38 venn diagram logic examples
The union symbol ∪. Venn diagrams are comprised of a series of overlapping circles, each circle representing a category. To represent the union of two sets, we use the ∪ symbol — not to be confused with the letter 'u.'. In the below example, we have circle A in green and circle B in purple. This diagram represents the union of A and B ... Venn diagrams are visual representations of mathematical sets—or collections of objects—that are studied using a branch of logic called set theory. Set theory is one of the foundational systems for mathematics, and it helped to develop our modern understanding of infinity and real numbers.
A class can also be infinite, containing an infinite number of objects. The class of even number is an example. It has infinitely many members, including 2, 4, 6, 8, and so on. 2. Classes are represented by circles As you can see in the diagram above, the class of black hats, C, is represented by a circle.
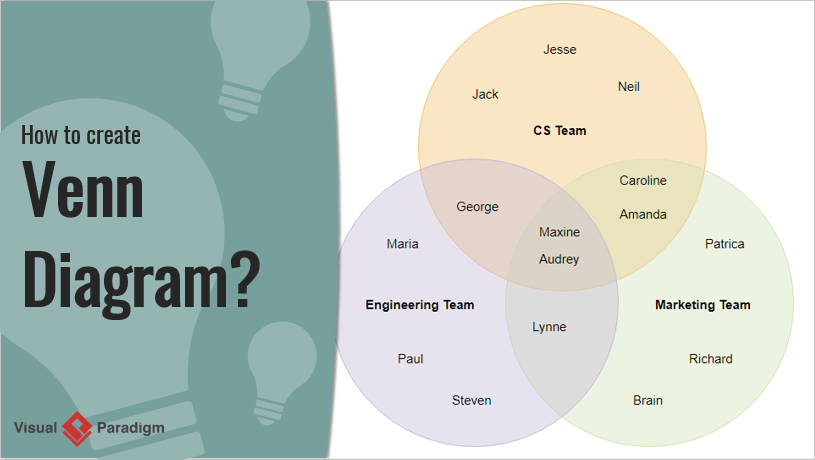
Venn diagram logic examples
Note: (1) The contraposition of the top and the bottom examples yields a Venn diagram that is exactly the same. (2) The conversion of the middle two examples yields a Venn diagram that is NOT the same. (A) and (O) preserve truth value. (E) and (I) do not: So, this time, the top and bottom Example: (above) Show a Venn diagram for A'B (A-not AND B). Solution: Starting above top left we have red horizontal shaded A' (A-not), then, top right, B. Next, lower left, we form the AND function A'B by overlapping the two previous regions. Most people would use this as the answer to the example posed. For example, in science and mathematics, our logic will apply when talking about circles, points, frictionless planes, and freely falling bodies even though these entities do not physically exist. c. This diagram illustrates the contemporary topic called the problem of existential import. When can we reasonably conclude something exists?
Venn diagram logic examples. Venn Diagram: A Venn’s diagram may be a commonly used diagram vogue that shows the relation between sets.Venn Diagrams area unit introduced by English logician John Venn \(\left( {1834 – 1883} \right).\)The Venn Diagrams area unit accustomed teach pure elementary mathematics, and as an instance, easy set relationship in chance, logic, statistics, linguistics, and engineering. Take a look upon various possible cases of venn diagram and know when it is applicable. Among three columns, first one shows the type of venn diagram, second one is for description and third one sites an example to give a clear picture of the description. Examples of Categorical Logic and Venn Diagrams . In each of these examples, two premises and a conclusion will be presented. The goal is to determine if the conclusion is valid assuming that the premises are true. First, all and only the premises will be represented in a single Venn diagram. Then we will see if the content of the conclusion is ... A venn diagram is the easiest way to express the relationship between sets. Based on the variety of questions that are asked in various competitive exams, we have classified these logical Venn diagrams into following categories, which are given below. Types of Venn Diagram As now we know what consists of the questions related to the Venn ...
In math, a Venn diagram is used to visualize the logical relationship between sets and their elements and helps us solve examples based on these sets. How do You Read a Venn Diagram? These are steps to be followed while reading a Venn diagram: First, observe all the circles that are present in the entire diagram. Typical Examples of syllogism with Venn diagrams Example 1. The form written out is; No M is P. All S is M. No S is P. Note, in the diagram below how the area is common between S and P has been completely shaded out indicating that No S is P. The conclusion has been reached from diagramming only the two premises. All syllogisms of the form are ... An example of a logic circuit. Figure 2.12. Addition of binary numbers. Figure 2.13. Proof of DeMorgan's theorem in 15a. Figure 2.14. The Venn diagram representation. Please see "portrait orientation" PowerPoint file for Chapter 2. Figure 2.15. Verification of the distributive property. A Venn diagram is also called a set diagram or a logic diagram showing different set operations such as the intersection of sets, union of sets and difference of sets. It is also used to depict subsets of a set. For example, a set of natural numbers is a subset of whole numbers, which is a subset of integers.
Venn diagrams are illustrations used in the branch of mathematics known as set theory. They show the mathematical or logical relationship between different groups of things (sets). A Venn diagram shows all the possible logical relations between the sets. Venn Diagram In Logic Examples Answer - A. Explanation. Q lies only in the triangle area. Choose which of the following diagram represents relationship among the given elements in a much logical way. Q 8 − Operating systems, XP, Vista. Options : A -. B -. C -. Examples of Categorical Logic and Venn Diagrams In each of these examples, two premises and a conclusion will be presented. The goal is to determine if the conclusion is valid assuming that the premises are true. First, all and only the premises will be represented in a single Venn diagram. Venn diagrams are illustrations used in the branch of mathematics known as set theory. They show the mathematical or logical relationship between different groups of things (sets). A Venn diagram shows all the possible logical relations between the sets. Venn Diagram Logic
Venn Diagrams of Arguments Venn diagrams can be used to test syllogistic forms for validity or invalidity. An argument form is valid if and only if it has no substitution instances with true premises and a false conclusion. Otherwise it is invalid. To construct a Venn diagram for a categorical syllogistic form, we need three
Below are examples of uses of Venn diagrams. Example 1: Subjects Taken by Students A study is being done at a school on students who take the subjects mathematics and economics. There are 12 students who attend both classes and 2 students who do not take either of the subjects.
An argument is INVALID if we are able to draw a Venn diagram that agrees with every PREMISE but denies the CONCLUSION. Venn diagrams that are used to analyze arguments are usually called Euler diagrams, in honor of the mathematician Leonhard Euler. A Venn diagram (Euler diagram) that agrees with every premise but denies the conclusion
The best way to explain how the Venn diagram works and what its formulas show is to give 2 or 3 circles Venn diagram examples and problems with solutions. Problem-solving using Venn diagram is a widely used approach in many areas such as statistics, data science, business, set theory, math, logic and etc.
introducing the Venn diagram •Used in set theory, probability, logic, statistics, ... •In categorical logic “some” means “at least one”, which is considered its minimal meaning. •“Some” is the standard form particular quantifier. •So, for example, the I statement, “Some buses used by the city are roadworthy machines”,
Logical Venn Diagrams. A Venn diagram is a diagram that shows the relationship between and among a finite collection of sets. If we have two or more sets, we can use a Venn diagram to show the logical relationship among these sets as well as the cardinality of those sets. In particular, Venn Diagrams are used to demonstrate De Morgan's Laws.
Figure 3: Triple Venn Diagram. Note that the VennDiagram package provides further functions for more complex venn diagrams with multiple sets, i.e. draw.quad.venn, draw.quintuple.venn, or the more general function venn.diagram, which is taking a list and creates a TIFF-file in publication-quality.. However, for simplicity we'll stick to the triple venn diagram in the remaining examples of ...
Logic: Venn diagrams are used to determine the validity of particular arguments and conclusions. In deductive reasoning, if the premises are true and the argument form is correct, then the conclusion must be true. For example, if all dogs are animals, and our pet Mojo is a dog, then Mojo has to be an animal.
Logical Venn Diagrams Questions and Answers with Explanation covered for all competitive exams, like SSC, CAT, bank, Interviews, Entrance tests etc. Free Q&A Aptitude and Reasoning
Venn Diagram Examples - Venn Diagram - The Definition and the Uses of Venn Diagram Venn Diagram Examples - You've probably been exposed to or encountered the Venn diagram earlier. Anyone who's attended Mathematics particularly Algebra and Probability, must be already familiar with this diagram. It is a visual tool that shows the relationship between various items.
Venn diagrams are used heavily in the logic of class branch of reasoning. Example Sets A (creatures with two legs) and B (creatures that fly) This example involves two sets, A and B, represented here as coloured circles. The orange circle, set A, represents all types of living creatures that are two-legged.
2.5.2 Rules for Venn Diagrams. We can also view drawing Venn diagrams as a matter of shading some areas and placing X s within the three circles. In the above example, the Venn diagram for the argument form AOO-2 is completed by shading Area 6 and Area 7, and placing an X in Area 5. Superimposing the blue and the green pairs over the three circles is an easy way to see which areas are shaded ...
For example, in science and mathematics, our logic will apply when talking about circles, points, frictionless planes, and freely falling bodies even though these entities do not physically exist. c. This diagram illustrates the contemporary topic called the problem of existential import. When can we reasonably conclude something exists?
Example: (above) Show a Venn diagram for A'B (A-not AND B). Solution: Starting above top left we have red horizontal shaded A' (A-not), then, top right, B. Next, lower left, we form the AND function A'B by overlapping the two previous regions. Most people would use this as the answer to the example posed.
Note: (1) The contraposition of the top and the bottom examples yields a Venn diagram that is exactly the same. (2) The conversion of the middle two examples yields a Venn diagram that is NOT the same. (A) and (O) preserve truth value. (E) and (I) do not: So, this time, the top and bottom


0 Response to "38 venn diagram logic examples"
Post a Comment