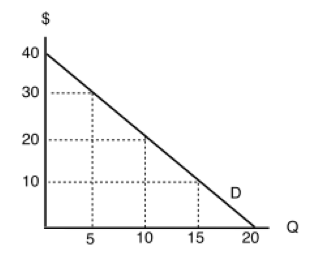
41 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
... the last 30 years, trade openness, which is defined as the ratio of exports and imports to national income, has risen from 25% to around 40% for ... You are watching: A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5. economics 0 0 Add a comment Next > Sortanswers by oldest Homework Answers recommended Answer See more: Which Of The Following Is True Of Enzymes And Substrates, Which Of The Following ...
In this paper, we build a computational model for the analysis of international wheat spot price formation, its dynamics and the dynamics of ...

A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
Consumer surplus is the amount that buyers are willing to pay less than the amount actually paid, measures the benefit that buyers receive from a good in terms in which they perceive. For example , if John wants a product and that product is willing to pay 100. And when you get to the store is that the product is now on sale and costs 80. Find the point of equilibrium for the following supply and demand equations where x is number of units and p is the price per unit. Demand: p = 241 - 0.000060x Supply: p = 73 + 0.000500x Number of Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 11 Economics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.. January 13, 2017 - ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the concept of consumer’s equilibrium, explained with the help of suitable diagrams and graphs. A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he “cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or ... This is because if the price floor is set below the equilibrium, then the price floor is set below the market value. In other words, the firm is able to sell at a higher price than the minimum price set. For example, the iPhone sells for around $699. Yet if the price floor was set at $500 (below the equilibrium), it would have no effect. Demand is the quantity of a particular good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various price levels at a given point in ... In the following figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer’s income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium ...
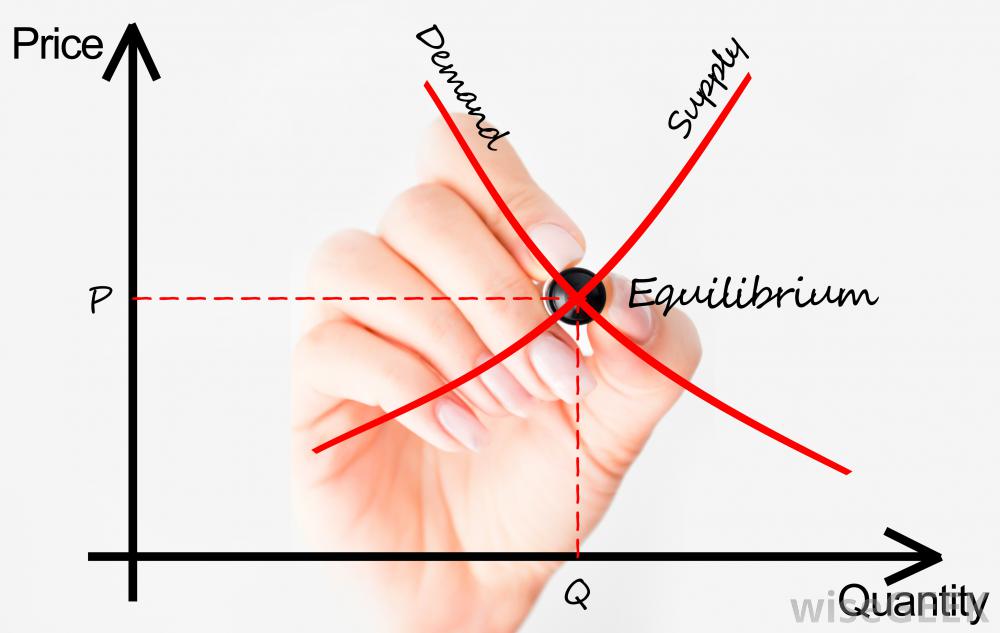
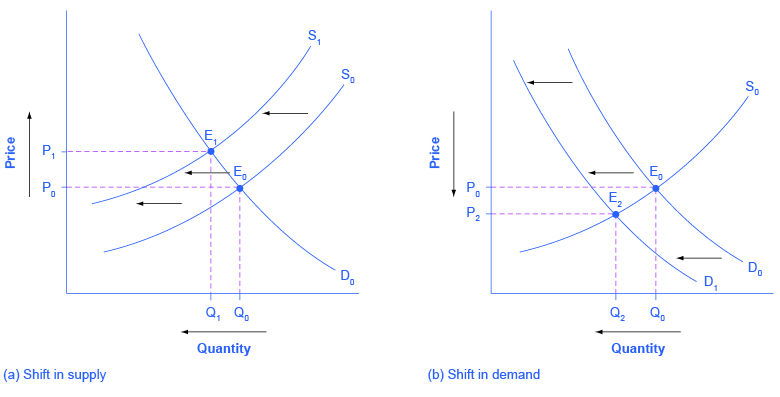
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X. For instance, the consumer may be willing to spend a maximum of $5 on a bagel. This is the price at which maximizes the consumer's utility, but also the price paid to the producer. As the price increases, the level of utility or satisfaction decreases. For instance, few would enjoy a croissant if they had to pay $50 for it. The y-axis (the vertical line) is showing us the price of a box of soap bars. You can see in the graph that the price starts at $0 and then rises. The prices shown on the graph are dependent on ... In other words, the long-run effect of a shift in aggregate demand is a nominal change (the price level is lower) but not a real change (output is ...
A. The price of pizza falls to $5, the price of soda falls to $1, and his income falls to $50. B. The price of pizza rises to $20, the price of soda rises to $4, and his income remains the same. C. The price of pizza falls to $8, the price of soda falls to $1, and his income rises to $120. D. Consumer equilibrium in case of single commodity is attained where MUx / MUm = Px. If a consumer consumes less than this point i.e MUx / MUm > Px, it means that additional satisfaction obtained from consuming one more unit of commodity X in terms of money is more than the price paid for it. In this diagram when · I=10 px=2 & py=1 We get the budget line (AA).the consumer is in equilibrium at E1purchasing Ox1 of x. We suppose that when: · I=10 px=1 & py=1 As a result the AB is the new BL .as we concerned with the SE of price of fall.there fore we will offset the real increase in income by illustration of a new budget-line CC(according to the method asdescribe by J.R.HICKS) ,and ... Q2. Which of the shaded area in the diagrams below represent total utility? ... Q3. What does the area under the marginal utility curve depict? (a) Average Utility (b) Total Utility (c) Indifference Curve (d) Consumer Equilibrium

Managerial Economics A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Accompanying Figure The Price Of Good X Is 5 Homeworklib
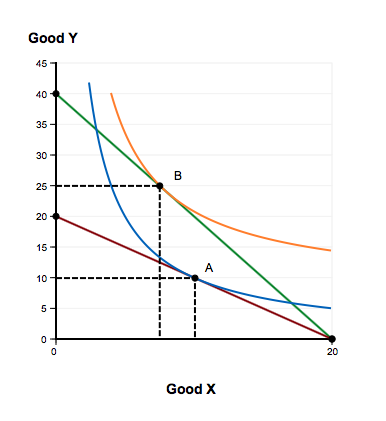
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y?$ b. What is the consumer's income?$ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium?
For a price floor to be effective, it must be set above the equilibrium price. If it's not above equilibrium, then the market won't sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant. In the diagram above, the minimum price (P2) is below the equilibrium price at P1.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. Good Y 45 40 35 30-1 B 25 20 15 10 5 - 0 20 Good X 2 a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer's income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? units d.
consumer surplus? A $0.15 B $0.85 C $0.90 D $1.35 13 A market is in equilibrium at price $5. Market supply changes from being inelastic at each price to become elastic at each price. The market equilibrium price does not change. What is the effect on consumer surplus and producer surplus? consumer ...
... the above quotation is found, to chapter 17, we see on page 224, the following passage in which Keynes extends the idea of a commodity or “ own ...
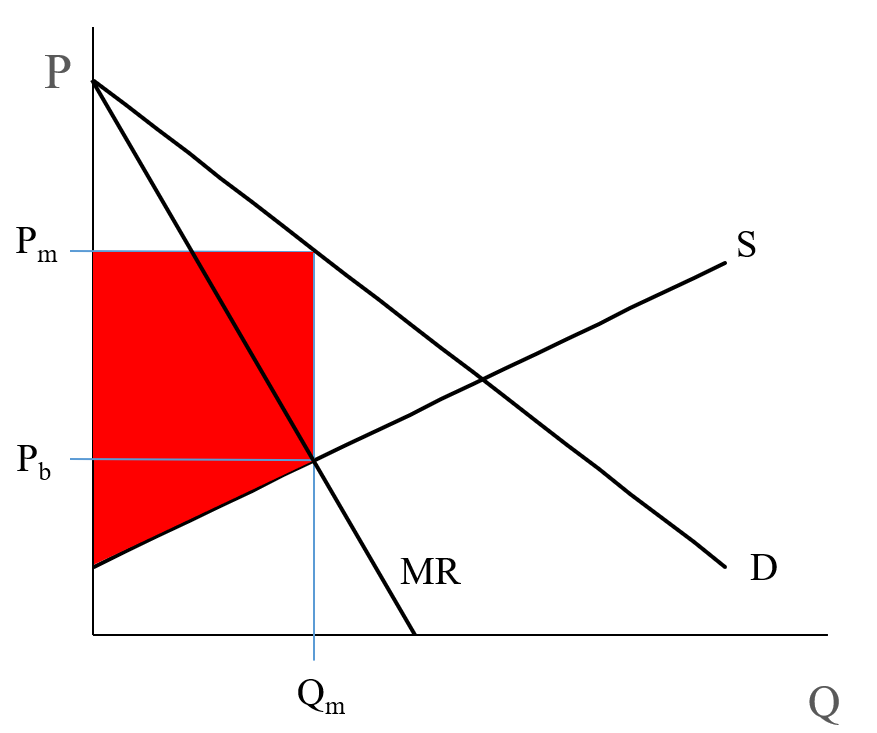
A price ceiling would never be implemented above the equilibrium - as highlighted at P and Q*. This is because it would not have the intended effect - i.e. make it affordable to consumers. What happens is the price ceiling is set BELOW the equilibrium point in order to reduce the producer surplus and make it affordable to the consumer.
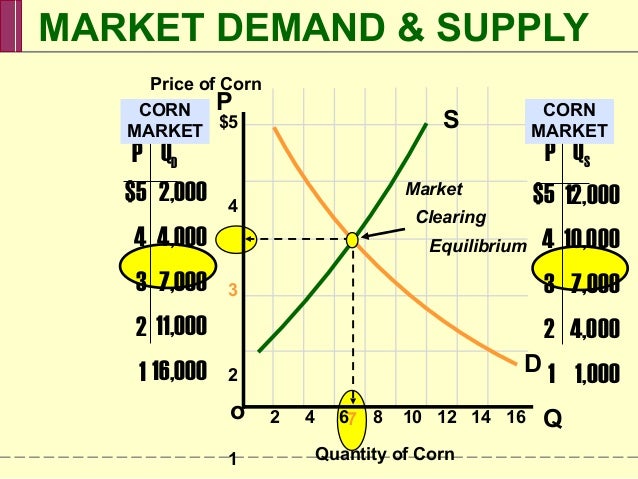
If the price of a good is below the equilibrium price, a. the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied and the price remains unchanged. b. there is a surplus and the price will rise. c. there is a shortage and the price will fall. d. there is a shortage and the price will rise. e. there is a surplus and the price will fall.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of good Y? $_____ B. What is the consumer's income? $_____ C. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? _____ units. D. Suppose the budget line changes so that ...
The Price Of Good X Is $5. A. What Is The Price Of Good Y If The Price Of Good X Is $ 5 At Equilibrium, Price Of Good Y Would Be $5 B. What Is The Consumer's Income? X= M/px The Price Of Good X1 Px =$5 And The Maximum Affordable Quantity Of Good X Is 20 Units So 20= M/$5 So M = $100 Which ...
Example of Equilibrium . A store manufactures 1,000 spinning tops and retails them at $10 per piece. But no one is willing buy them at that price. To pump up demand, the store reduces its price to $8.
As BGG point out, “ the ratio of private consumption to GDP (in constant prices) increased from 62% to 72%, [and] the ratio of investment to GDP ...
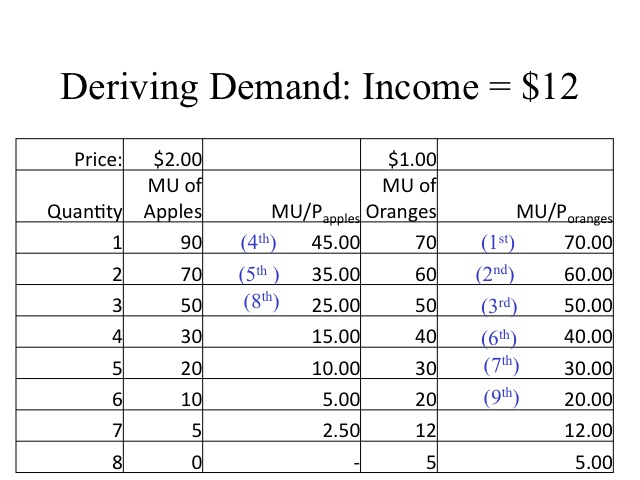
It is explained with the help of following example and diagram: - Let price of good X = ₹5 MU of money i.e. MU m (1₹) = 4 utils. In the above tabular representation, consumer equilibrium is attained at 5 units of the product where marginal utility of the product in terms of money = price of the good.

Managerial Economics A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Accompanying Figure The Price Of Good X Is 5 Homeworklib
In a recent blog post , Cho responded to this criticism, sharing his thoughts on the future of photography and the value of a photograph that is given ...
If the free-market equilibrium price for some product is $25, then a legal price ceiling set at $15 will bring about the same general effects as an equilibrium price of $15. a surplus of the good. a shortage of the good. no change in the market outcomes. the same general effects as a price ...
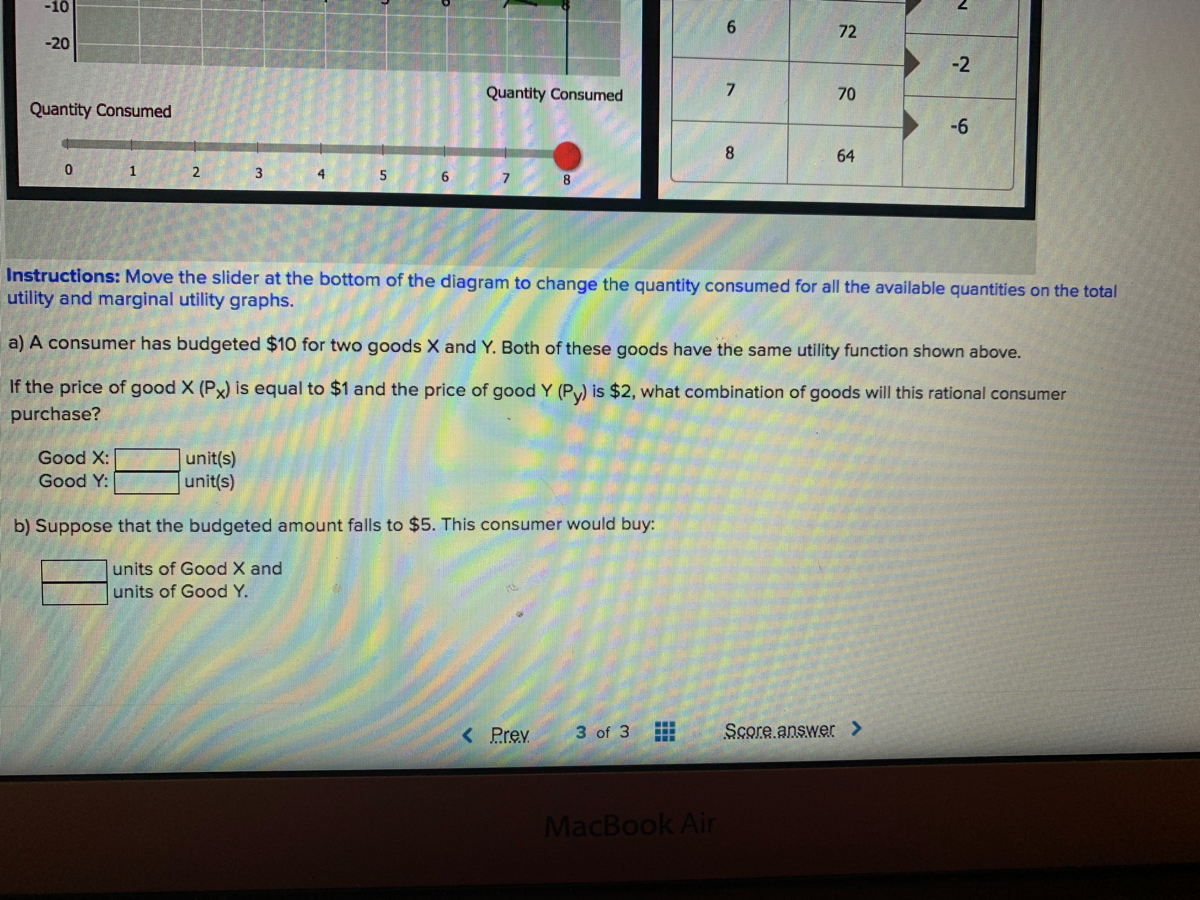
Solved Problem 04 01 A Consumer Has 300 To Spend On Goods X And Y The Market Prices Of These Two Goods Are Px 15 And Py 5 A What Is The M Course Hero
344. The consumer is in equilibrium and is consuming good-X only. The MU from last unit of good X consumed is 50 utils and Mu m =10. What is the price of good X? (a) ₹ 5 (b) ₹ 40 (c) ₹ 10 (d) ₹ 4. 345. The principal limitation of utility analysis re¬lates to the basic assumption that utility can be expressed in terms of-(a) cardinal ...
... consumption goods to the uses of durable factors through capitalization , in which the total stream of income from a factor is summed into its rental ...
Economics Q&A Library A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ b. What is the consumer's income? $ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? units
For some, it costs $2 to produce, whilst it costs others $3 and a few pays $5. At the equilibrium point, the coffee is sold at $5 - where supply and demand meet. The producer surplus refers to all those who produce at a cost lower than $5. The companies that produce at a cost of $5 make a loss instead of a surplus.
Solved In The Diagram Below Where U0 And U1 Are Indifference Curves Suppose The Budget Line Shifts So That The Consumer S Equilibrium Position Cha Course Hero
... all points of tangency between the indifference curves of both individuals, the contract curve is constructed and represents all Pareto efficient ...
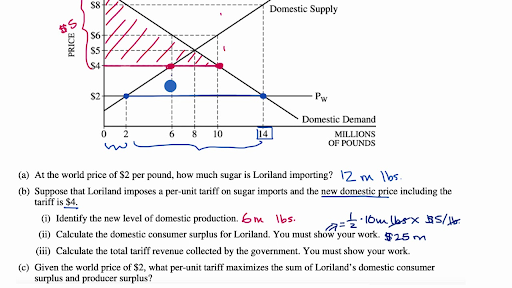
That means the quantity at Q2 is what is being produced and sold to the market. So the consumer and producer surplus cannot go beyond Q2 as this is now the new equilibrium point. Previously, the equilibrium point was at E1, which meant there were greater demand and supply at the lower price.
... the author of your link bother referring to low income elasticity to explain why consumption of the taxed good falls? If we keep income constant (for ...
Chapter 4 HW 1) A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. 2) A consumer must divide $600 between the consumption of product X and product Y .

Suppose That The Supply Of A Good Is Perfectly Elastic At A Price Of 5 The Market Demand Curve For This Good Is Linear With Zero Quantity Demanded At A Price Of
c. perfectly inelastic. Suppose the current price of gasoline at the pump is $1 per gallon and that 1 million gallons are sold per month. A politician proposes to add a 10¢ tax to the price of a gallon of gasoline. She says the tax will generate $100,000 tax revenues per month (1 million gallons ...

Week 2 Chapter 4 Problems Docx Chapter 4 Question 1 A Consumer Has 300 To Spend On Goods X And Y The Market Prices Of These Two Goods Are Px 15 And Course Hero
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ 5 5 Correct b. What is the consumer's income? $ 100 100 Correct c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? 10 10 Correct units d.
A movement from point X to point Y along the demand curve D1 A decrease in the price of video games Which of the following will cause a movement along the demand curve for chicken, a normal good, resulting in an increase in the quantity demanded?
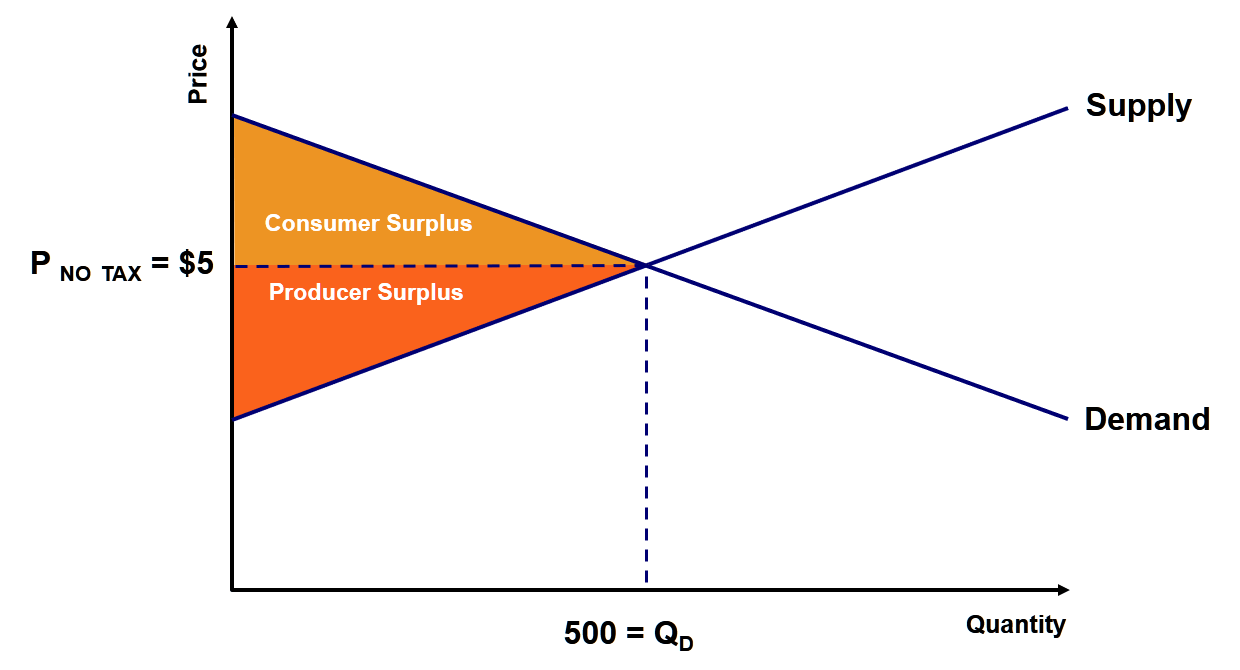
A customer is willing to spend $8.00 on a new energy drink, but most customers are willing to pay only $5.00, which is the equilibrium point where supply meets demand. At a $5.00 retail value, the company supplies a store with 500 bottles to meet the demand. Plugging these values into our formula gives us (½) x 500 x ($8 - $5) for a total of ...
Solved Problem 04 01 A Consumer Has 300 To Spend On Goods X And Y The Market Prices Of These Two Goods Are Px 15 And Py 5 A What Is The M Course Hero
December 10, 2019 - Therefore, we can say that consumers equilibrium is achieved when the price line is tangential to the indifference curve. Or, when the marginal rate of substitution of the goods X and Y is equal to the ratio between the prices of the two goods. Solved Question on Consumers Equilibrium.
A price control is instituted when the government feels the current equilibrium price is unfair and intervenes and adjusts the market price. More specifically, a price ceiling (in other words, a maximum price) is put into effect when the government believes the price is too high and sets a maximum price that producers can charge; this price must lie below the equilibrium price in order for the ...
Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 11 Economics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Find the point of equilibrium for the following supply and demand equations where x is number of units and p is the price per unit. Demand: p = 241 - 0.000060x Supply: p = 73 + 0.000500x Number of
Consumer surplus is the amount that buyers are willing to pay less than the amount actually paid, measures the benefit that buyers receive from a good in terms in which they perceive. For example , if John wants a product and that product is willing to pay 100. And when you get to the store is that the product is now on sale and costs 80.


.png)











0 Response to "41 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5."
Post a Comment