40 h2 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments Second, the atomic orbital energies must be similar. When the energies differ greatly, the change in the The diagram shows the order of energy levels for the molecular orbitals, assuming significant... Basically, molecular geometry only takes into account the atoms of the molecules while determining the shape. The repulsion changes the bond pairs from a straight to bent shape. All these explain the molecular geometry of H2S. H2S Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
H2 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2 : Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6. Hello guys ! I have my finals in less than a month and I'm definitely stuck on this part of the program; I would like someone trying to explain me how you actually make a molecular orbital diagram through a relatively simple example like H2 or less simple like O2 in the form of an infographic, with a lot of arrows in it or something in this kind :) This would really help me, thanks in advance for your time ! Have a wonderful day ! The general procedure for constructing a molecular orbital diagram for a reasonably simple molecule can be summarized as follows Because the H2 molecule has two electrons, they can both go in the bonding orbital, making the system lower in energy (hence more stable) than two free hydrogen atoms.
H2 molecular orbital diagram. Figure 8.35 The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. We predict valence molecular orbital electron configurations just as we predict electron configurations of atoms. Valence electrons are assigned to... The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital. Hi guys, I noticed that recently several users have posed queries about H3 Chem. I'd be happy to answer any questions regarding the subject! You can also ask about other H3s, I'll answer based on my friends' and my own knowledge as well. Other users please feel free to contribute! Also below is a comment that I made previously regarding whether one should take H3 Chem. You can take a look if you want. I'm going to list out 4 reasons why H3 might be helpful for you (at least, imho). If they don... In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the same result. This MO diagram depicts the molecule H2, with the contributing AOs on the outside sandwiching the MO.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory. Energy Level Diagram. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion. Linear Combination Of Atomic Orbitals. Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of H2CO. eg= trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar. Good morning, I'm looking for a way to compute molecular orbital diagrams using fragments or different molecules. I mean something like the diagram linked [here](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:H2O-MO-Diagram.svg), where, instead of considering the H2 fragment and the oxygen atom I could put two fragments chosen by me or two molecules. I searched but, at the moment, I didn't find anything useful. I can use Gaussian or Orca for the calculations so if it was possible to obtain such dia... Each molecular orbital can only have 2 electrons, each with an opposite spin. Once you have the molecular orbitals and their energy ordering the ground state configuration is found by applying the Pauli principle What is the molecular orbital diagram for for the diatomic hydrogen molecule, H2?
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+. Before we can draw a correlation diagram for b2 we must first find the in phase and out of phase overlap combinations for borons atomic orb... In a bonding molecular orbital, the electron density is high between the two atoms, where it stabilizes the arrangement by exerting a strong attraction for both nuclei. The energy level diagram for He2 is similar to that for H2 except that it has two more electrons. Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation diagram) An orbital correlation attempts to show how the atomic orbitals belonging to the individual atoms in a molecule interact to form the molecular...
Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Show transcribed image text construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify...
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms.
Because of their simplicity they have been extensively studied. Bonding order is 1 and it is diamagnetic. Mo Theory...
Molecular orbital mo theory of the h2 molecule. Mo diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me...
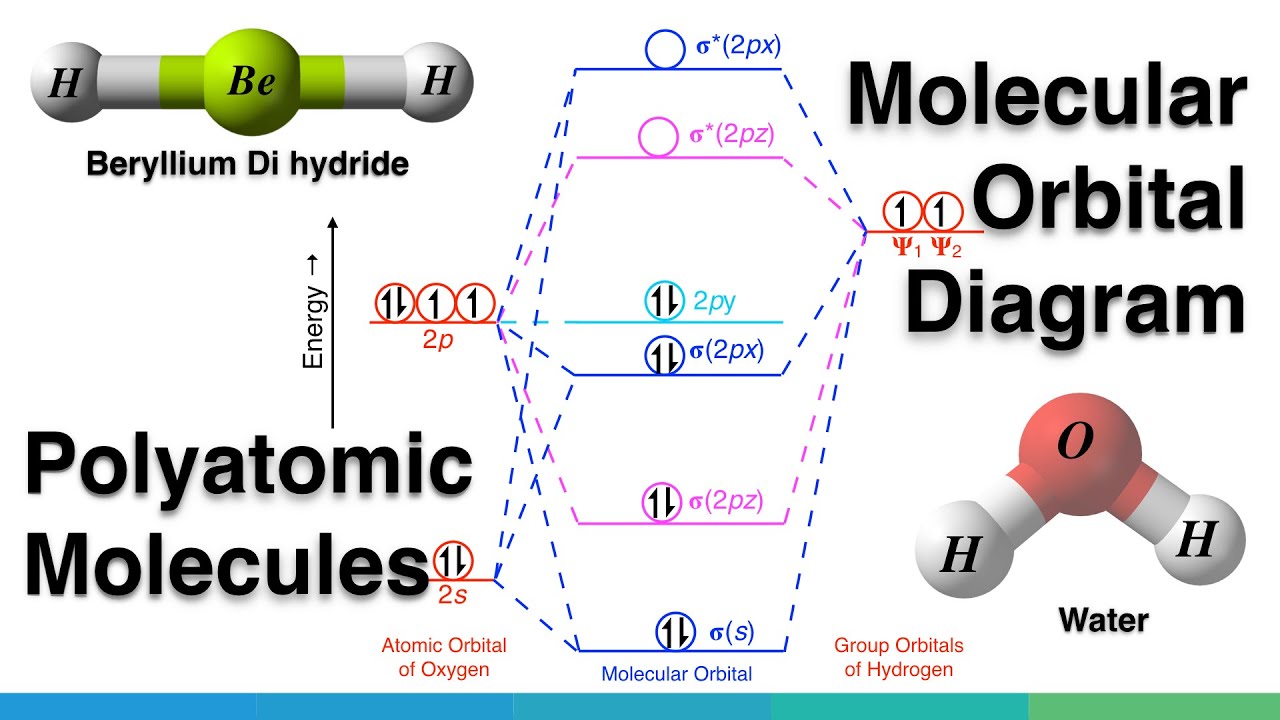
Molecular Orbital diagram of water (H2O) The molecular orbital diagram is a pictorial representation of determining chemical bonding between the molecules of a Molecular orbital diagrams say about the mixing of orbitals in a compound. Using a MO diagram, the bond order of a compound can be...
• Bonding - Review VSEPR and Hybridisation - Linear combination of molecular orbitals (LCAO), bonding / antibonding - Labelling of molecular orbitals (MOs) (σ, π and g, u) - Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams - mixing of different AO's - More complex molecules (CO, H2O ….)
Hello! Just finished a lecture in my ochem class and was going through the notes and had some questions if yall don't mind. I am already watching some youtube videos on molecular diagram and orbitals because I have no clue whats going on there but if you guys could please help out that would be great! * **First starting off with conjugation and energy, here is a pic: https://imgur.com/lmg6PDn** Does higher energy = less stable? So the first one monoene has a higher energy than the two dienes c...
The molecular orbital energy level diagram for dioxygen molecule is shown below Ans: The molecular orbital theory characterizes the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It is used to calculate bond order, bond length, bond strength, paramagnetic and...
• Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and...
Molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms in the molecule. Molecular orbital mo theory of the h2 molecu...
Hello! Just finished a lecture in my ochem class and was going through the notes and had some questions if yall don't mind. I am already watching some youtube videos on molecular diagram and orbitals because I have no clue whats going on there but if you guys could please help out that would be great! * **First starting off with conjugation and energy, here is a pic: https://imgur.com/lmg6PDn** Does higher energy = less stable? So the first one monoene has a higher energy than the two dienes c...
Hello! Just finished a lecture in my ochem class and was going through the notes and had some questions if yall don't mind. I am already watching some youtube videos on molecular diagram and orbitals because I have no clue whats going on there but if you guys could please help out that would be great! * **First starting off with conjugation and energy, here is a pic: https://imgur.com/lmg6PDn** Does higher energy = less stable? So the first one monoene has a higher energy than the two dienes c...
1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. Assume the valence 5s-orbitals of Xe are sufficiently lower in energy than the valence Does your MO diagram agree with this expectation? Determine the primary MOs that determine the bond order.
Figure 13: A molecular orbital energy-level diagram showing the relative energies of the atomic orbitals of atoms A and B (1sA and 1sB) and the bonding (1σ) and antibonding (2σ) molecular orbitals they form.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
The general procedure for constructing a molecular orbital diagram for a reasonably simple molecule can be summarized as follows Because the H2 molecule has two electrons, they can both go in the bonding orbital, making the system lower in energy (hence more stable) than two free hydrogen atoms.
Hello guys ! I have my finals in less than a month and I'm definitely stuck on this part of the program; I would like someone trying to explain me how you actually make a molecular orbital diagram through a relatively simple example like H2 or less simple like O2 in the form of an infographic, with a lot of arrows in it or something in this kind :) This would really help me, thanks in advance for your time ! Have a wonderful day !
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2 : Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6.

0 Response to "40 h2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment