41 sn2 reaction coordinate diagram
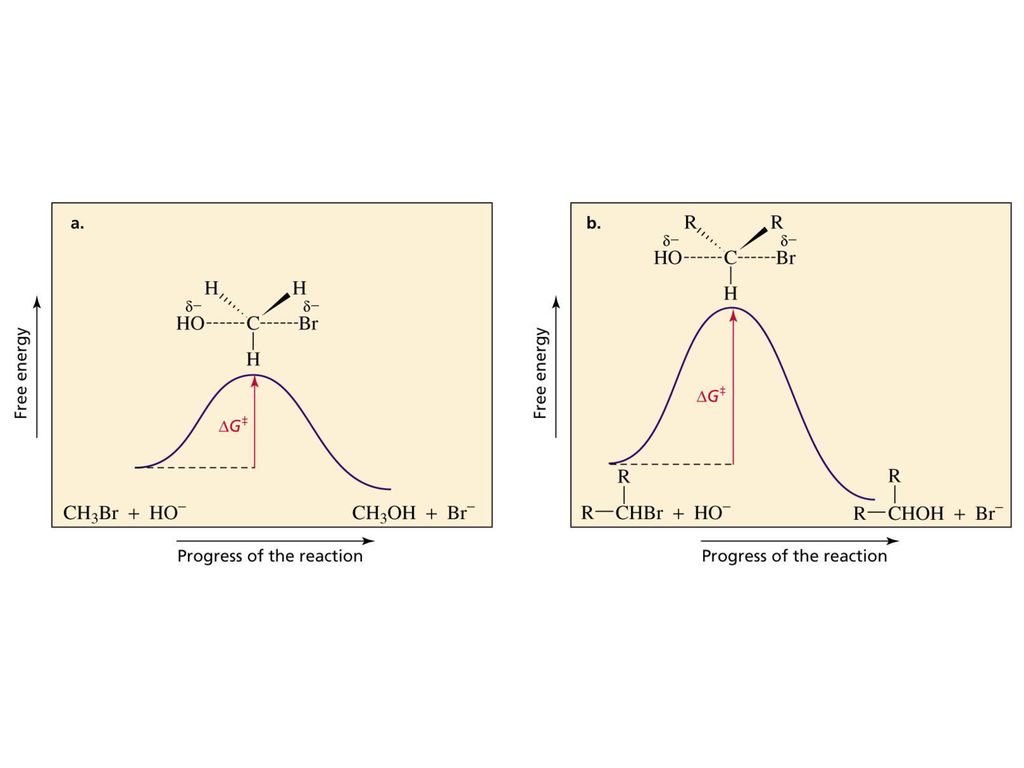
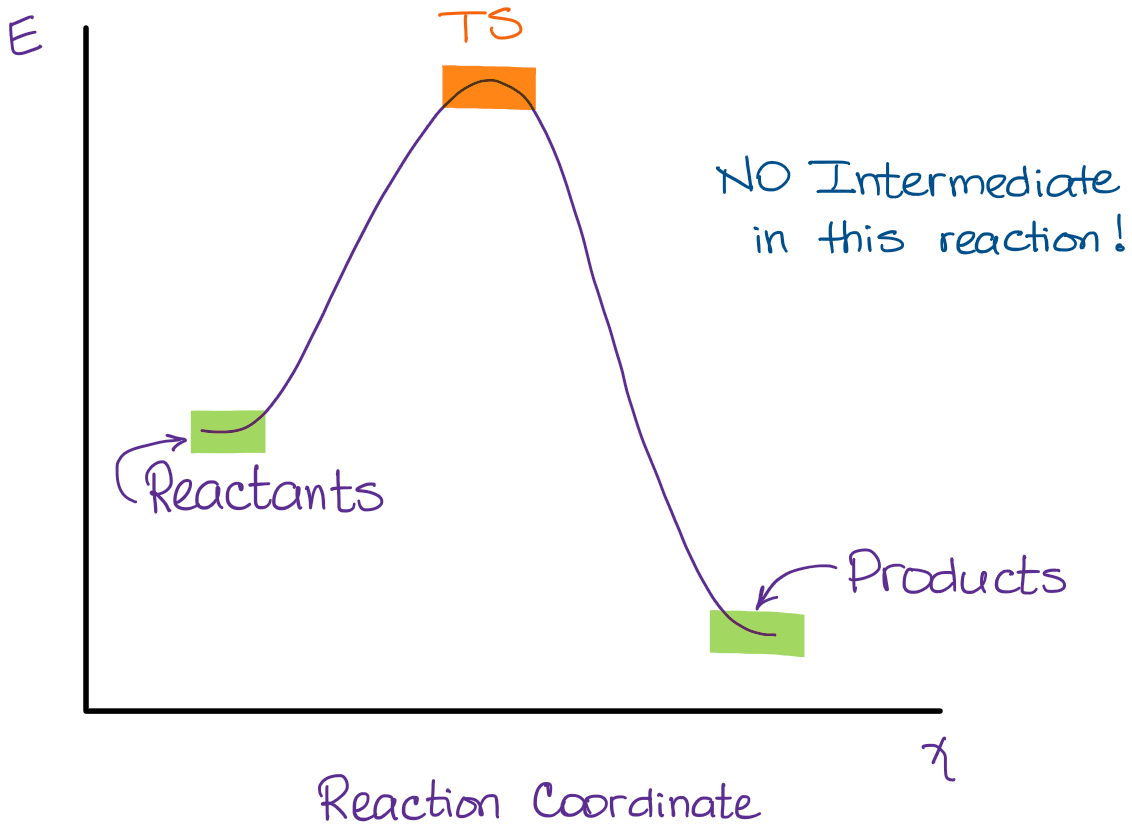
The reaction coordinate is the direct connection of starting products, transition state (mountain pass), and products on the mountain's surface (the red line in the illustration). A mountain pass that is relatively broad in cross direction represents a reaction with a lower free energy of activation ΔG ‡ than a narrow mountain pass does. SN2 mechanism. SN2 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular reaction, described by the expression rate = k [Nu][R-LG] . This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group.
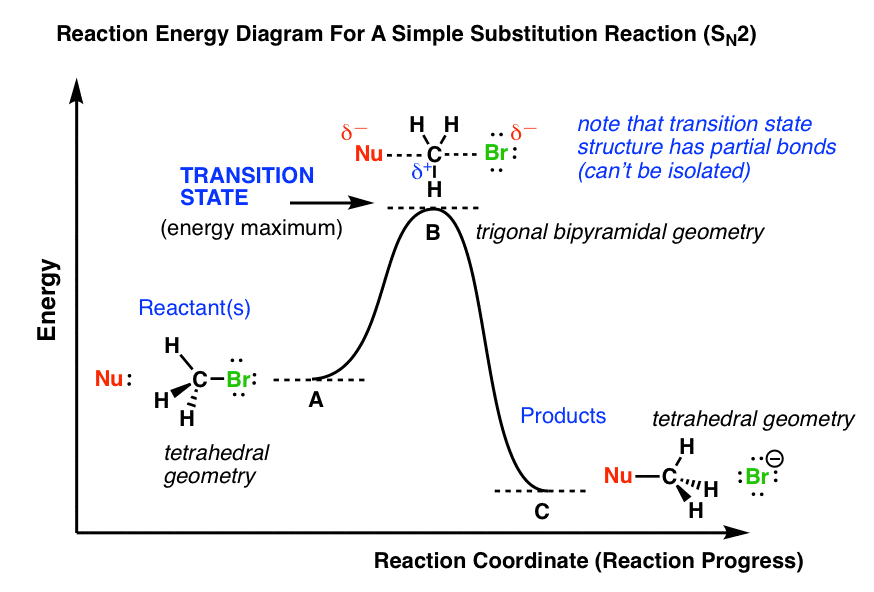
SN2 reaction coordinate diagram In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea).
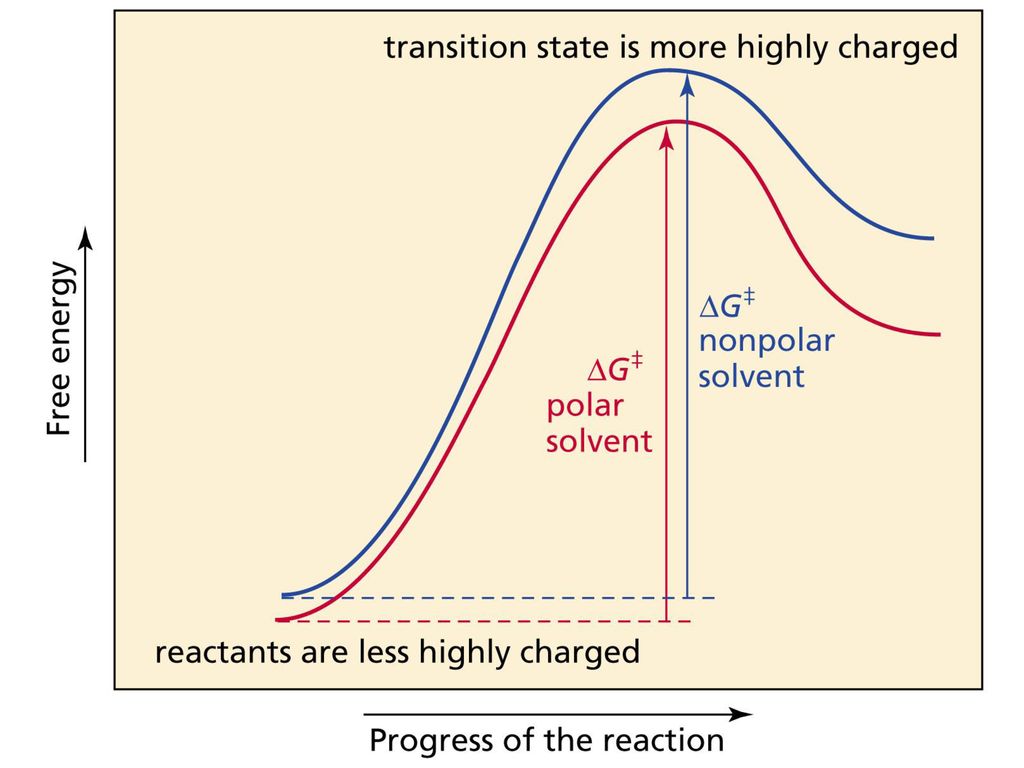
Sn2 reaction coordinate diagram
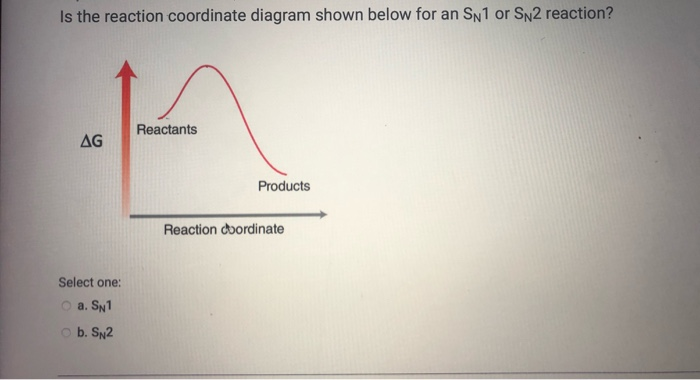
The reaction coordinate energy diagram below corresponds to which mechanism? a. SN1 b. SN2 ๕. El d. E2 ฯ กาก Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo the slowest Sn1 reaction? مسلم C D E ; Question: The reaction coordinate energy diagram below corresponds to which mechanism? a. SN1 b. SN2 ๕. El d. The SN2 reaction mechanism stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular and is a fundamental mechanism in organic chemistry. In an SN2 mechanism, a nucle... Aug 08, 2012 · 3. The Mechanism For The SN2 Is Concerted. The Mechanism Of The SN1 Is Stepwise. The S N 2 reaction is concerted.That is, the S N 2 occurs in one step, and both the nucleophile and substrate are involved in the rate determining step. Therefore the rate is dependent on both the concentration of substrate and that of the nucleophile.; The S N 1 reaction proceeds stepwise.
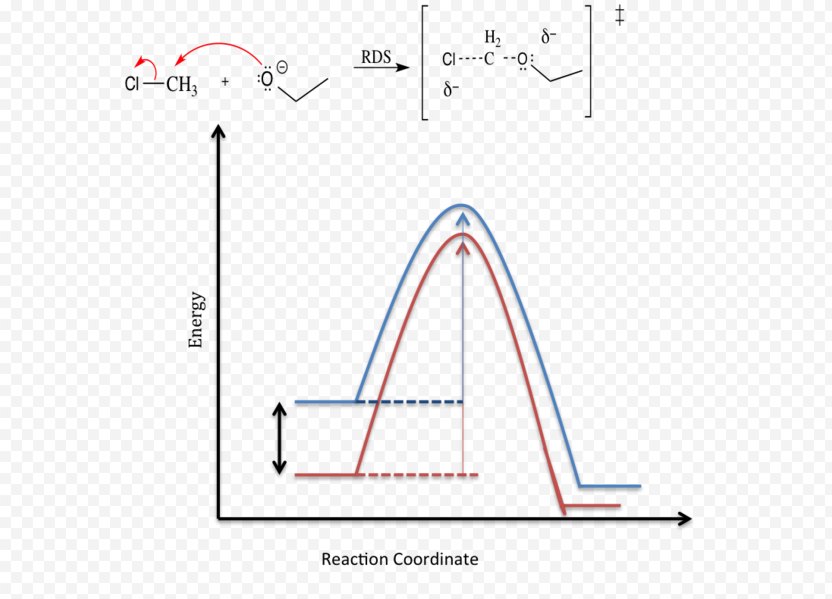
Sn2 reaction coordinate diagram. The S N 2 Reaction Notes: In the SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the most δ+ region: behind the leaving group. This is called a back-side attack. This back-side attack causes an inversion (study the previous slide): after the leaving group leaves, the other substituents shift to make room for the newly-bonded nucleophile, changing the stereochemistry of the molecule. Figure 9.3 shows the reaction coordinate diagram in the S N 2 reaction of hydroxide ion with chloromethane to give methanol and chloride ion. We see that the transition state contains both hydroxide ion and the substrate. As the reaction proceeds through the transition state, a bond forms between carbon and hydroxide ion, and the bond between carbon and chlorine breaks. Unformatted text preview: ! 1 CHEM 232 Worksheet SN2 1. Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for the SN2 reaction of 1-iodopropane with -NH2 to form a neutral organic product. Be sure to include the starting materials, any intermediates, and products on the diagram. Draw the transition state for the rate-determining step. Reaction Coordinate Diagram of an S N 2 Reaction. 1 – Create a list of reagents. For the following reaction, label the nucleophile, electrophile, and leaving group, Br + + Br Nucleophile Select] Electrophile (Select] Leaving Group [Select] For each of the following pairs, indicate with molecule is the better (stronger) nucleophile.
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. The mechanism, rate law, and stereochemistry of Sn2 reactions. How the sterics of the alkyl halide affect the reaction rate. Created by Jay. Sn1 and Sn2. Identifying nucleophilic and electrophilic centers. Curly arrow conventions in organic chemistry. Intro to organic mechanisms. Alkyl halide nomenclature and classification. Oct 24, 2018 · SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea). The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. http://Leah4sci.com/substitution-elimination presents: SN2 Energy Diagram Need help with Orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets to Acing Organic Chemistry'...
Reactants are the substances to the left of the arrow in a reaction that are present before the reaction begins. Products are the substances to the right of the arrow in a reaction and they are formed during the reaction and are present when the reaction is over. 1.29 (a) (b) (c) N2, nitrogen, Br2. bromine. O2, oxygen I2, iodine. F2, fluorine Select all the statements that correctly describe the reaction coordinate vs. energy diagram for an SN1 reaction. A. The energy diagram shows two energy maxima corresponding to the 2 transition states B. The carbocation intermediate is more stable than the starting material. C. (simultaneously); there are no intermediates. Although the reaction coordinate energy diagram illustrates the activation energy and the ΔG°, we are often interested only in the shape of the diagram: for the SN2 reaction, that there is one transition state, one step. For now, the quantities for E a and ΔG° are not important. SN1 is a two-stage system, while SN2 is a one-stage process. The carbocation can form as an intermediate during SN1 reactions, while it is not formed during SN2 reactions. 3. What determines sn1 or sn2? Ans: In the rate of reaction, Sn1 reactions are unimolecular and have a step-wise mechanism.
Construct the gas phase Reaction Coordinate Diagram for the Cl + CH3Cl SN2 reaction by plotting the relative energy in kJmol 1 versus Cl + C | {z} Distance H3 Cl. Place the Reaction Coordinate Diagram on the graph provided below and plot the energies on a relative energy scale. Label the various species along the reaction pathway. 0 5 10 15 20 ...
Chemistry 202. Lecture 17. Organic Reaction Mechanisms II: Kinetics and Rate Equations, Part 2 (English) Chemistry 202. Lecture 18. Organic Reaction Mechanisms II: Thermodynamic vs Kinetic Control (English) Chemistry 202. Lecture 19. Organic Reaction Mechanisms II: Selectivity & Transition State Theory (English) Chemistry 202. Lecture 20.
Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1). Substrate: Sterics reaction coordinate (SN1) en er g y en erg Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams. Predicting the. SN1 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular reaction, described by the expression rate = k reaction coordinate diagram for a two step process. SN1 reaction The S1 reaction is a ...
This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and ... nucleophile is very important in an SN2 reaction. The more reactive the nucleophile, the more likely the reaction will be SN2 rather than SN1.
A diagram of the reaction of the SN2 type substitution coordinate between methyltosylate and nucleophile iodide and chloride are presented in the graph below. Based on the relative potential energy, the CH3-Cl bond is stronger than the CH3-I bond, so the SN2 product (methylchloride) has a lower energy than methyl iodide.
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Sn2 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Why is R-I better for Sn1? the rate determine step involves C+ formation and the breaking of the R-X bond, the weaker the R-X (C-X) bond the easier it is to break. R-I is the most reactive because it is the weakest R-X bond.
Figure 9.5 shows a reaction coordinate diagram for the S N 1 mechanism. The rate of the reaction depends on the energy barrier to the formation of the carbocation intermediate. The energy barrier in the second step, the reaction of the nucleophile with the carbocation, is much smaller, so step 2 is very fast.
[1988 - 2 Marks] What is the weight of sodium bromate and molarity of solution necessary to prepare 85.5 mL of 0.672 N solution when the halfcell reaction is + 6H+ + 6e– → Br– + 3H2O (ii) What would be the weight as well as molarity if the half-cell reaction is : + 12H+ + 10e– → Br2 + 6H2O [1987 - 5 Marks] 57.
SN2 mechanism. SN2 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecularreaction, described by the expression rate = k [Nu][R-LG]. This implies that the rate determining step involves an interaction between two species, the nucleophile and the organic substrate. This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group.
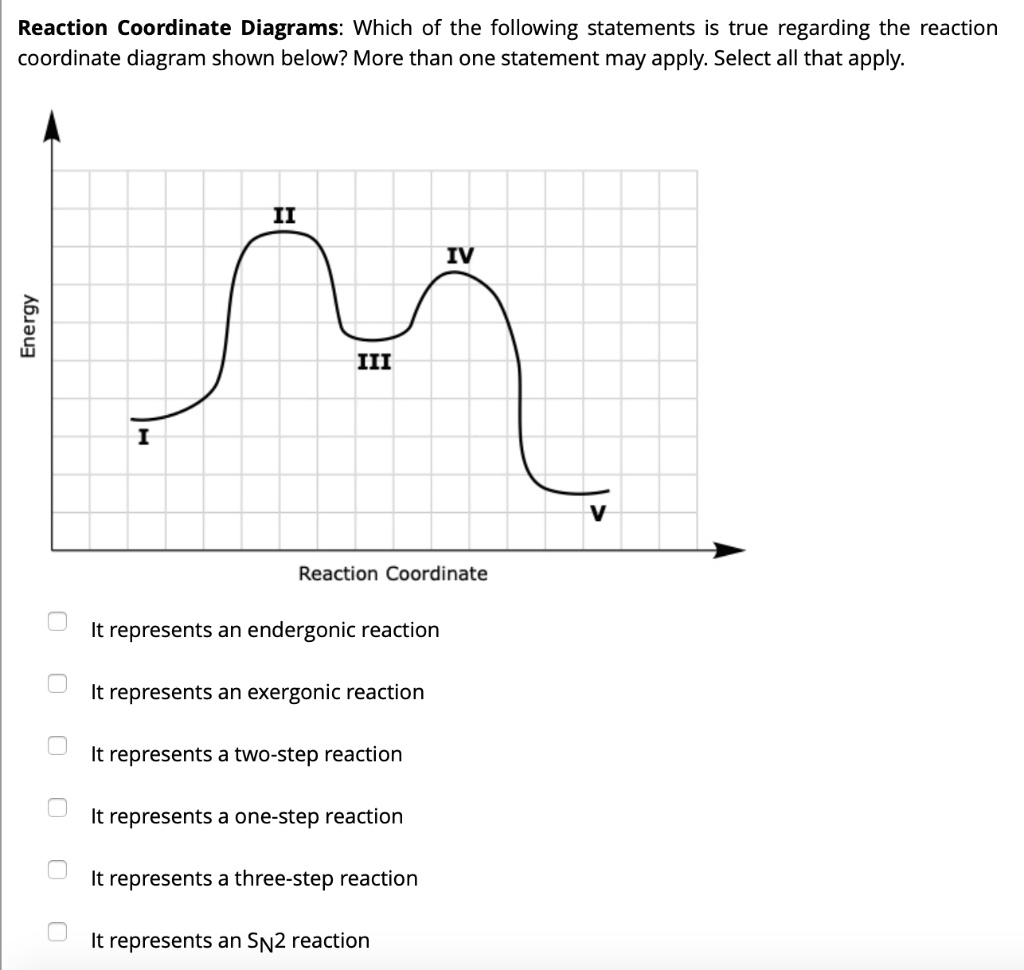
The three general rules for reaction coordinate diagrams are as follows: ... Does Wurtz-Fittig-reaction involves Sn1 or Sn2? 2. How to explain the selectivity between methanol and methanethiol in an SN1 reaction with an halogenated hydrocarbon? 0. 2-step reaction mechanism for the decomposition of NO2Br. 2.
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. a key skill how to calculate formal charge — master in this blog post i explain how to calculate formal charge for molecules however you might find my videos containing 10 solved examples of formal charge features of an organic acid and base alkene c=c organic mechanism describes the overall reaction using a series of simple steps stoichiometry calculate ...
Sn2 Energy Diagram. Fig Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses. It starts with the kinetics of SN2 reaction and covers the energy diagrams including questions on activation energy, enthalpy, the order of reaction and curved.

Sn1 Energy Diagram Transition States Activation Energy Intermediates Energy Activities Organic Chemistry Reactions
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1.

Physics Page This Diagram Illustrates The Reaction Coordinate Diagram For The Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution Sn2 Reaction Between Bromomethane And The Hydroxide Anion Transition State Theory Tst Explains The Reaction Rates Of
S N 2 mechanism. S N 2 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular reaction, described by the kinetic expression : rate = k [Nu][R-LG] . This pathway is a concerted mechanism (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group.
Aug 05, 2011 · Alkylation of enolates with alkyl halides is an SN2 reaction, and SN2 reactions will only occur at sp3-hybridized carbons. In the reaction you describe, only the 1-carbon is sp3-hybridized, and thus the enolate will perform substitution at C-1. The C-Br bond at C2 will be unaffected. Sorry for taking so long to get back to you.
reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The
Figure 2 identifies these species in a reaction coordinate diagram like the one in the right-hand panel of Figure 1. Here the nucleophile is hydroxide ion. Figure 2 The 2-Step. As the figure indicates, the activation energy for the first step of the reaction is much larger than that for the second step. Thus the first step is much slower.
The higher the temperature, the faster a non-biological reaction tends to occur. For #S_N1# and #S_N2# reactions, the higher the temperature, the more elimination products you get.The more elimination products you get, since the amount of reactant is limited, the less substitution products you get, as well. This is because the activation energy for a particular reaction with particular ...
Aug 08, 2012 · 3. The Mechanism For The SN2 Is Concerted. The Mechanism Of The SN1 Is Stepwise. The S N 2 reaction is concerted.That is, the S N 2 occurs in one step, and both the nucleophile and substrate are involved in the rate determining step. Therefore the rate is dependent on both the concentration of substrate and that of the nucleophile.; The S N 1 reaction proceeds stepwise.
The SN2 reaction mechanism stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular and is a fundamental mechanism in organic chemistry. In an SN2 mechanism, a nucle...
The reaction coordinate energy diagram below corresponds to which mechanism? a. SN1 b. SN2 ๕. El d. E2 ฯ กาก Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo the slowest Sn1 reaction? مسلم C D E ; Question: The reaction coordinate energy diagram below corresponds to which mechanism? a. SN1 b. SN2 ๕. El d.
Transition State Search And Characterization Of A Ziegler Natta Catalyst Tutorials 2021 1 Documentation

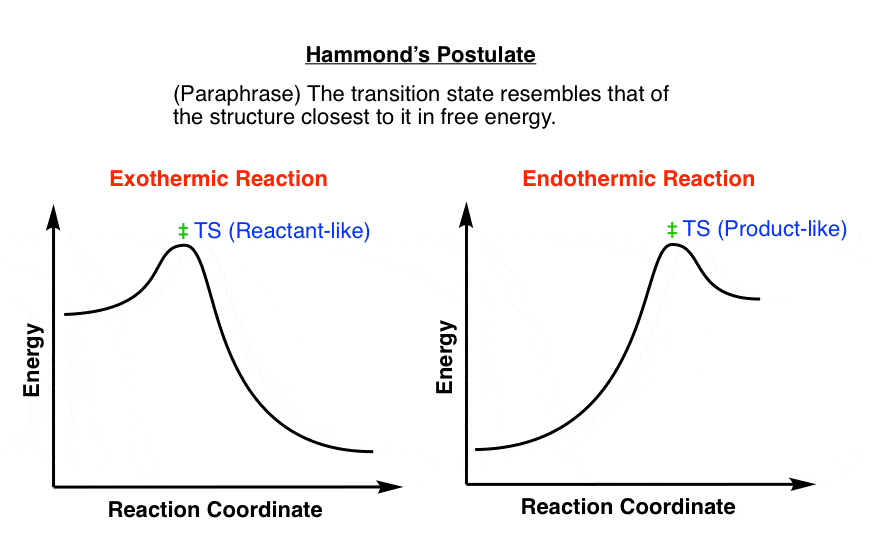
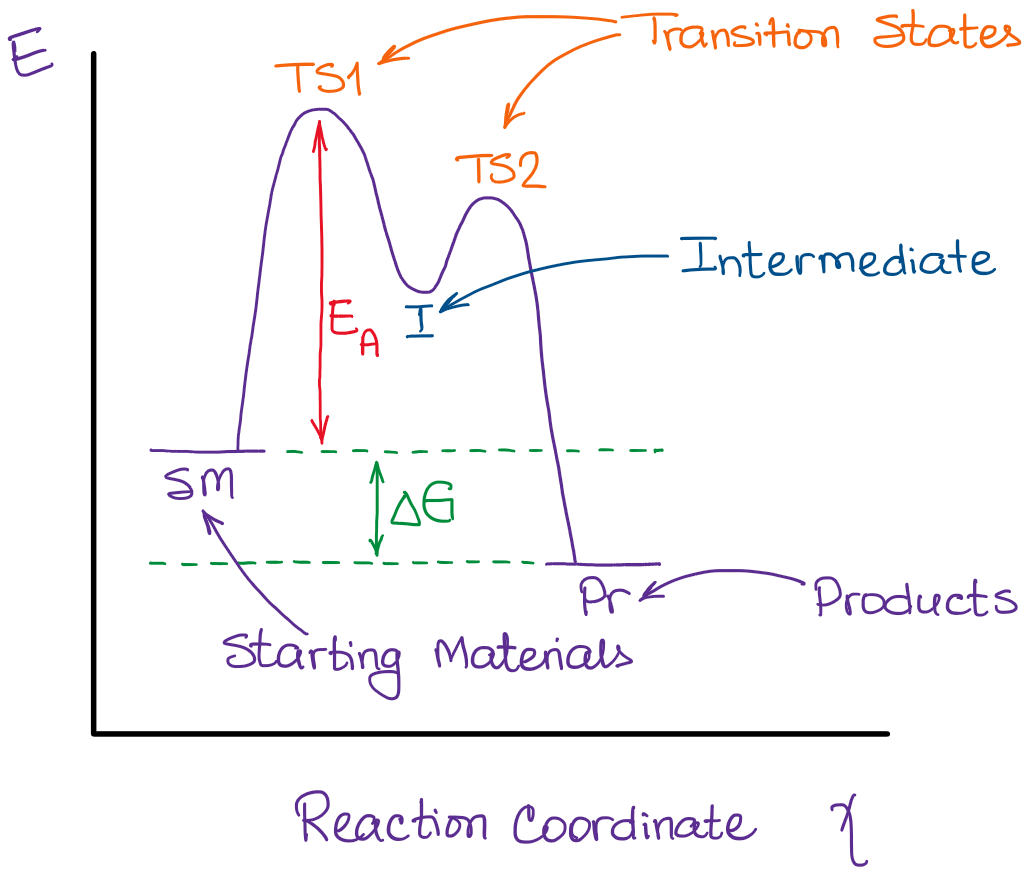

















0 Response to "41 sn2 reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment