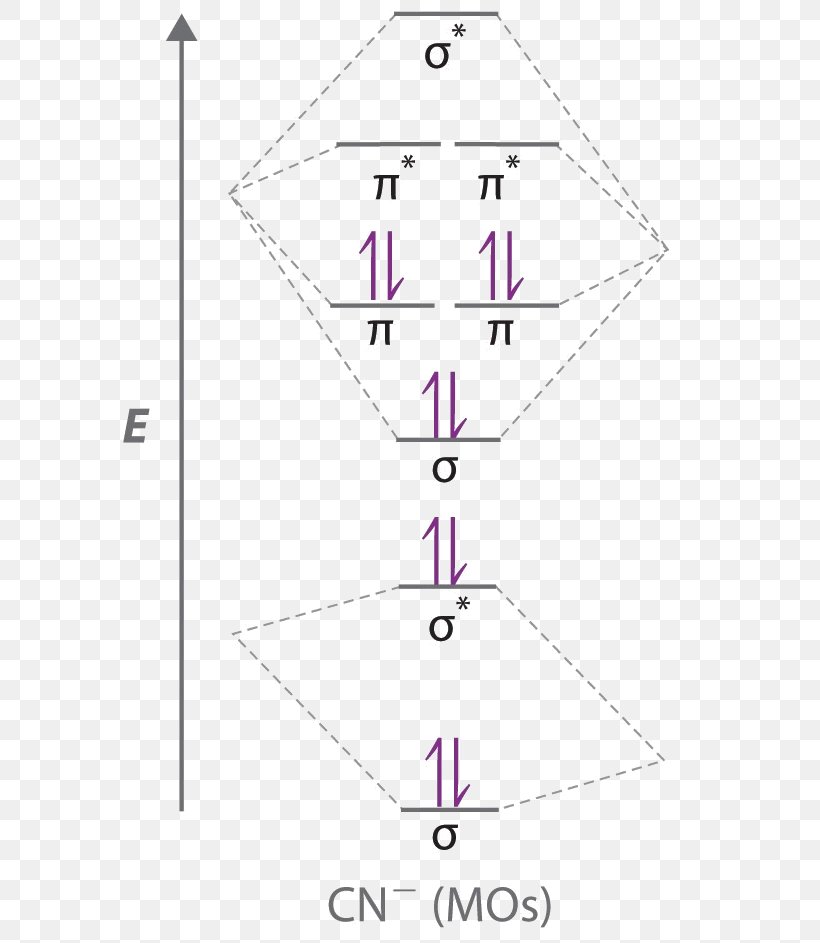
Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Cyanide Png 631x943px Diagram Anion Area Atomic Orbital Bond Order Download
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the H2+ ion. The bond order of H2+ is also calculated and the meaning of this number ...
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
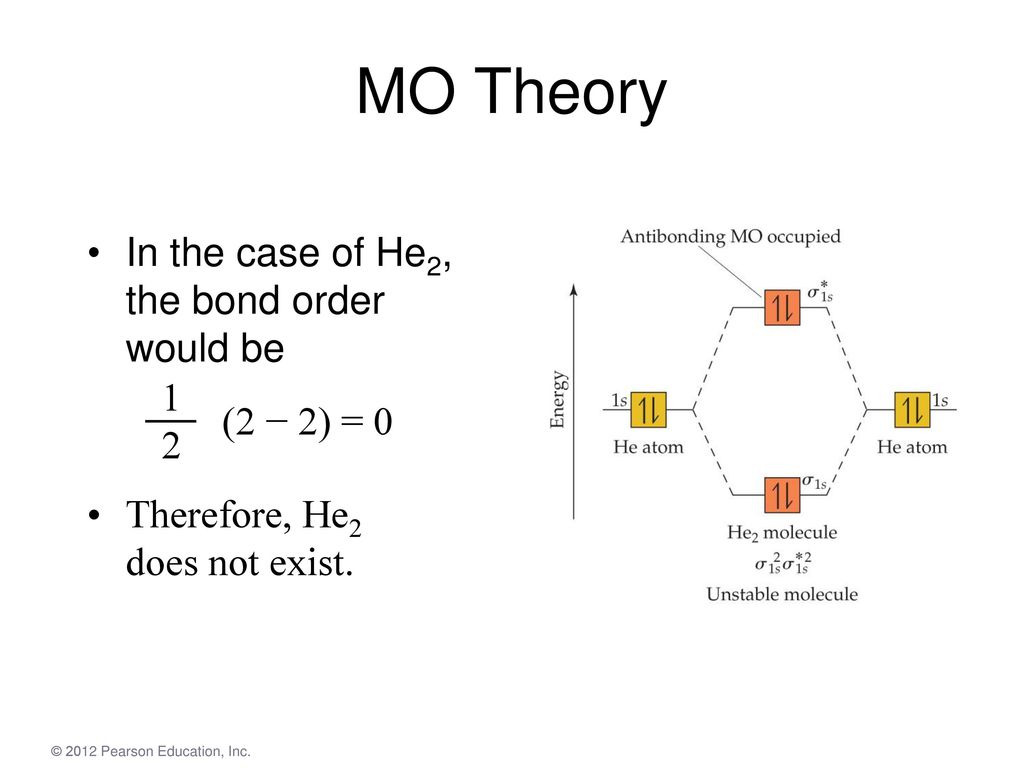
Mo Theory In H2 The Two Electrons Go Into The Bonding Molecular Orbital The Bond Order Is One Half The Difference Between The Number Of Bonding And Antibonding Ppt Download
This problem has been solved! A.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^2+ and then identify the bond order. B.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. C.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^- and then identify the bond order. D.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^+ and then ...
5.2 a. Li2 has a bond order of 1.0 (two electrons in a bonding orbital; see Figures 5.7 and 5.1). Li2 + has a bond order of only 0.5 (one electron in a bonding orbital). Therefore, Li2 has the shorter bond. b.2 has a bond order of 1.0 (see Figure 5.7). F F 2 + has one less antibonding (π*) electron and a higher bond order, 1.5. F2
Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond order of the molecule.
Hydrogen atom's valence orbitals, before bonding, include every orbital, and all are the same energy for a specific n. At that point, there is only one electron. HAVING MORE THAN ONE ELECTRON SPLITS ENERGY LEVELS When introducing more electrons into the system, i.e. with another hydrogen wanting to bond, the repulsion splits the energy levels of the AOs of hydrogen. They start out where each n ...
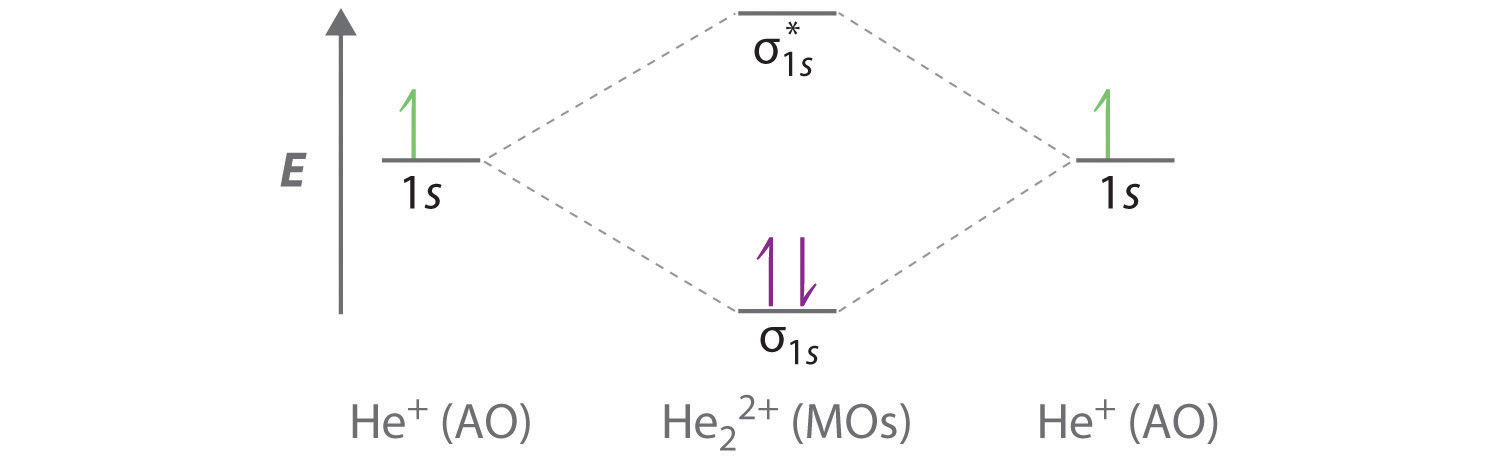
1. Problem: Draw MO energy diagrams for the molecular ions H2+ and H Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 1/2, they are approximately equally.Solution: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 + and then identify the bond order. Problem Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 + and then identify the bond order.
Testin g qualitative MO theory prediction of Bond Order with experiment for homonuclear diatomics made from elements in the 1st row of the Periodic Table (using the "Molecular Orbital Aufbau" principle): BondOrder [# ' # ' ]/2≡−bondinge s antibondinge s [D.A. McQuarrie, Quantum Chemistry]
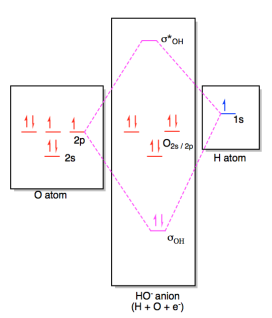
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here. Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can ...

Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2 And Then Identify The Bond Order Bond Order Click Homeworklib
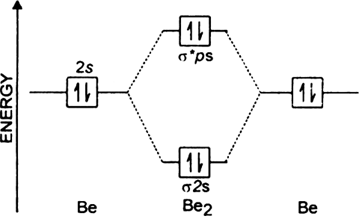
Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For I Be2 Ii B2 And Predict Bond Order And Magnetic Properties From Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Class 11 Haryana Board English Medium

Molecular Orbital Diagram White Atomic Orbital Molecular Orbital Theory Molecule Bond Order Electron Valence Electron Nitrogen Molecular Orbital Diagram Diagram Molecular Orbital Png Pngwing














0 Response to "37 molecular orbital diagram for h2- and bond order"
Post a Comment