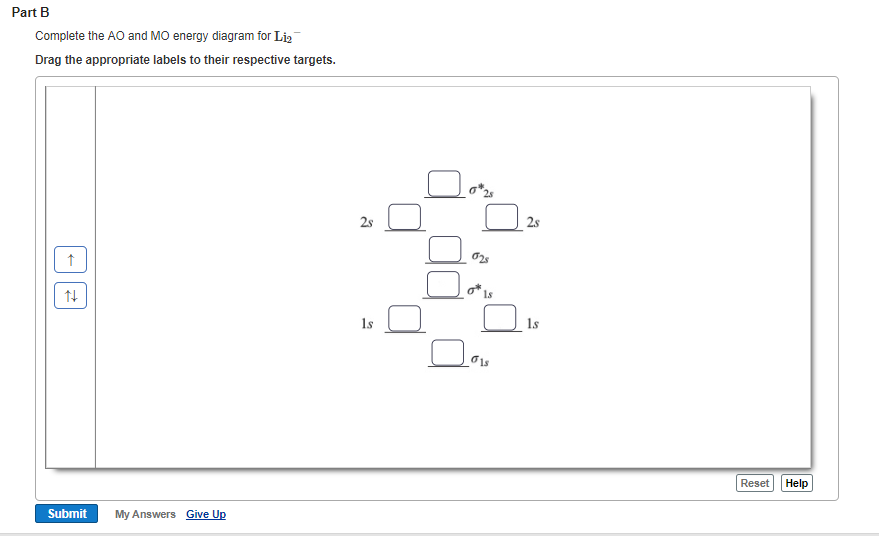
37 complete the atomic orbital (ao) and molecular orbital (mo) energy diagram for li2+
Question: 1)Complete the atomic orbital (AO) and molecular orbital (MO) energy diagram for Li2+ and Li2-. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. Unlike an atomic orbital, which is centered on a single atom, a …
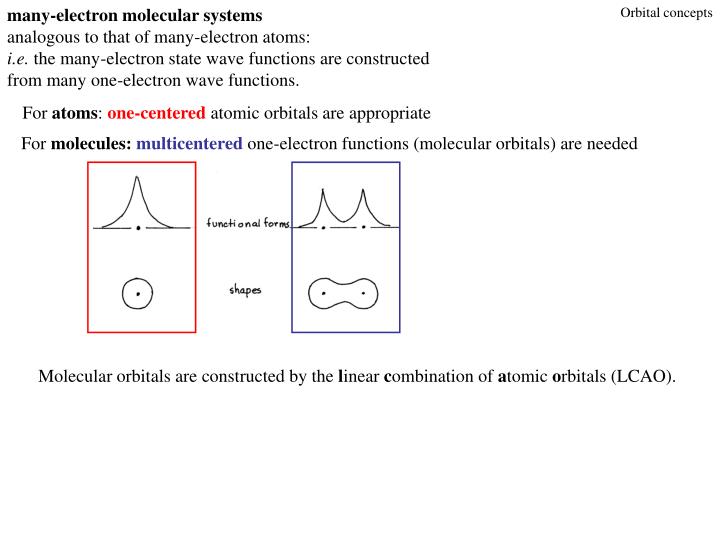
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. What is energy level diagram? The energy level diagram is used to represent the energy states available ...
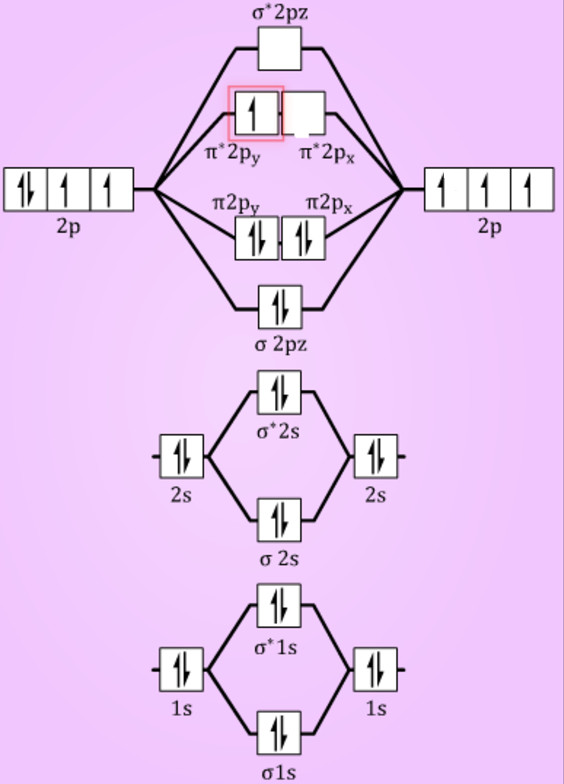
Complete the atomic orbital (ao) and molecular orbital (mo) energy diagram for li2+
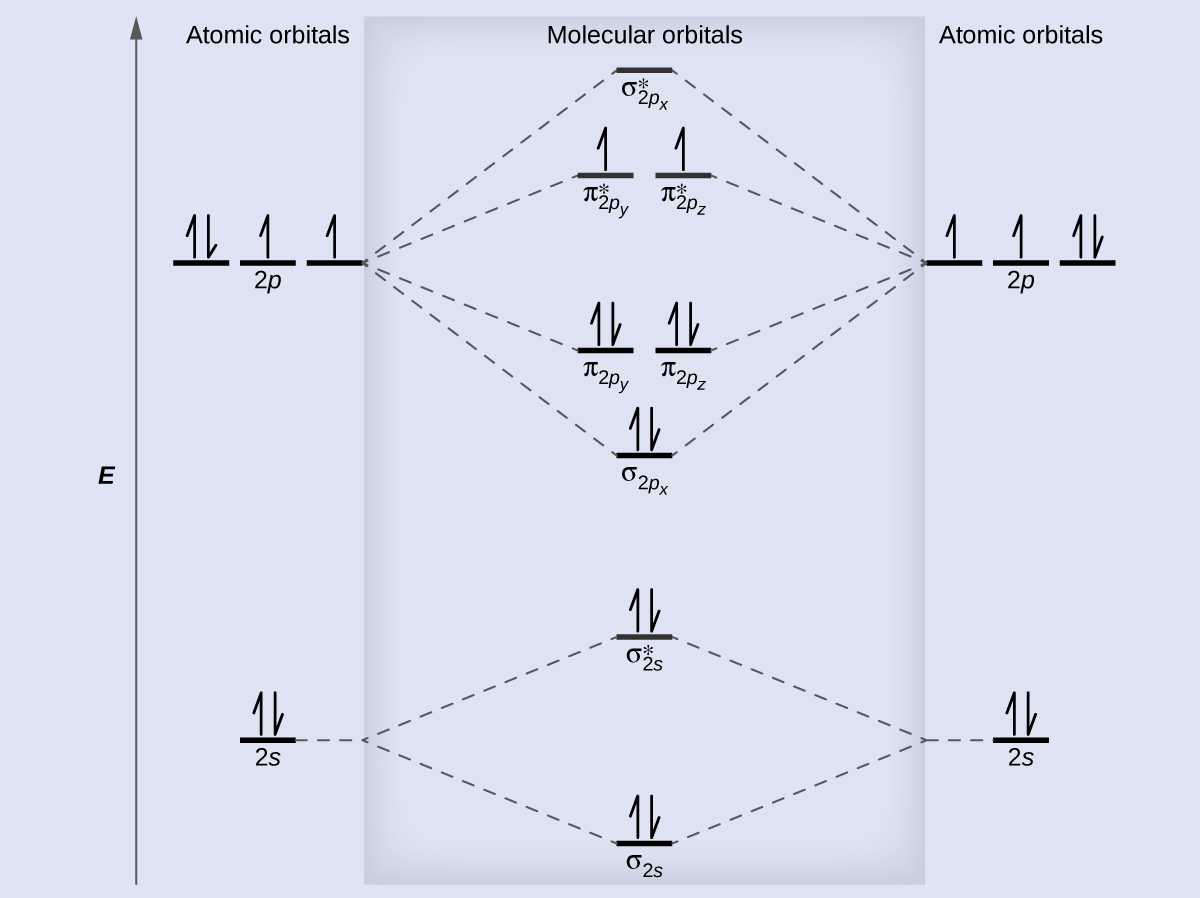
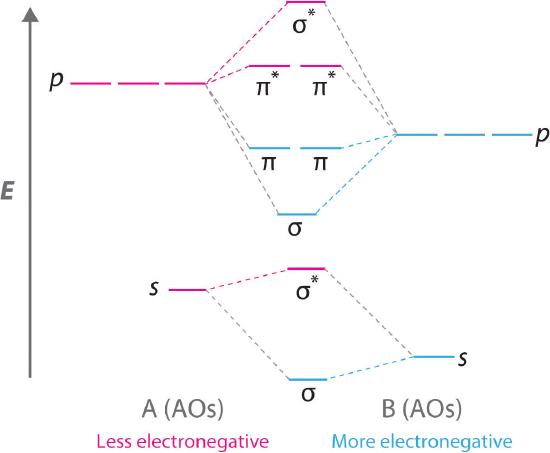
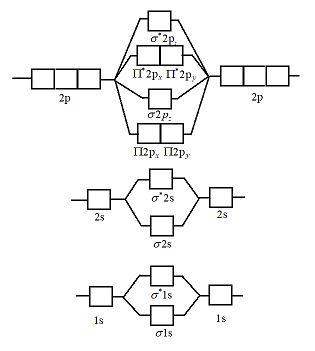
In `MO` energy diagram for heteronuclear diatomic molecule is similar However, the energies of the `AO` s of the atom having higher atomic number being l A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
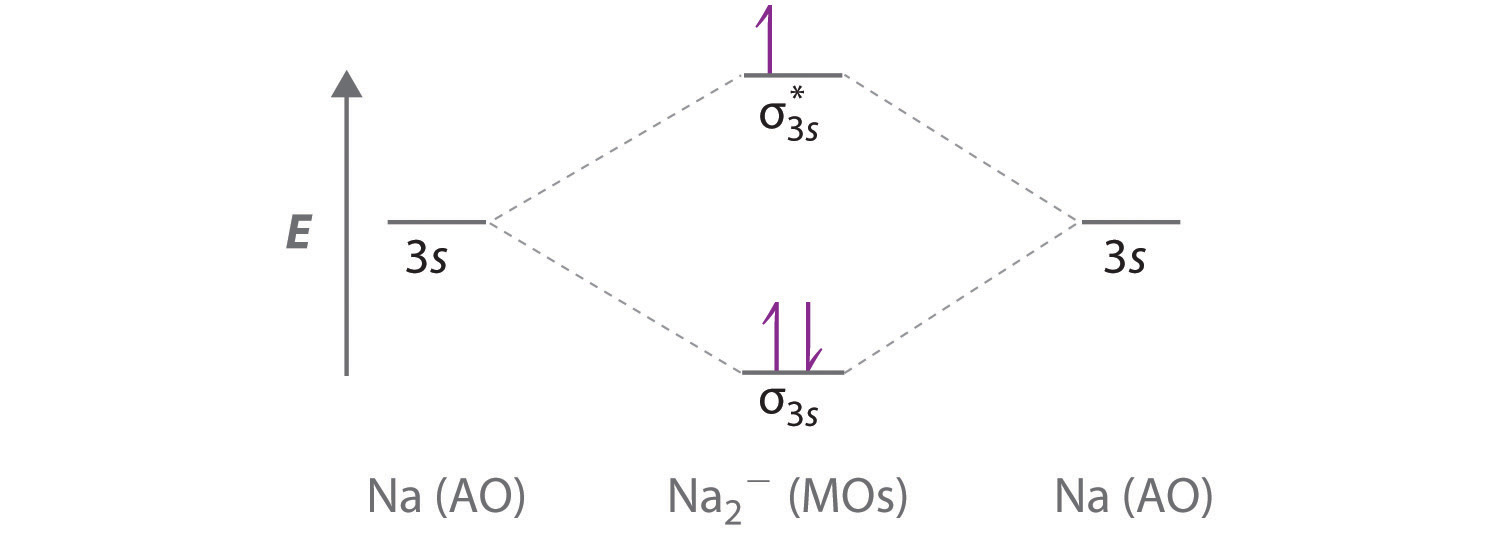
Complete the atomic orbital (ao) and molecular orbital (mo) energy diagram for li2+. Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron. Get the detailed answer: Sketch and label correctly a potential energy curve for a diatomic molecule. Free unlimited access for 30 days, limited time only! Get access In `MO` energy diagram for heteronuclear diatomic molecule is similar However, the energies of the `AO` s of the atom having higher atomic number being lower, A molecular orbital (MO) is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. Unlike an atomic orbital (AO), which is centered on a single atom, a molecular orbital extends over all the atoms in a molecule or ion. Hence the molecular orbital theory of bonding is a delocalized approach.
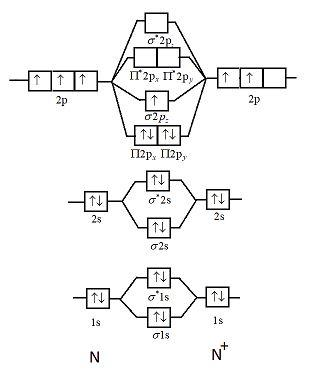
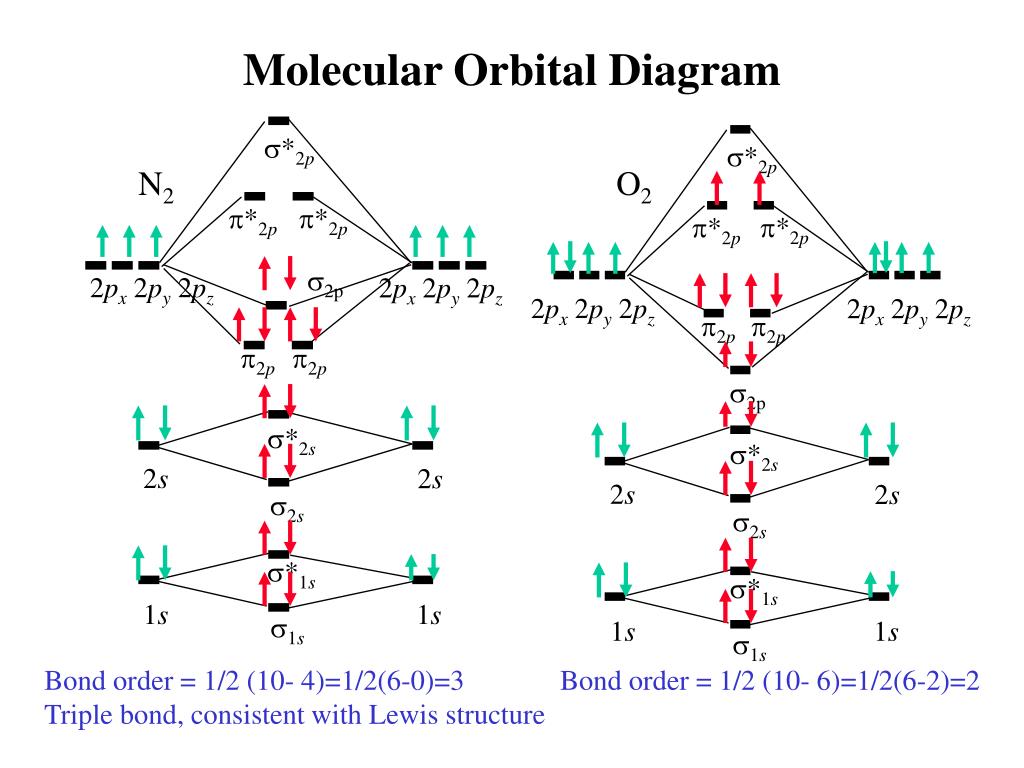
Each set of quantum numbers, ( n, l, m l ), describes a different wave function. The radial wave function is only dependent on n and l, while the angular wavefunction is only dependent on l and m l. So a particular orbital solution can be written as: Ψ n, l, m l ( r, θ, ϕ) = R n, l ( r) Y l, m l ( θ, ϕ) Where. n = 1, 2, 3, …. FREE Answer to 1)Complete the atomic orbital (AO) and molecular orbital (MO) energy diagram for Li2+ and Li2-1 answer · Top answer: Molecular orbital theory is also used to explain bonding in molecules using linear combination of atomic orbitals. According to molecular orbital theory, ... 1 answerProblem: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) energy diagram for Li2+. FREE Expert Solution. The total number of valence electrons present in Li2+ is:. When two orbitals are added, the result is stable bonding molecular orbital and when orbitals are subtracted, it is called unstable anti-molecular bonding (*) which has more energy than the latter one. Considering the energy level diagram, the configuration of N2 is σ1S2, σ *1S2, σ2S2, σ*2S2, π2Px2, π2Py2, σ2Pz1. Conclusion
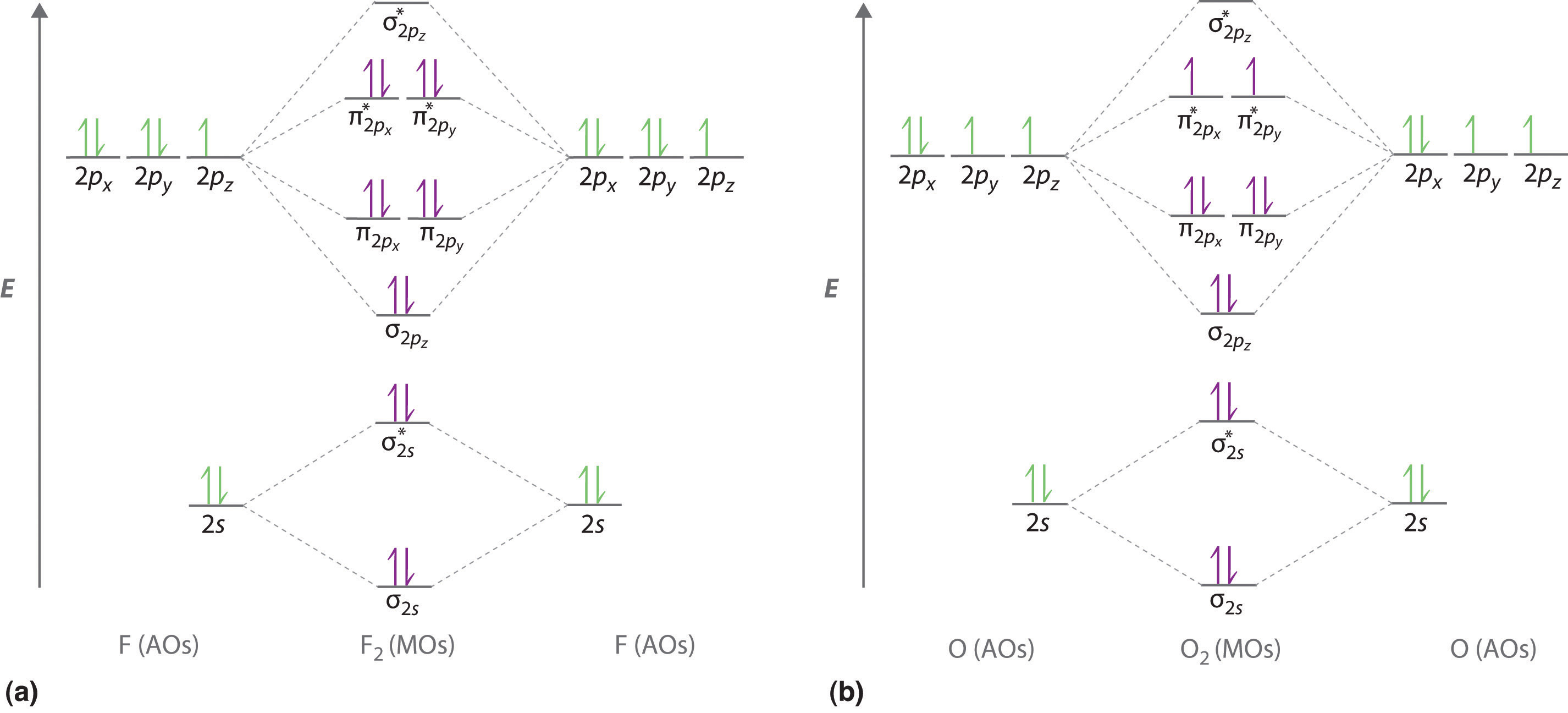
Dec 11, 2019 — Get the detailed answer: complete the atomic orbital (ao) and molecular orbital (mo) energy diagram for li2+.1 answer · Top answer: The Molecular Orbital Theory states that each atom tends to combine together to form molecular orbitals. In MOT, electrons in a molecule are not assigned ... As a result of the Z 2 dependence of energy in Equation 2.24, electrons in the 1s orbital of carbon, which has a nuclear charge of +6, lie roughly 36 times lower in energy than those in the hydrogen 1s orbital, and the 1s orbital of tin, with an atomic number of 50 is roughly 2500 times lower still. The most stable and tightly bound electrons ... In `MO` energy diagram for heteronuclear diatomic molecule is similar However, the energies of the `AO` s of the atom having higher atomic number being lowe As of December 2014, up to 46% of the energy in sunlight could be converted into electricity using solar cells. Example 8.4. 2: M olecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2.
Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. Within the diagram, orbitals are represented by horizontal lines. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of.
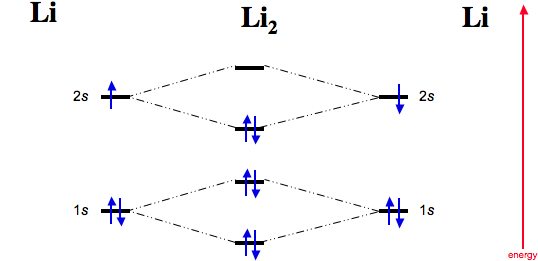
Li 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram.Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of.
34 Be2 + Molecular Orbital Diagram.A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbital s method in particular. C would this ion exist. The first ten molecular orbital s may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ(1s ) ∗(1s ...
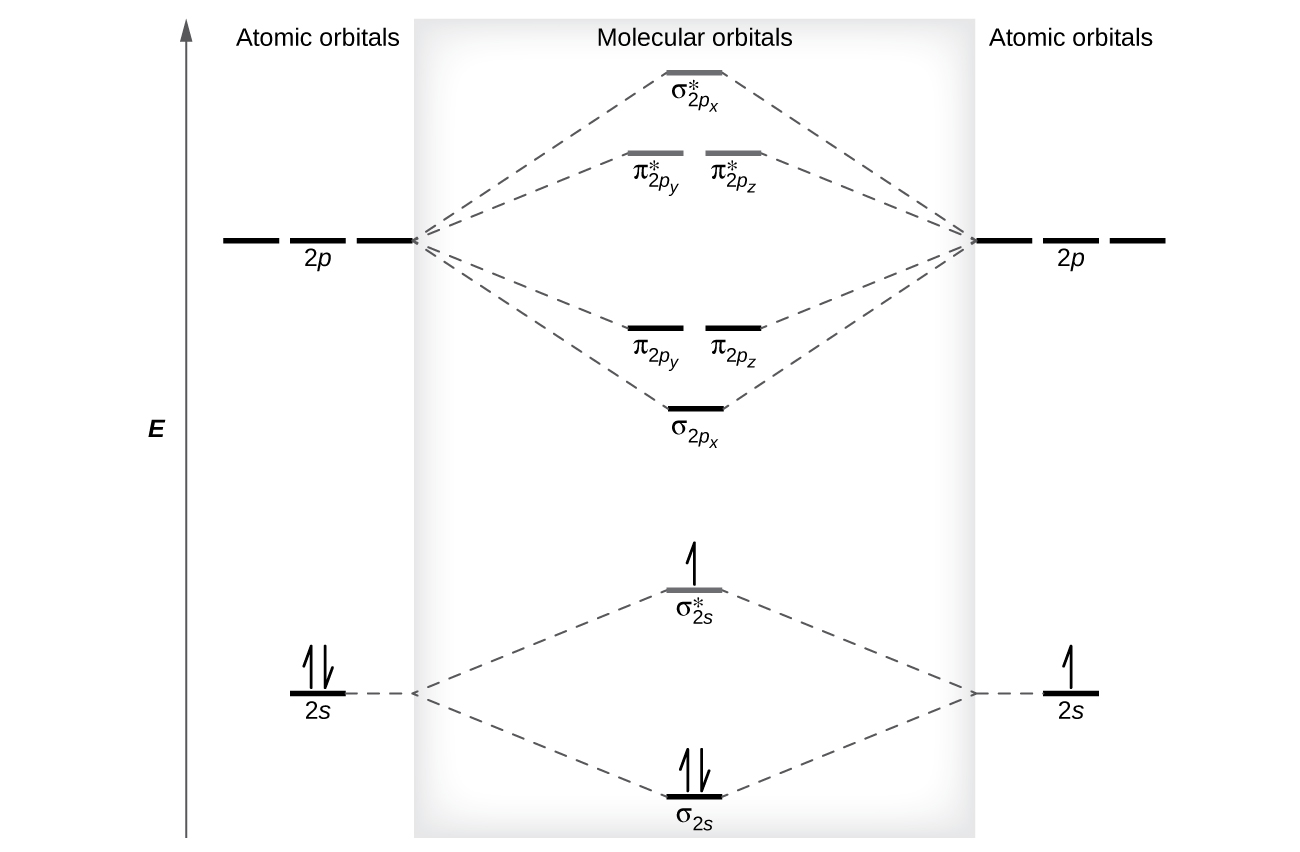
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams - chem-textbook. 6 hours ago Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams.The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram ( [link] ). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
Complete the atomic orbital ao and molecular orbital mo energy diagram for li2 . Removal of one e from li2 to give li2 results in an mo scheme of σσ0. The same method can be applied to other diatomic molecules but involving more than the 1 s atomic orbitals.
Figure 5.3.2 Mo lecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for H 2 The two available electrons (one from each H atom) in this diagram fill the bonding σ 1 s mo lecular orbital. Because the energy of the σ 1 s mo lecular orbital is lower than that of the two H 1 s atomic orbitals, the H 2 mo lecule is mo re stable (at a lower energy) than the two ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
In `MO` energy diagram for heteronuclear diatomic molecule is similar However, the energies of the `AO` s of the atom having higher atomic number being l

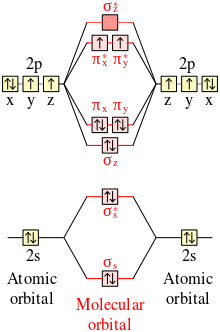


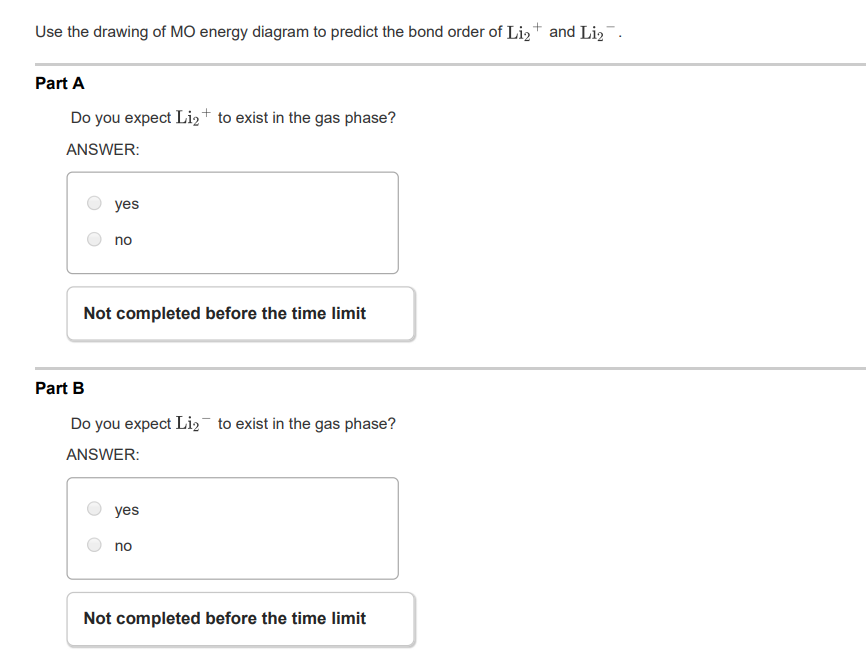



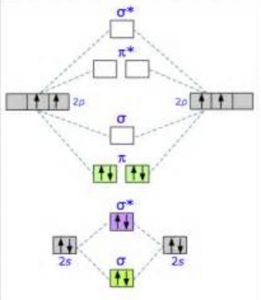







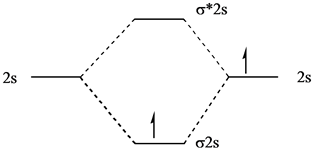





0 Response to "37 complete the atomic orbital (ao) and molecular orbital (mo) energy diagram for li2+"
Post a Comment