41 convex mirror ray diagram class 10
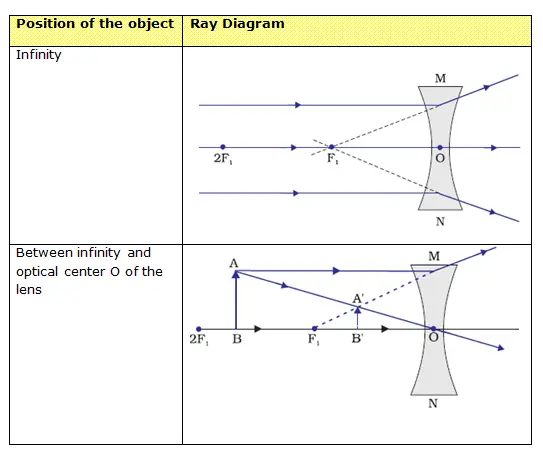
Application of Concave Mirror. (1) Reflectors (head light, torch, search light) (2) Shaving and make up mirrors. (3) Solar cookers (when parallel beam of sunlight fall on mirror,it is brought to focus.As a result temperature increases and hence food is cooked) (4) ENT specialist uses spherical mirror. Filed Under: Class 10, Light-Reflection and ... 28 Mar 2021 — Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams ... As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a ...Position of object: Position of imageWithin focus(Between P and F): Behind the mir...Between F and C: Beyond CBeyond C: Between F and C
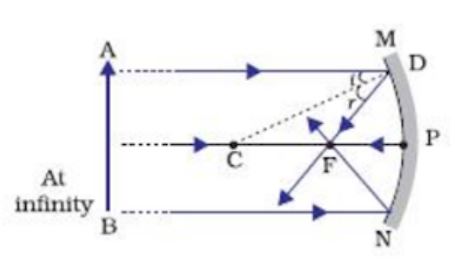
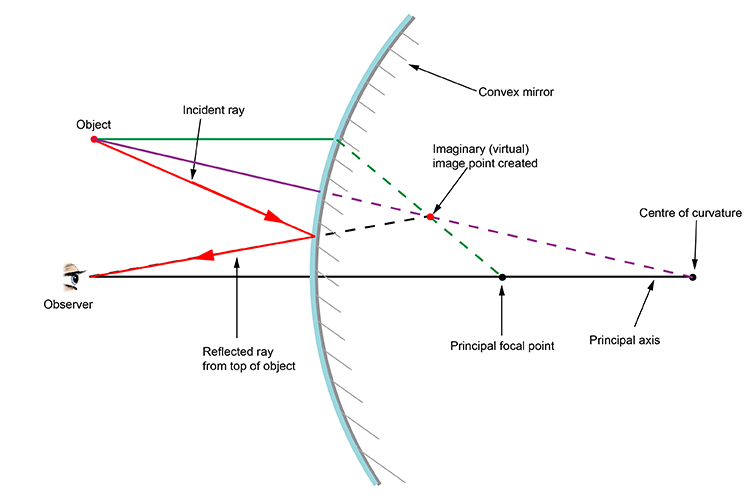
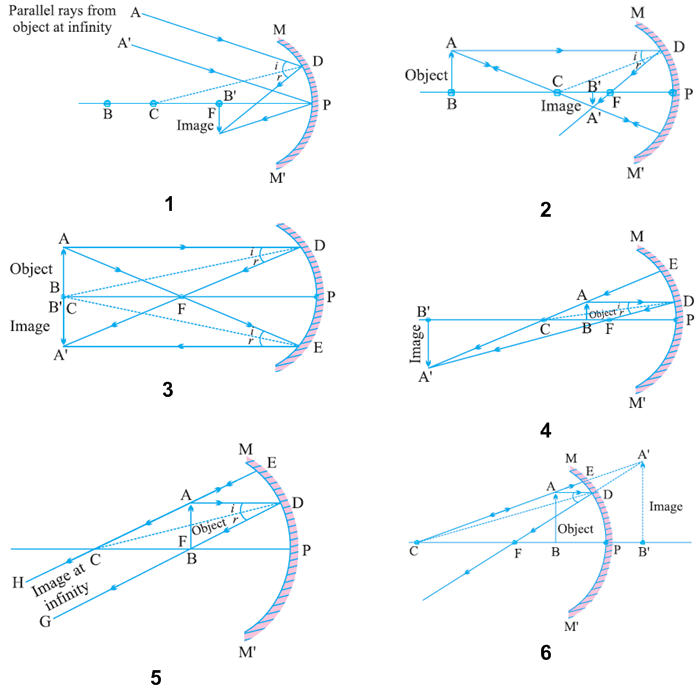
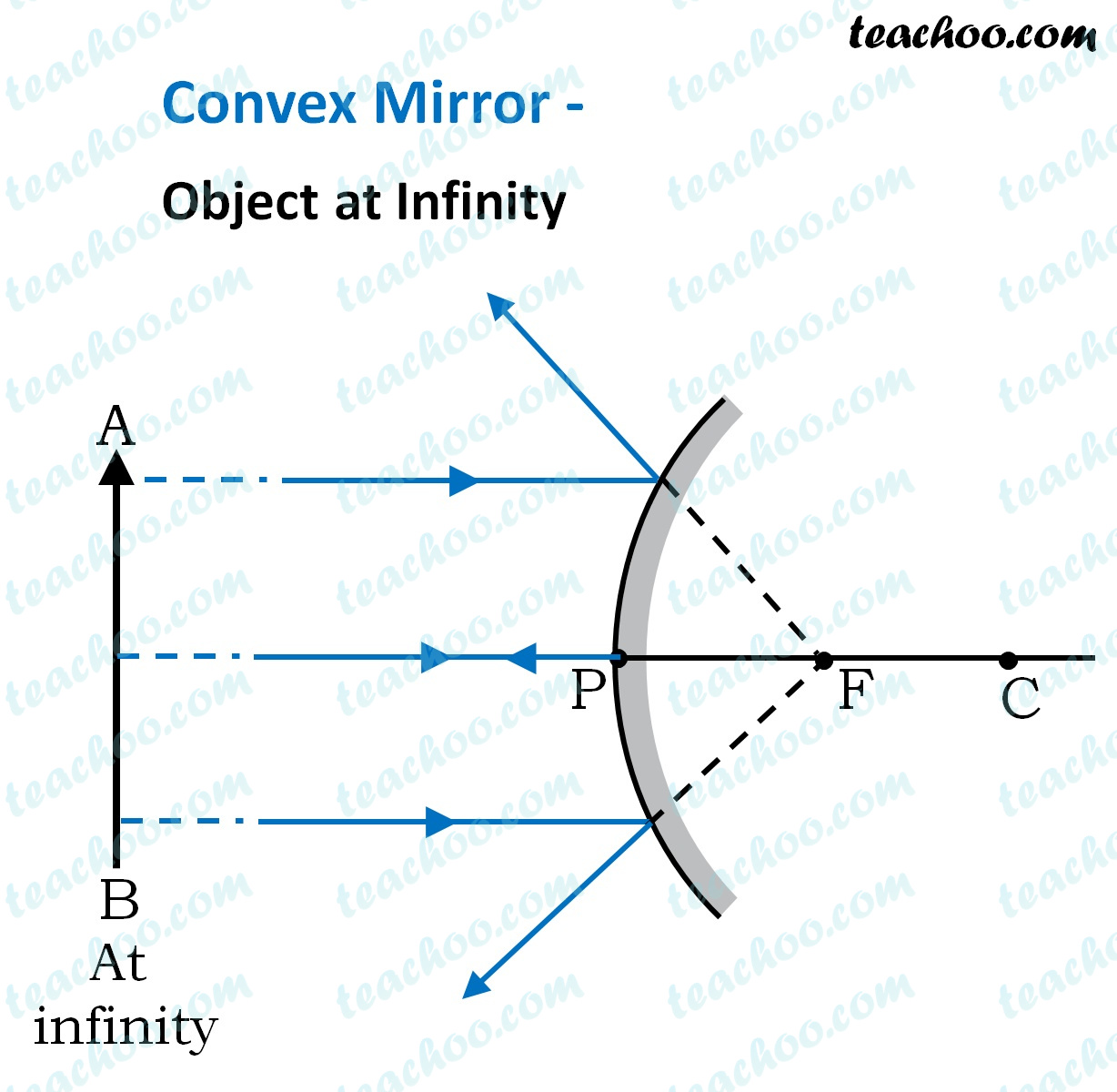
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.

Convex mirror ray diagram class 10
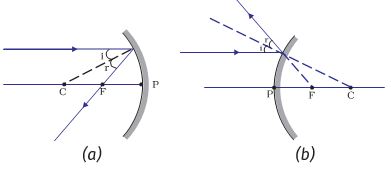
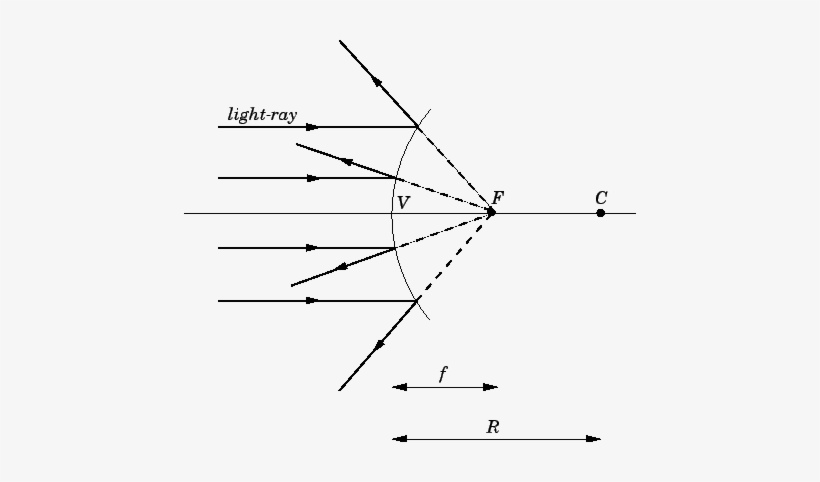
Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror. Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Guidelines for Rays Falling on the Concave and Convex Mirrors. When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely. Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. In case of a convex mirror any ... For both concave and convex mirror , if the incident ray to the Pole makes an angle of incidence i, then it will go back making an angle of reflection r with Principal axis as the normal and Angle of Incidence = Angel of Reflection Next: Concave Mirror - Ray diagram→ Class 10; Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1 ...
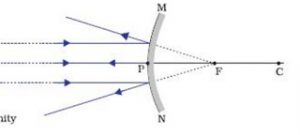
Convex mirror ray diagram class 10. 23 Apr 2020 — For a Convex Mirror,The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirrorSo, there will only be 2 cases.Between infinity and the pole P of the mirror: B...At infinity: At the focus F, behind the mirrorPosition of the object: Position of the image An object is placed between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror. Draw a ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of the image formed. (CBSE 2011) Answer: Position of the object: Between infinity and P of the mirror. Position of image: Between P and F, behind the mirror Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 10 Solutions Page No:249. Question 44: An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens. Solution : Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 10 Solutions Page No:251. Question 1: When an object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a convex mirror, the magnification produced is 1/2. Where should the object be placed to obtain a magnification of 1/3? Easy. View solution > In a car a rear view mirror having a radius of curvature 1.50 m forms a virtual image of a bus located 10.0 m from the mirror. The factor by which the mirror magnifies the size of the bus is close to ...
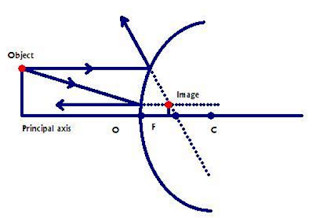
(a) Draw a ray diagram to represent a convex mirror. On this diagram mark the principal axis, principal focus F and the centre of curvature C if the focal length of the convex mirror is \[3\,cm\]. (b) An object \[1\,cm\] tall is placed \[30\,cm\] in front of a convex mirror of focal length \[20\,cm\]. Find the size and position of the image ... Question 2 The image formed by a convex mirror is seen to be erect,virtual and diminished.What is the position of the object? Images formed by convex mirror using ray diagram. (1) Object is between infinity and pole. (a) Image is formed between pole and focus. (b) It is erect,virtual,diminished. 27.09.2019 · Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction ... An object 5cm in length is held 25cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Answer: Therefore, the mage ¡s formed between F 2 and 2F 2 on the other side of the lens. It is real and inverted, and … In this video I have taught how to draw ray diagrams of image formation by Convex Mirror in easy way.
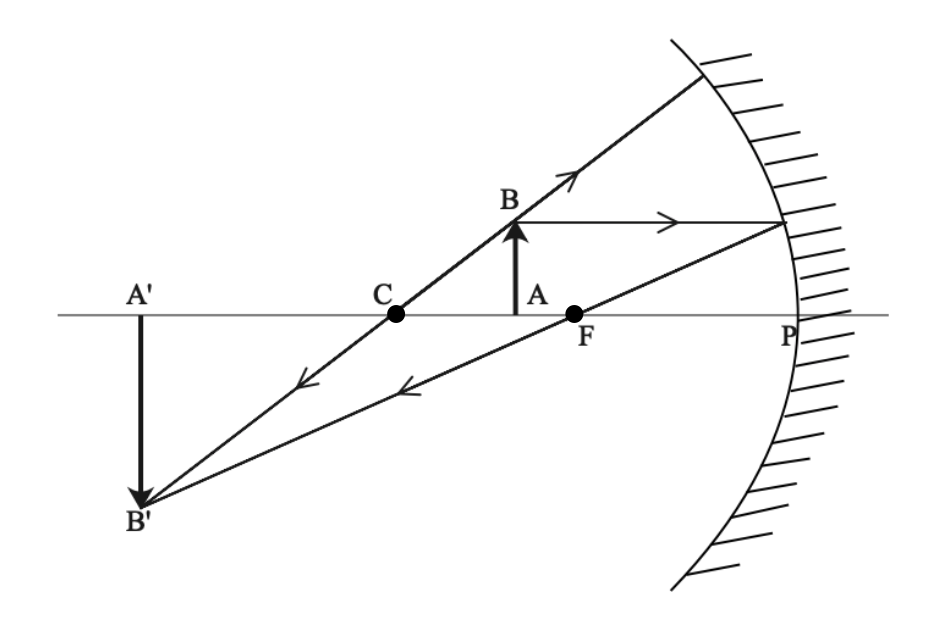
Convex and concave mirror have same radii are the distance between mirrors 2R and what point on the common optical axis of the mirror should a point source of light A be placed for the rays to coverage at the point A after being reflected first on convex and the on concave mirror. Medium. View solution > With the help of ray diagram, illustrate the change in position, nature and size of the ... For both concave and convex mirror , if the incident ray to the Pole makes an angle of incidence i, then it will go back making an angle of reflection r with Principal axis as the normal and Angle of Incidence = Angel of Reflection Next: Concave Mirror - Ray diagram→ Class 10; Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1 ... Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. In case of a convex mirror any ... Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror. Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Guidelines for Rays Falling on the Concave and Convex Mirrors. When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely.

Ppt Convex Mirrors Diverging Mirrors How To Locate An Image Using Ray Diagrams Powerpoint Presentation Id 2640548
Which Of The Following Ray Diagrams Is Correct For The Ray Of Light Incident On A Concave Mirror Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
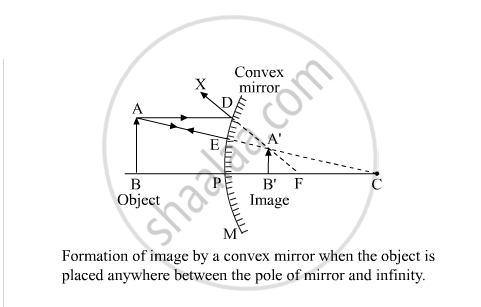
Draw A Labelled Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Image Of An Object By A Convex Mirror Mark Clearly The Pole Focus And Centre Of Curvature On The Diagram Science

Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Image Of An Object Kept In Front Of A Convex Mirror State Three Characteristics Of The Image Physics Shaalaa Com

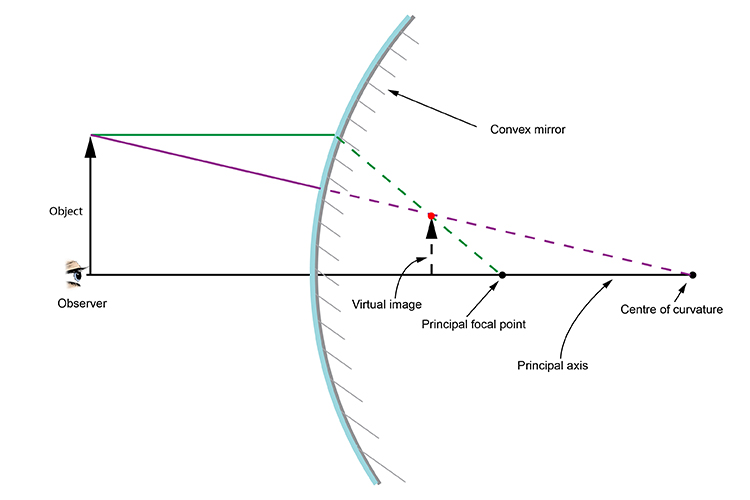
With The Help Of A Ray Diagram Explain Why A Convex Mirror Is Preferred For Rear View Mirrors In Motor Cars Amdirac





















0 Response to "41 convex mirror ray diagram class 10"
Post a Comment