40 simple cellular respiration diagram
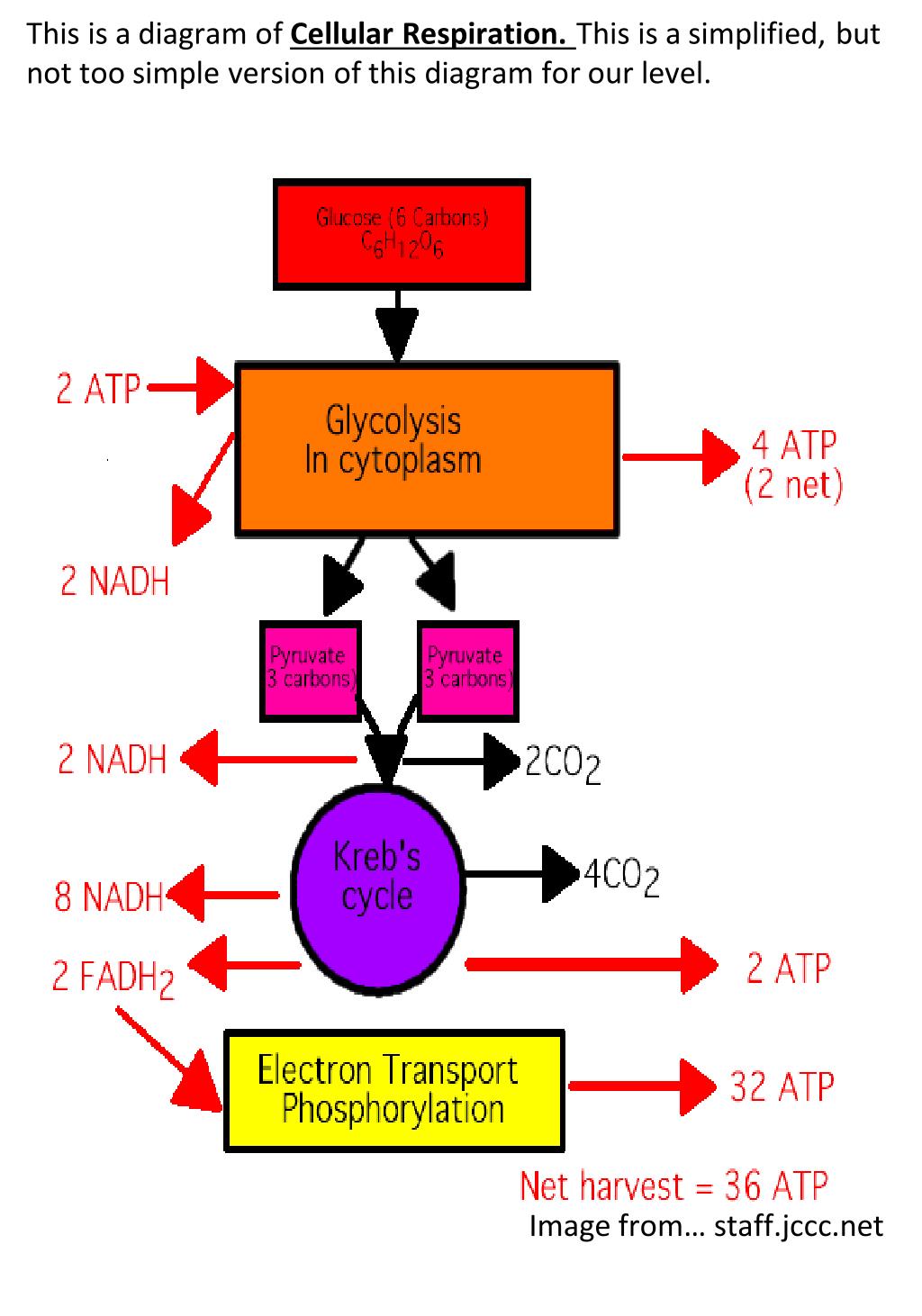
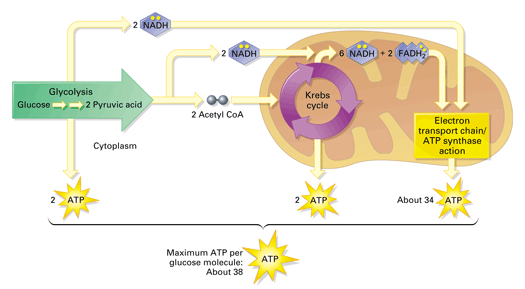
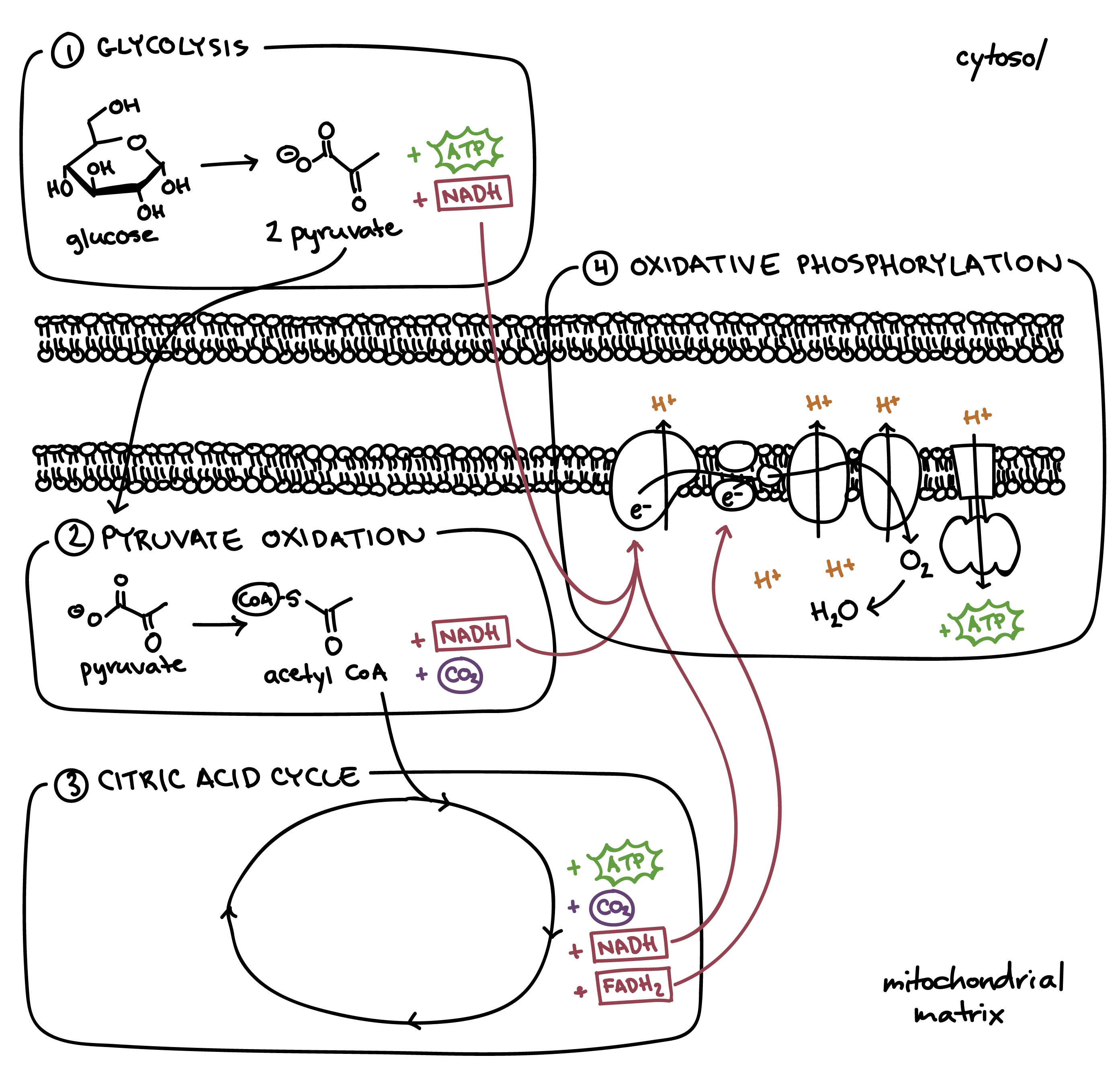
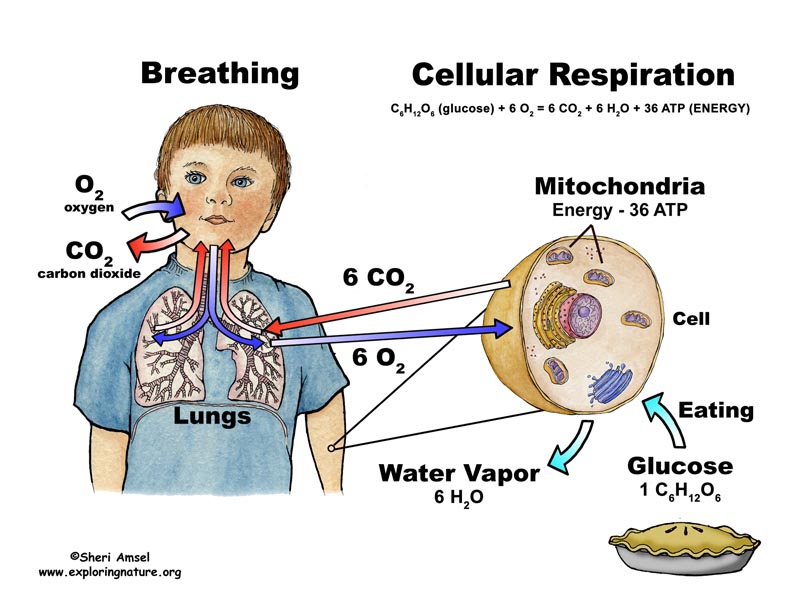
Cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic. In order to move from glycolysis to the citric acid cycle, pyruvate molecules (the output of glycolysis) must be oxidized in a ... Cellular Respiration gives both plant and animal cells the useable energy, aka ATP, that they need to do stuff. This is the overall equation: C6H12O6(glucose) + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ≈38 ATP
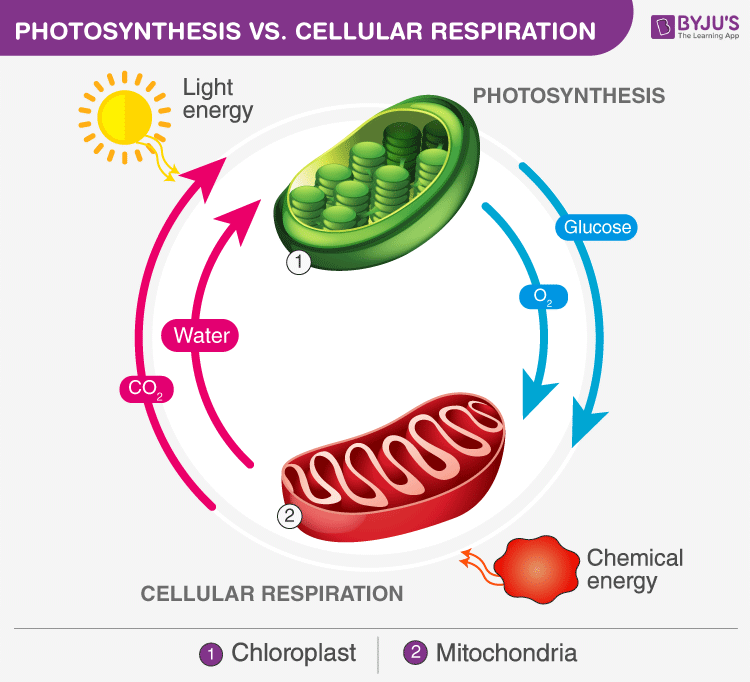
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Diagram Simple. A simple sugar that is an important energy source in living organisms; Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are connected through an important relationship. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are both part of a mutually beneficial relationship.
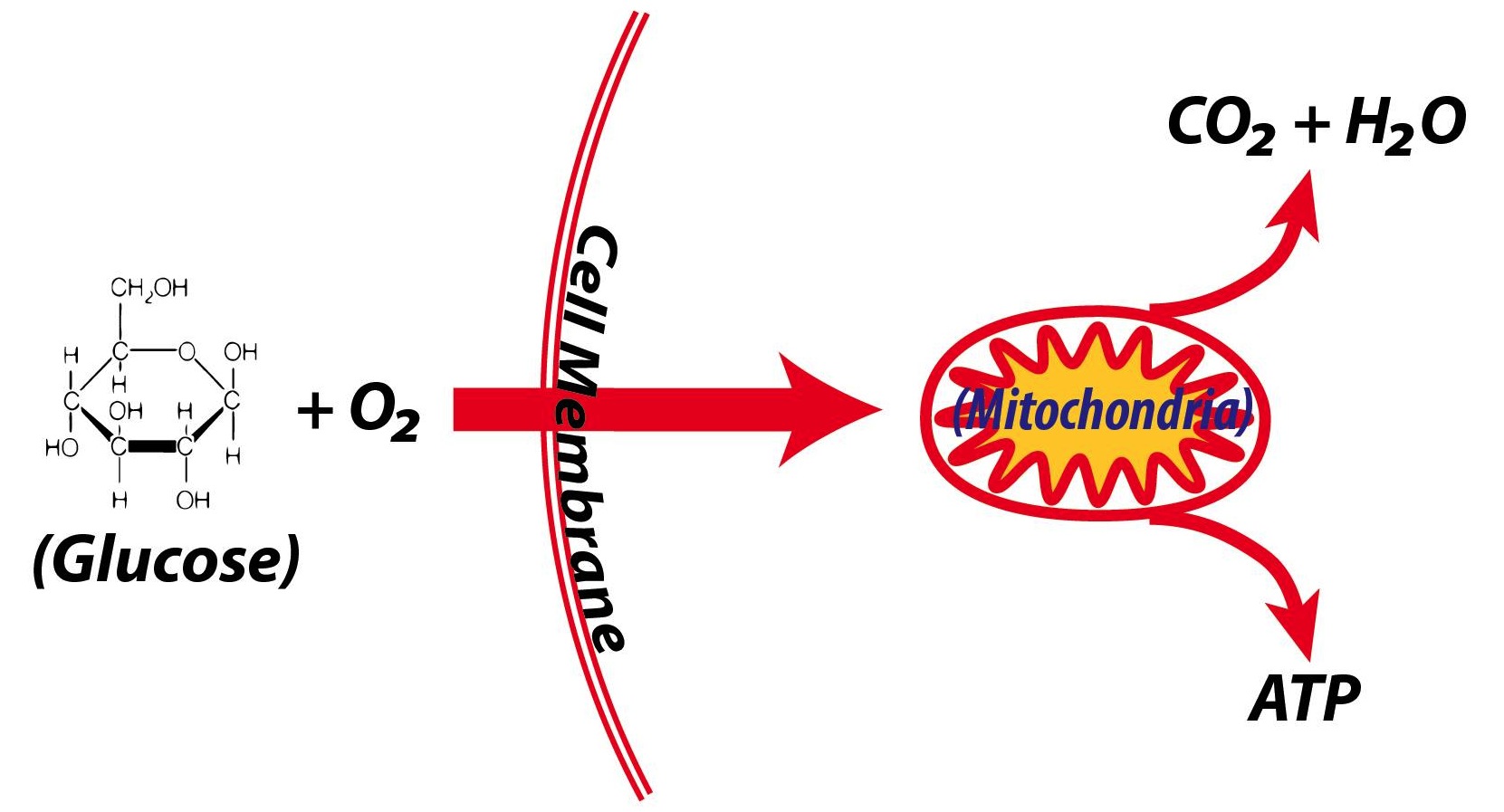
Simple cellular respiration diagram
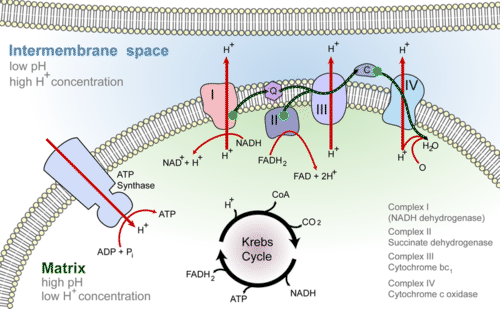
• In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD+) represents Oxidative phosphorylation within cellular respiration: Cellular respiration diagram simple. The overall reaction is broken into many smaller ones when it occurs in the body, most of which are redox reactions themselves. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 + 6h 2 o → 12h 2 o + 6 co 2. It fit into cellular respiration here: Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms. In this process, both plants and animals break down simple sugars into carbon dioxide and water and release energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The ATP is used for all the processes that occur within a cell that need energy.
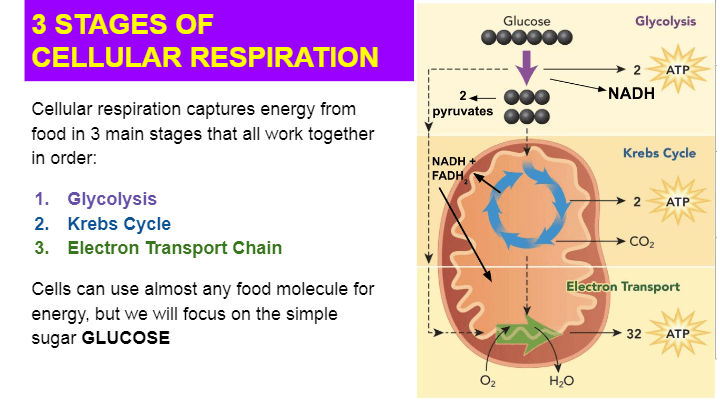
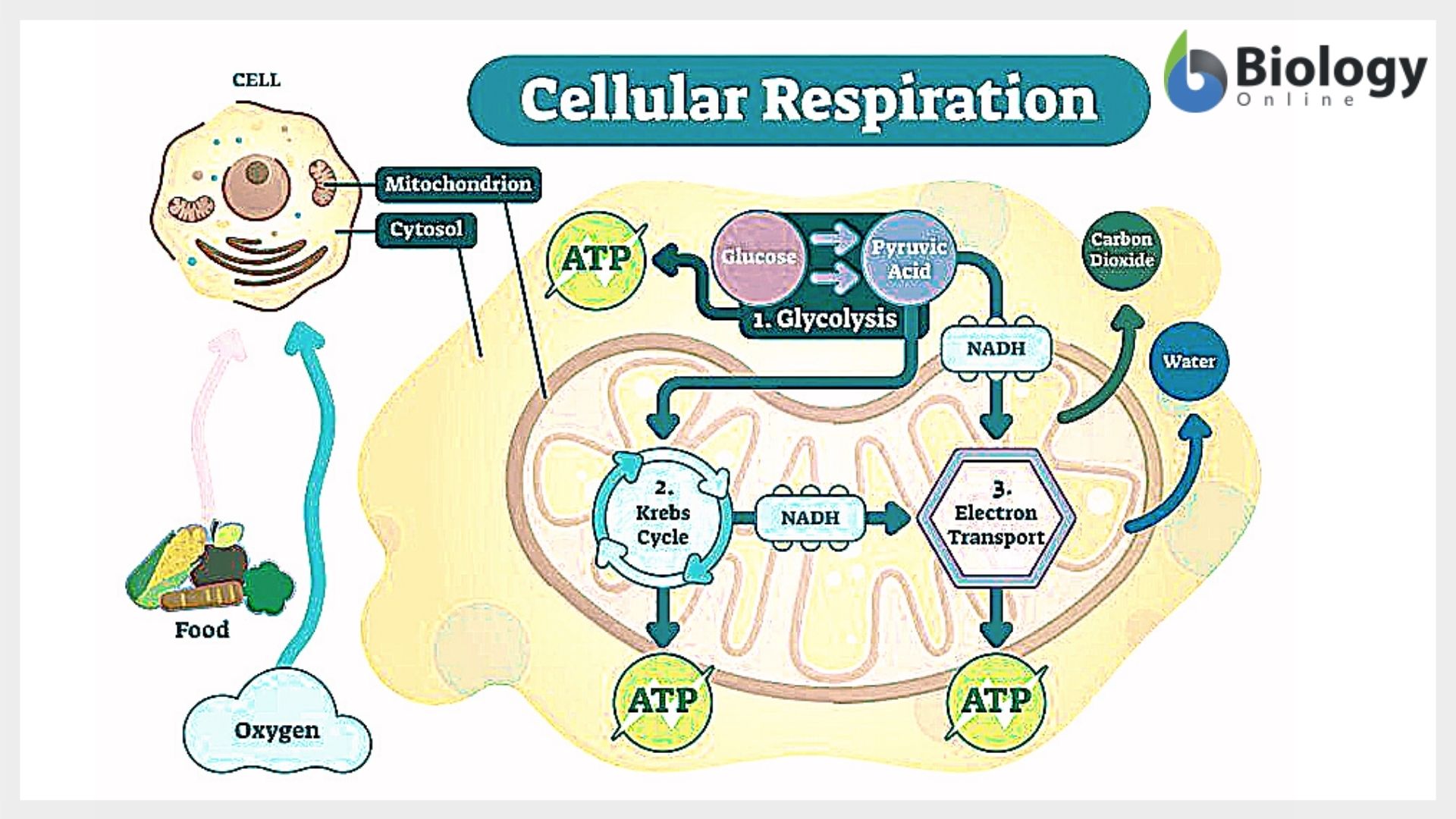
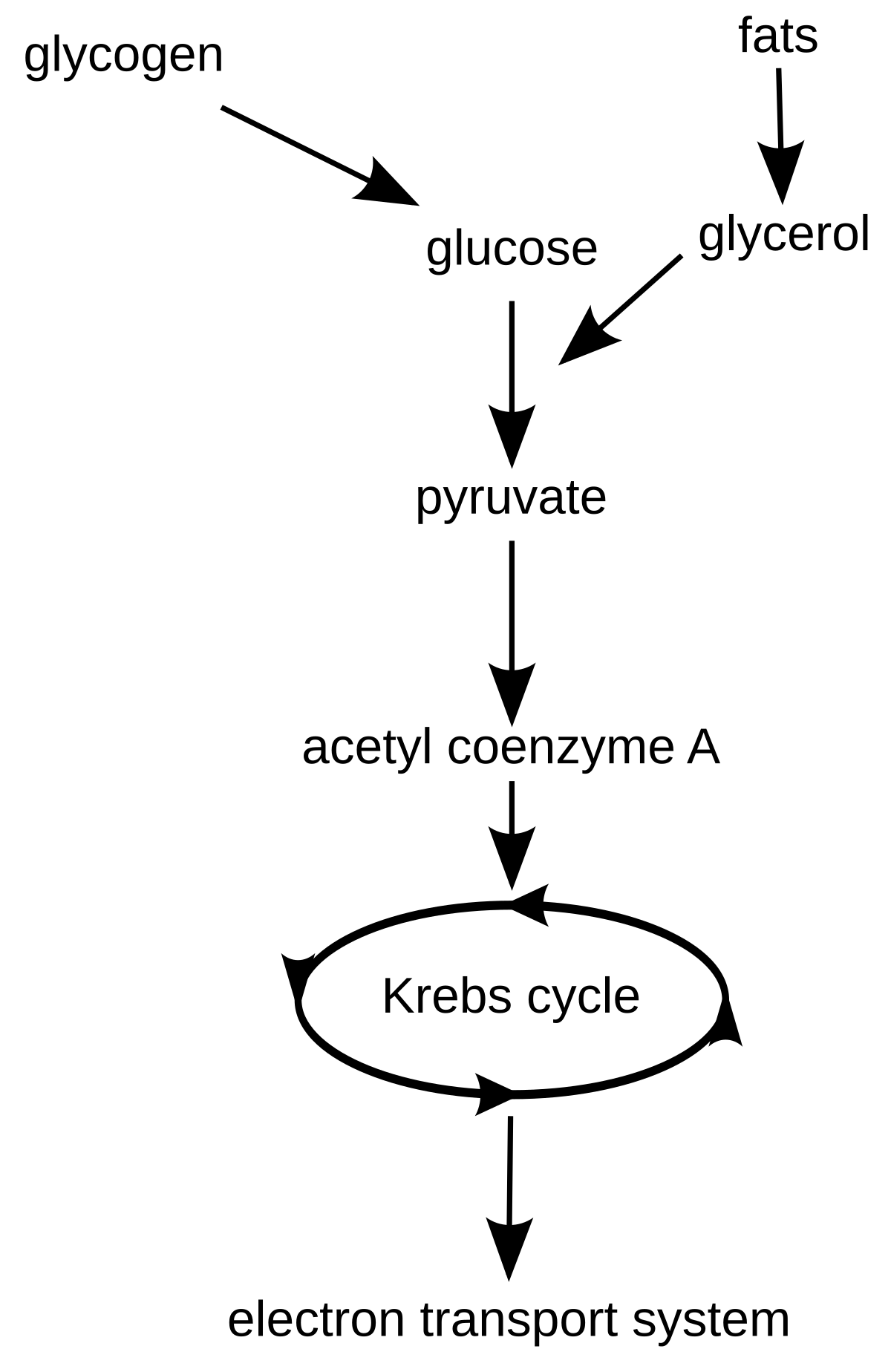
Simple cellular respiration diagram. Stage 1: Glycolysis. Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis. The word "glycolysis" means to "split sugar." In glycolysis, one molecule of glucose (6-carbon sugar) is broken in half by enzymes in the cytoplasm, producing 2 molecules of 3-carbon pyruvic acid (or, pyruvate).Splitting a molecule in half sounds simple, but glycolysis actually involves a series of steps that are ... Cellular respiration makes energy from sugar. Cellular Respiration needs Oxygen to occur. Cellular Respiration takes place in the mitochondria; the powerhouse of the cell. Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration and commonly begins with the simple sugar glucose. Through a series of steps a single molecule of glucose is ... About: LET'S DRAW-Bio is a YouTube Channel, where you will find Science and Biology related Diagrams, videos..... 4 stages of cellular respiration are metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of ATP molecules in cells. The breakdown of glucose include such cellular respiration steps as glycolysis, the transition reaction, the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell. http://www.handwrittentutorials.com - This tutorial is the first in the Cellular Respiration series. This tutorial is an overview of the process of ATP produ... The Krebs cycle (named after Hans Krebs) is a part of cellular respiration. The diagram below shows how this part of respiration is an ever-repeating cycle. a) Krebs cycle ccurs in matrix of mitochondria. The diagram below is a very simple outline of the Krebs Cycle showing the removal of CO2, and the making of 3.
Steps 1 and 3 = - 2ATP. Steps 7 and 10 = + 4 ATP. Net "visible" ATP produced = 2. Immediately upon finishing glycolysis, the cell must continue respiration in either an aerobic or anaerobic direction; this choice is made based on the circumstances of the particular cell. A cell that can perform aerobic respiration and which finds itself ... Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration - an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration: Cellular Respiration. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. relating to organisms whose cells have a nuceleus. natural or artificial process of changing a food's sugars into alcohols. Cellular respiration is what cells do to break up sugars to get energy they can use. Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create ATP, a chemical which the cell uses for energy.. Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration.It has four stages known as glycolysis, Link reaction, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Thus, the total ATP yield in the cellular respiration process is 36 or 38 ATP molecules. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules.
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.
What is Cellular Respiration? Cellular or Aerobic (in air) Respiration is a series of chemical reactions in the mitochondrion where molecules of glucose are broken down to make CO 2, water, and ATP. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water 38 ATP
Cellular respiration involves four main steps in converting glucose molecules to harvest energy in one's body cells. These are: 1. Glycolysis - The glucose undergoes chemical processes where it gets converted into pyruvate. The energy released in these reactions is ATP.
More About Cellular Respiration. So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis ...
3 Cellular Respiration A cellular process that breaks down carbohydrates and other metabolites with the concomitant buildup of ATP Consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide (CO 2) Cellular respiration is aerobic process. Usually involves breakdown of glucose to CO 2 and water Energy extracted from glucose molecule: Released step-wise
Start studying Unit 3: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Cellular Respiration At-a-Glance is a single page worksheet that contains a simple diagram of cellular respiration. I use this as soon as I'm finished with notes; it is designed to be at the very early stages of cellular respiration scaffolding. Students analyze the diagram and answer 10 questions.
Cellular respiration is a biology topic that can be a bit complicated for students to understand. Diagrams and free homeschooling worksheets can help children understand this process that occurs in living cells. The worksheets below should reinforce a basic study on this concept.
Catabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the 3 steps of cellular respiration. Step 1: oxidation of fatty acids, glucose, and some amino acids yields acetyl-CoA. Step 2: oxidation of acetyl groups in the citric acid cycle includes four steps in which electrons are abstracted.
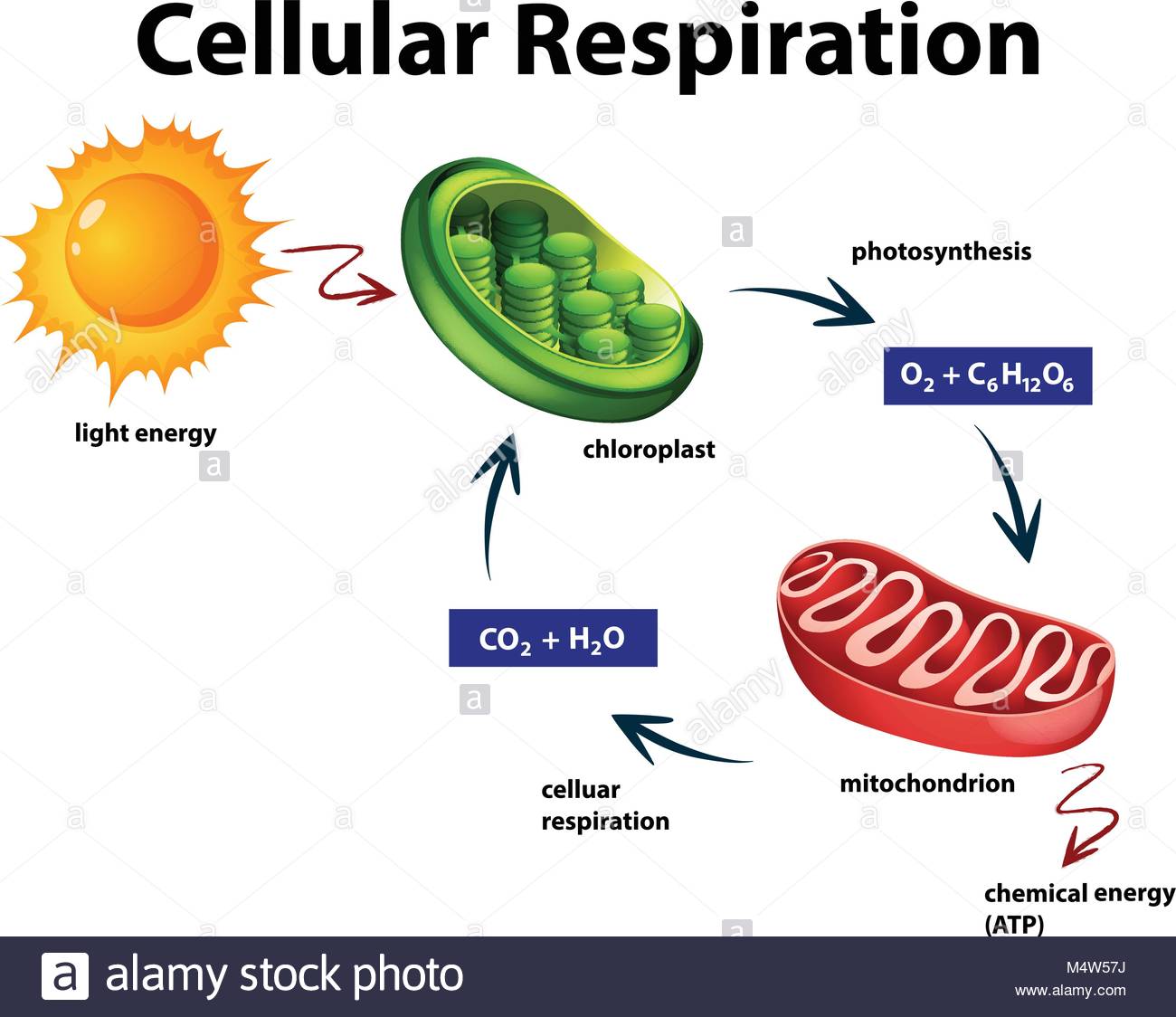
Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms. In this process, both plants and animals break down simple sugars into carbon dioxide and water and release energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The ATP is used for all the processes that occur within a cell that need energy.
Oxidative phosphorylation within cellular respiration: Cellular respiration diagram simple. The overall reaction is broken into many smaller ones when it occurs in the body, most of which are redox reactions themselves. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 + 6h 2 o → 12h 2 o + 6 co 2. It fit into cellular respiration here:
• In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD+) represents

The Diagram Below Shows The Relationship Between Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration And The Brainly Com

Animal And Plant Cell Energy Cycle Vector Illustration Diagram Vectormine Plant Cell Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
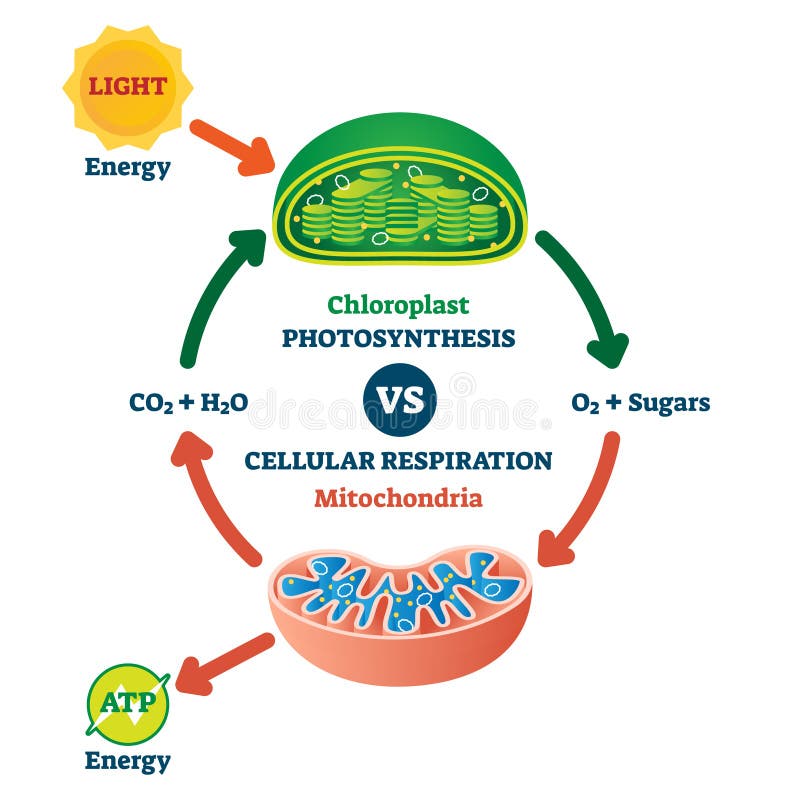
Cellular Respiration Medical Vector Illustration Diagram Respiration Process Scheme Stock Vector Illustration Of Research Biochemical 108051802

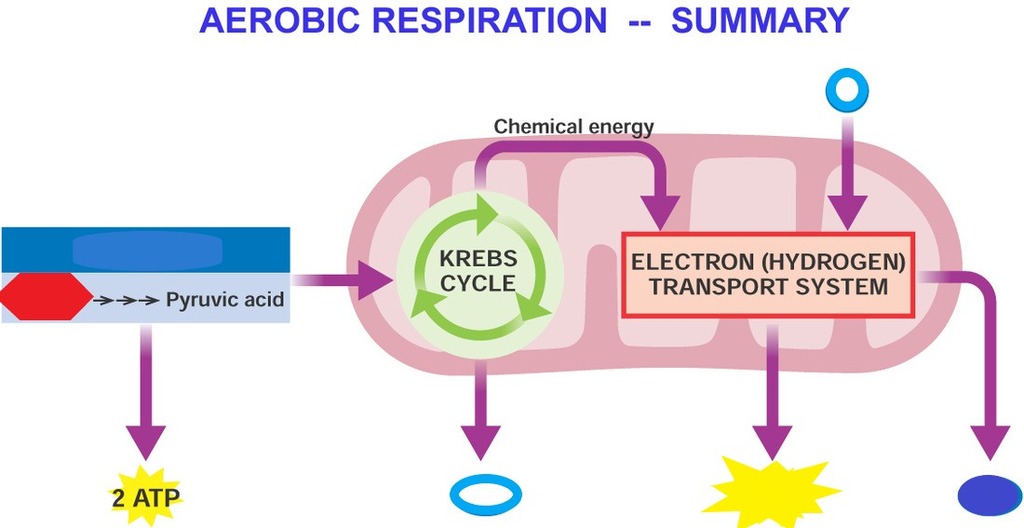


/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)















0 Response to "40 simple cellular respiration diagram"
Post a Comment