41 molecular orbital diagram cn-
Dr. Shields shows you how to draw the MO correlation diagram for cyanide (CN-), calculate the MO bond order, and write the MO electron configuration with an ...
Molecular orbital Diagram Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory heteronuclear ...
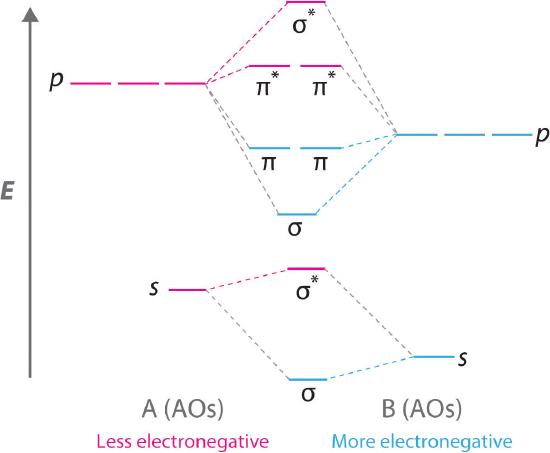
Molecular Orbital Mixing. More detail was added to this answer in response to input and questions from students in the class of 2008. If you have suggestions or contributions please e-mail me. First of all while the stage 1 (pre mixing diagram) of diatomics is very easy to produce, the mixing in diatomics is very difficult to evaluate because ...
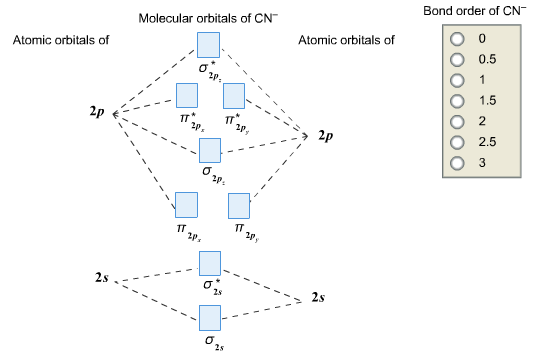
Molecular orbital diagram cn-
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN-
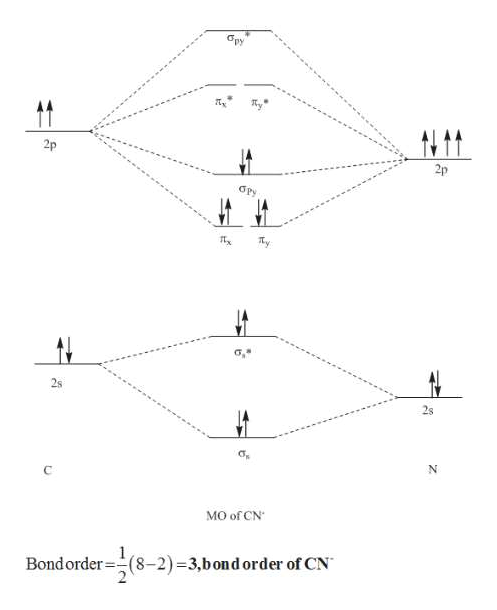
Dec 9, 2016 · 6 answers[math]\text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2}[/math] Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There ...What is the bond order of CN+?8 answersAug 6, 2017What is the molecular orbital energy diagram of CO?4 answersJan 7, 2017More results from www.quora.com
Molecular orbital diagram cn-.
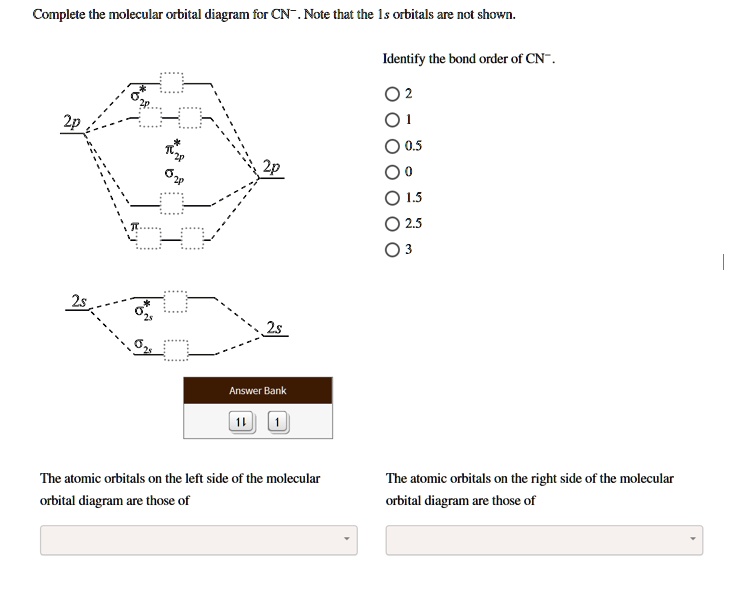
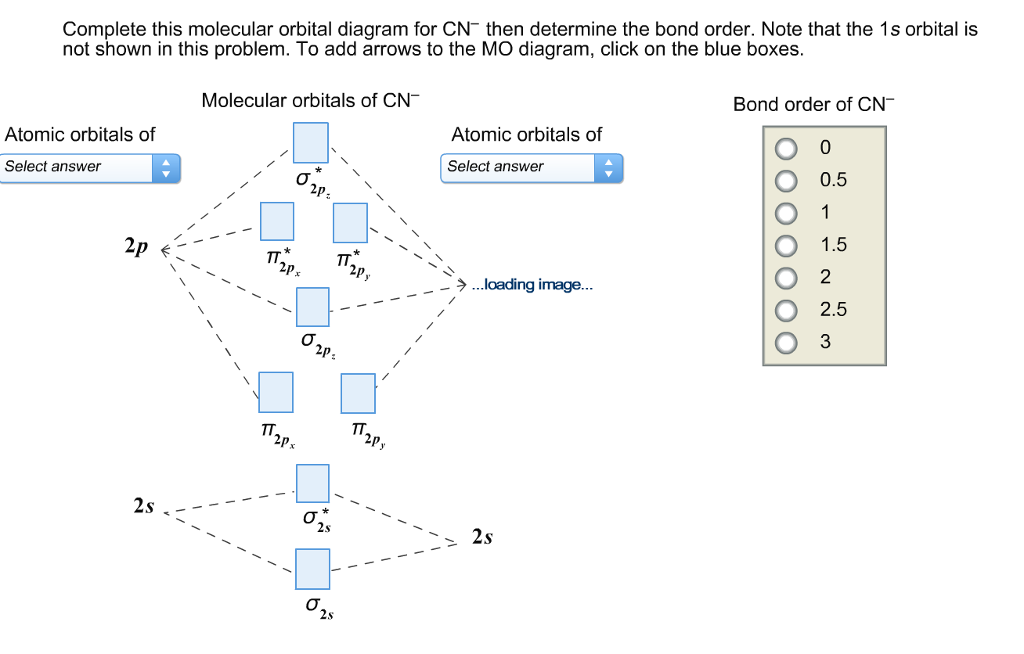
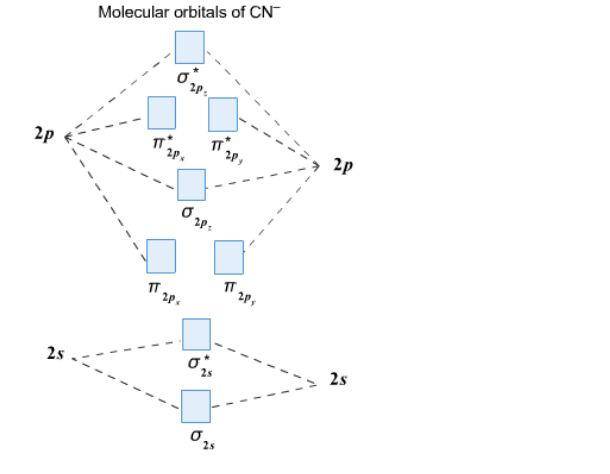
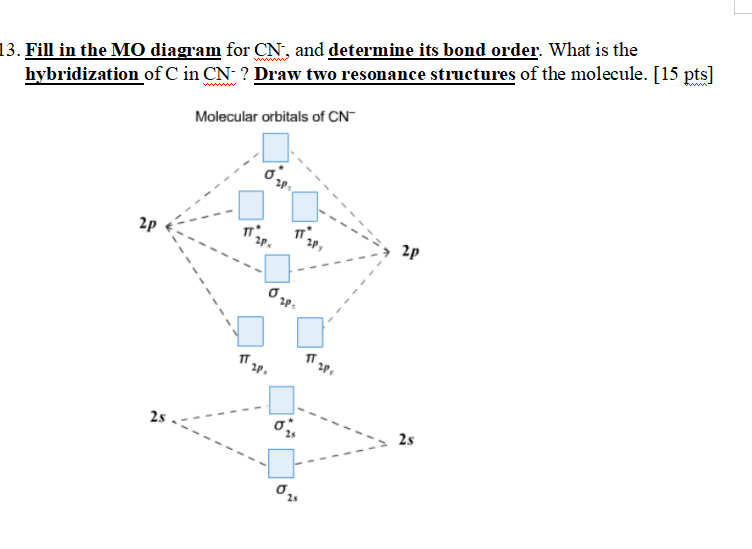
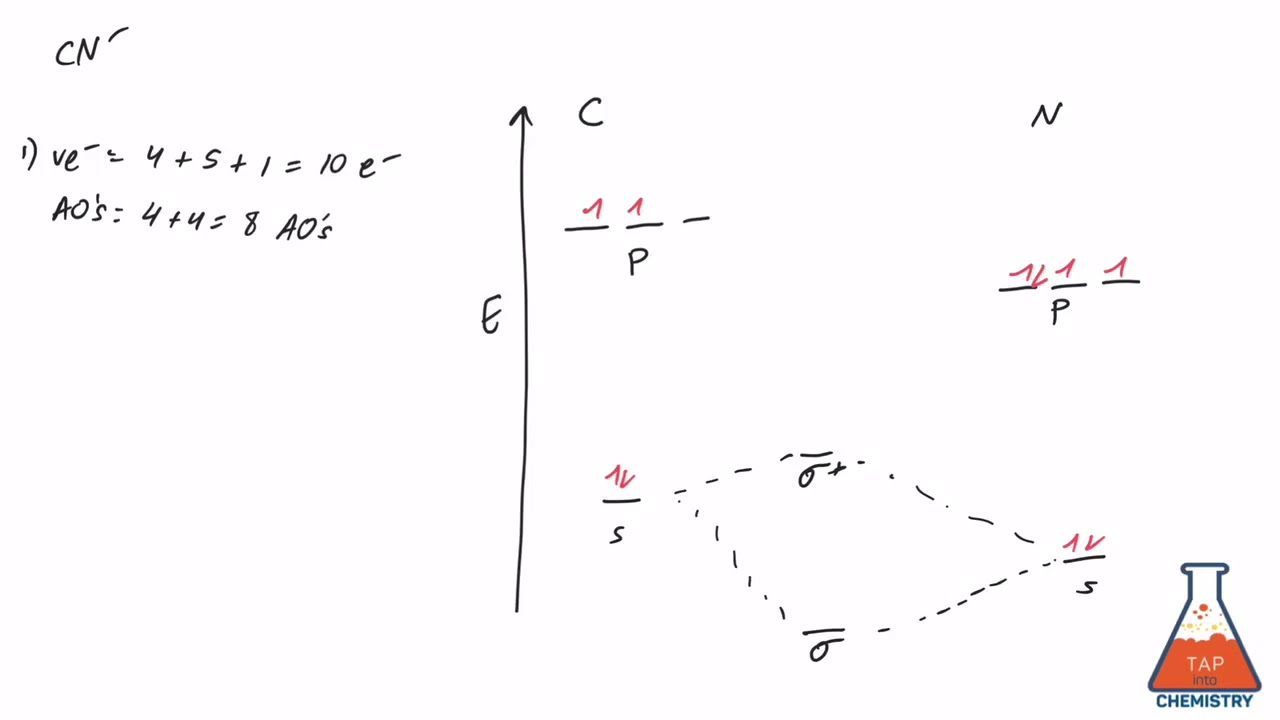
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
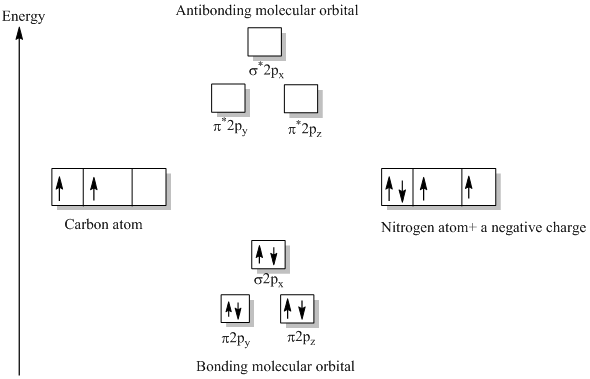
When two atomic orbitals combine, two molecular orbitals are formed. One is known as bonding molecular orbital and the other is called an anti-bonding molecular ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Jan 3, 2021 — Just as with atomic orbitals, we create an energy-level diagram by listing the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy.Bond Order in Molecular... · Molecular Orbitals Formed... · Molecular Orbitals for...
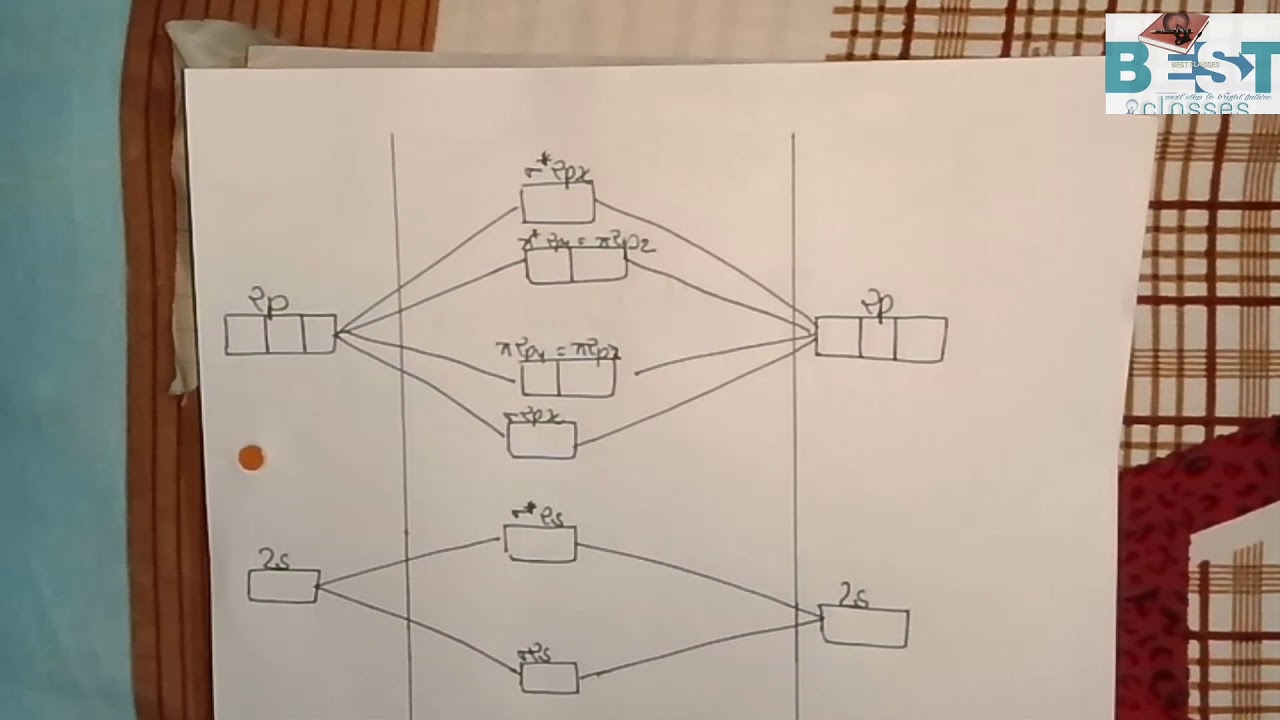
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
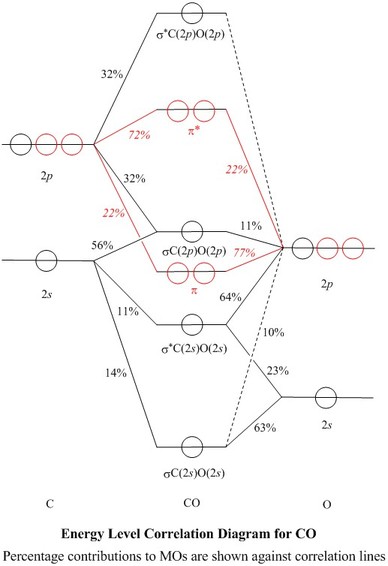
Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
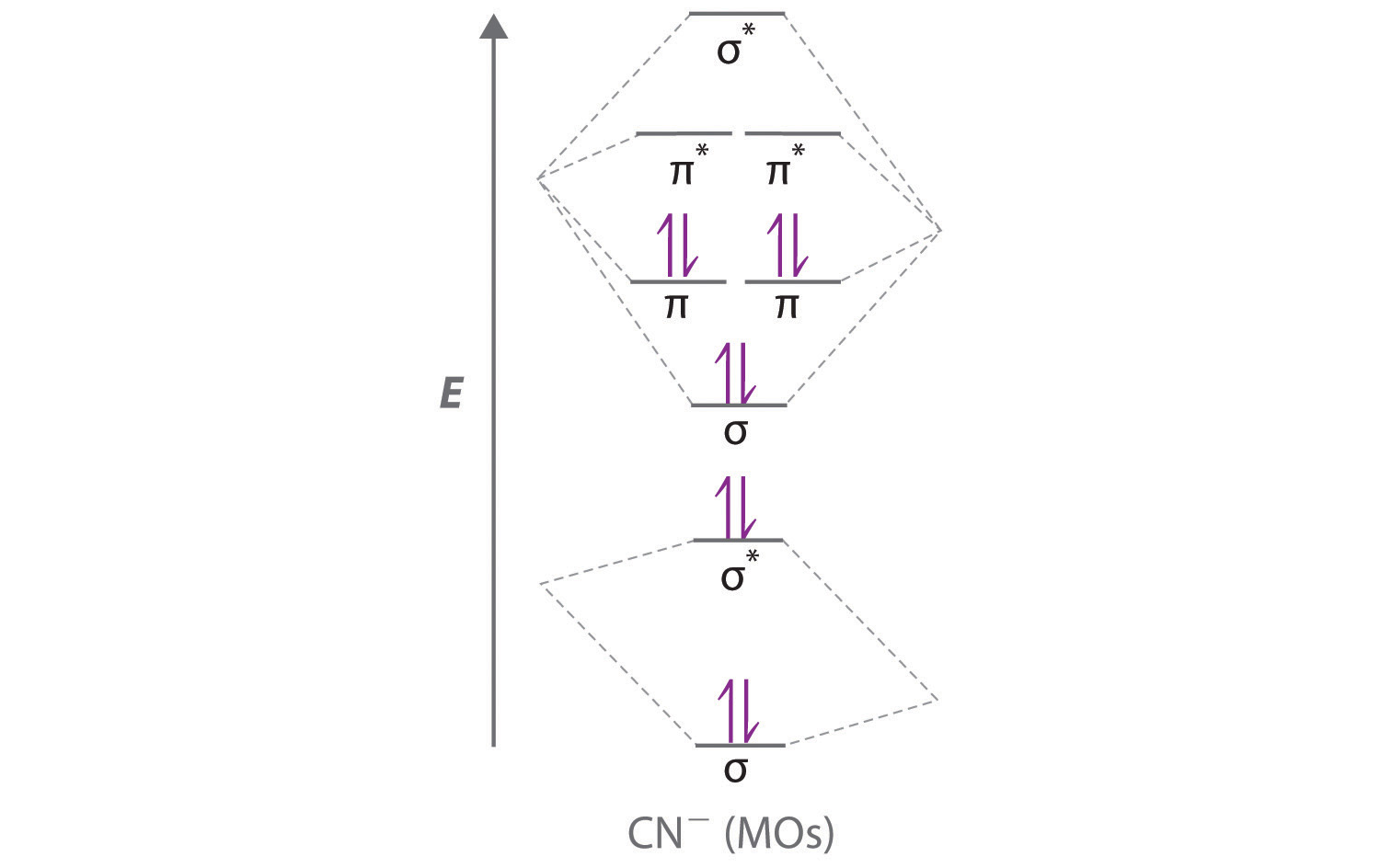
Answer (1 of 6): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
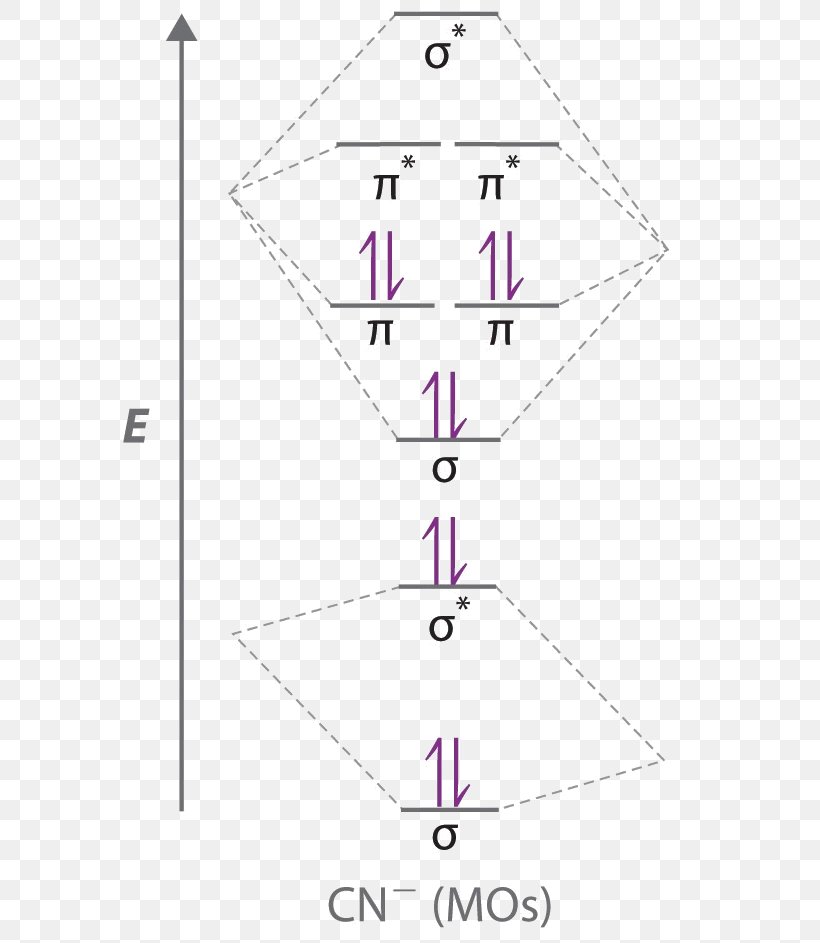
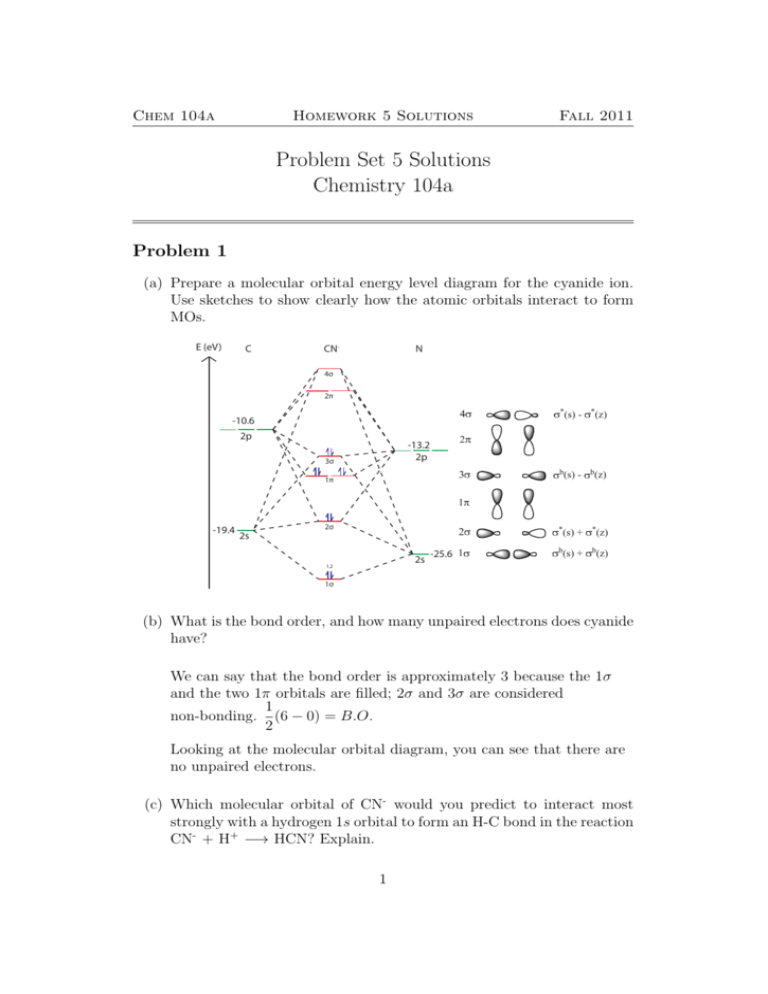
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ion (CN −). (Assume the ordering of moleculer orbitals to be like that in N 2.)Write the electron configuration of the cyanide ion (CN −).
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
FREE Expert Solution. We're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN- and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Step 2: Fill the molecular orbitals with electrons. Step 3: Determine the bond order. Step 1: Calculate the total valence ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Molecular orbital diagram for cn. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Maybe the best example for this is the mentioned ce cn and obviously the isoelectronic ceco. To add arrows to the mo diagram click on the blue boxes. Vijayta gupta is right the n atom is lower in energy.
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in ...
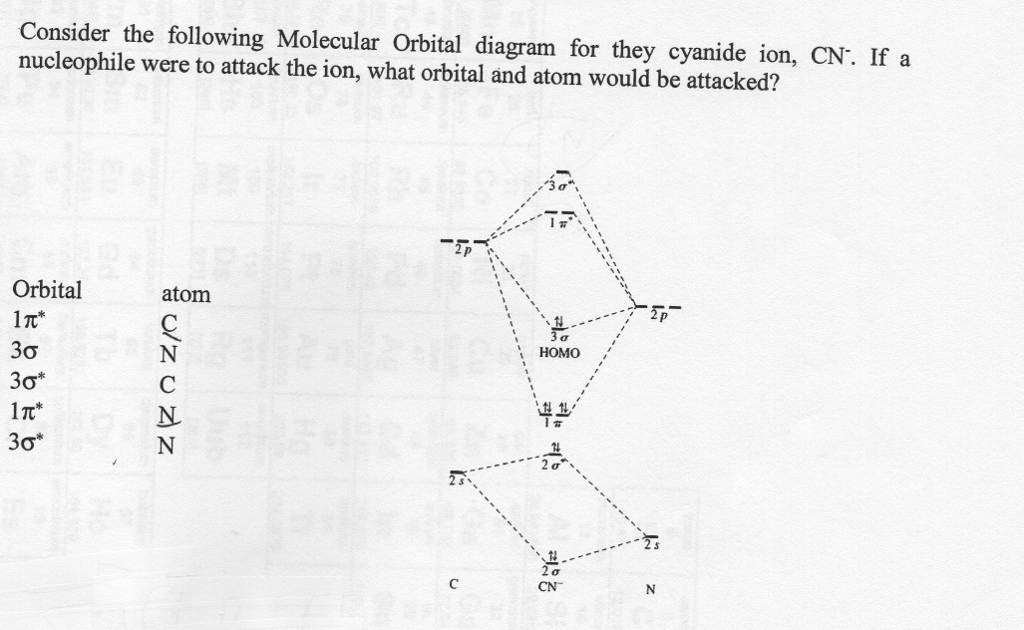
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram to figure out the electronic configuration for CN. Which of the following statements is correct?a) CN is diamagnetic.b) CN− is paramagnetic.c) If an electron is removed to give CN+, the bond order increases.d) The π*2p orbital is the highest energy orbital containing an electron in CNe) If an electron is added to give CN−, the bond length decreases.
Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).
longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN. – energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the.29 pages
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. Labels. Chemistry. Answers. Bond order of CN- is 2 =No of antibonding ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn– then determine the bond order. note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem.













0 Response to "41 molecular orbital diagram cn-"
Post a Comment