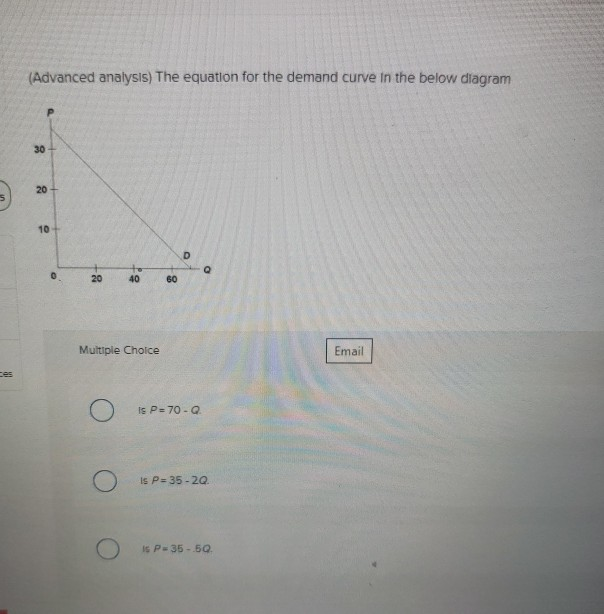
37 (advanced analysis) the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram
Demand is a table of numbers. Look at the table below. The whole table might represent my demand for pizza. Demand Schedule and Curve. As we learned in a previous lesson, any point on a graph represents two numbers, so we can plot our demand table as in the graph below. (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the above diagram: A) is P = 70 - Q. B) is P = 35 - 2Q. C) is P = 35 - .5Q. D) cannot be determined from the information given.
This raises demand for bonds and other financial assets: So the central bank shifts the demand curve for those assets to the right, which pushes up the price. This also decreases the yield and interest rate on bonds, as explained in the Einstein in Unit 10.

(advanced analysis) the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram
Below is a demand curve from a choice-based conjoint study of the chocolate market. It shows preference share for a 2-ounce Hershey milk chocolate When you want to create the demand curve in a dashboard so that it automatically updates when the user filters the data or changes the attribute... Guide to what is the demand curve and its definition. Demand Curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the prices of goods and demand quantity and is usually inversely proportionate. that means higher the price Below is the elastic demand curve for the above data (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: A. is P = 70 Q. B. is P = 35 2Q. C. is P = 35 .5Q.
(advanced analysis) the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram. Cheap essay writing sercice. If you need professional help with completing any kind of homework, Solution Essays is the right place to get it. Whether you are looking for essay, coursework, research, or term paper help, or with any other assignments, it is no problem for us. Solved (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve | Chegg.com. Business. Economics. Economics questions and answers. (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram 30 20 5 10 D о 0 to 40 20 60 Multiple Choice Email is P= 70 - Is P=35-20 Is P-35-50. The demand curve is important in understanding marginal revenue because it shows how much a producer has In the case of straight-line demand curves, the marginal revenue curve has the same intercept on the P axis as the demand curve but is twice as steep, as illustrated in this diagram. The Demand Curve. The quantity demanded of a good usually is a strong function of its price. The law of demand states that quantity demanded moves in the opposite direction of price (all other things held constant), and For basic analysis, the demand curve often is approximated as a straight line.
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the diagram shown. is P = 35 − .5Q. One reason that the quantity demanded of a good increases when its price falls is that the lower price increases the real incomes of buyers, enabling them to buy more. The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods (and services) demanded by the economy at different price levels. The aggregate demand curve, however, is defined in terms of the price level. A change in the price level implies that many prices are changing, including the wages... The demand curve is a visual representation of how many units of a good or service will be bought at each possible price. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past... A demand curve is a graphic representation of the relationship between price and quantity demanded. It is not necessarily linear in the real world. But there's no reason to think that all, or even most, demand curves will be linear, and in more advanced contexts, it can be more convenient to make...
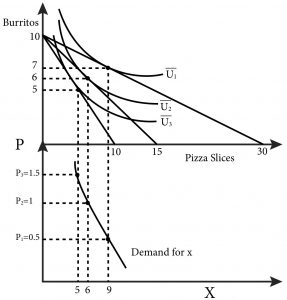
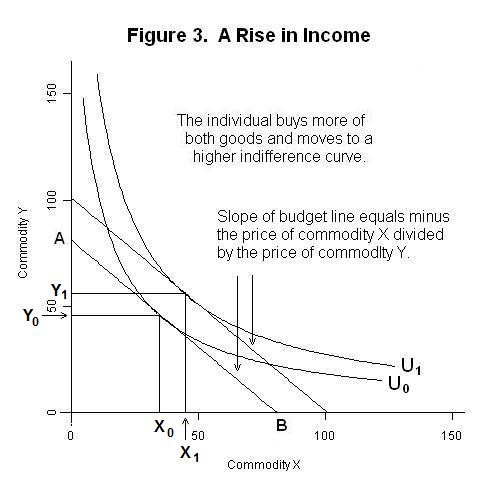
The indifference curve analysis work on a simple graph having two-dimensional. Each individual axis indicates a single type of economic goods. If the graph is on the curve or line, then it means that the consumer has no preference for any goods, because all the good has the same level of satisfaction or utility to the consumer. Explanation of demand curve formula with diagrams and examples Qd = a - b(P). Also inverse demand curve formula. This means that for the same price, demand is greater. It reflects a shift in the demand curve to the right. This could be due to a rise in consumer income which enables them... (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: ... (Advanced analysis) Answer the question on the basis of the following information. The demand for commodity X is represented by the equation P = 100 - 2Q and supply by the equation P = 10 + 4Q. Note: the demand curve should obey the law of demand; therefore, it should have a downward sloping shape to it. If you find anything in this video, please let us know in the comment section and hopefully we can get it fixed or clarify the error in the description!
The Phillips curve is a single-equation economic model, named after William Phillips, hypothesizing an inverse relationship between rates of unemployment and corresponding rates of rises in wages that result within an economy. Stated simply, decreased unemployment, (i.e., increased levels of employment) in an economy will correlate with higher rates of wage rises.
Supply and demand analysis is used by economists to explain the functioning of markets. This can be plotted as follows as an upward-sloping supply curve in the graph below. A supply and demand graph is a diagram which simultaneously shows the demand curve and supply curve and the...
The most noticeable feature of the aggregate demand curve is that it is downward sloping, as seen in . There are a number of reasons for this relationship. The first reason for the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve is Pigou's wealth effect. Recall that the nominal value of money is fixed, but...
Linear Demand Curve Formula: QD(Quantity Demanded) = 4250 - 25P. Since the equilibrium quantity (Q) and Price (P) in an ideal micro-econ market is determined by the point of intersection of the supply and demand curves we simply have to substitute one equation into the other. -6750+75P = 4250...
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. is P = 35 - .5 Q C. is P = 70 - Q D. is P = 35 - 2 Q . . . 9.
The aggregate demand curve for the data given in the table is plotted on the graph in Figure 7.1 A second reason the aggregate demand curve slopes downward lies in the relationship between John Maynard Keynes, a British economist whose analysis of the Great Depression and what to do about it...
In presenting the idea of a demand curve, economists presume the most ... (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram:.
This particular demand curve is illustrated in the following diagram Demand curves slope downwards because of the notion of declining marginal utility - the more of something that one has consumed, the less benefit (and, therefore, the less they are willing to pay) for the next unit of the...
Analysis (any type) Writer's choice. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Nursing. 2. View this sample Outline. How the courts address or respect our rights as citizens. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Political science ... Advanced This is a group of writers who have been commended positively by clients. The performance of writers in this group is evaluated regularly by ...
While understanding the meaning and analysis of a demand curve, it is also important to be able to When there is a change in the quantity demanded of a particular commodity, because of a change in The demanded quantities are plotted as demand curves DD and D'D' as shown below: From Fig.
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: is P = 35 - .5Q. The construction of demand and supply curves assumes that the primary variable influencing decisions to produce and purchase goods is:
Demand refers to the ability and the willingness of consumers to buy certain quantities of goods and A simple demand function for product X is presented below: Here 500 is a cumulative of all the The equation plotted is the inverse demand function, P = f(Qd). A point on the demand curve can be...
Click here to get an answer to your question ADVANCED ANALYSIS Assume that demand for a commodity is represented by the equation P...Supply is represented by the equation P=−10+3Qs, where Qd and Qs are quantity demanded and quantity supplied, respectively, and P is price.
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the supply curve in the below diagram is approximately In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X, (2)...
Romer Advanced Macroeconomics. Jose Sousa. Download Download PDF. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. This Paper. A short summary of this paper. 37 Full PDFs related to this paper. Read Paper. Download Download PDF.
The shape of the i–E curve determines the dependence of ln{i/(i d −i)} versus E, which should be linear with a slope of ±RT/nF. (This so-called log-plot analysis is often used for testing the reversibility of a reaction or for estimating the number of …
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the supply curve in the below diagram is approximately: P = 4 + 1/3Q. Refer to the diagrams for two separate product markets.
Drawing a Demand Curve. The demand curve is based on the demand schedule. The demand schedule shows exactly how many units of a good or service will be purchased at various price points. For example, below is the demand schedule for high-quality organic bread: It is important to note that as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases.
The Inverse Demand Curve: Economic Interpretation. If both goods are consumed in positive Slutsky Equation. We want a way to decompose the eect of a price change into "simpler" pieces. Hicks substitution eect a change in demand for a good due to a change in the relative prices while keeping...
The equation for demand is therefore Q=658-94P. To find the supply curve, recall the formula for the elasticity of supply and follow the same method as above The new demand is 20 percent below the original (using our convention that quantity demanded is reduced by 20% at every price)
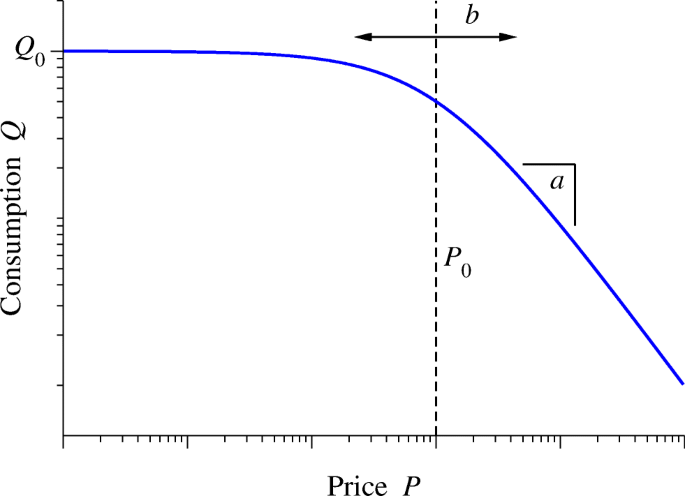
A demand curve is a downward sloping function that shows the quantity demanded at different prices. A change in demand refers to a shift in the demand curve. As a result, the demand for laptops was reduced in the face of competition from tablets. In electronics, advances in technology are constantly...
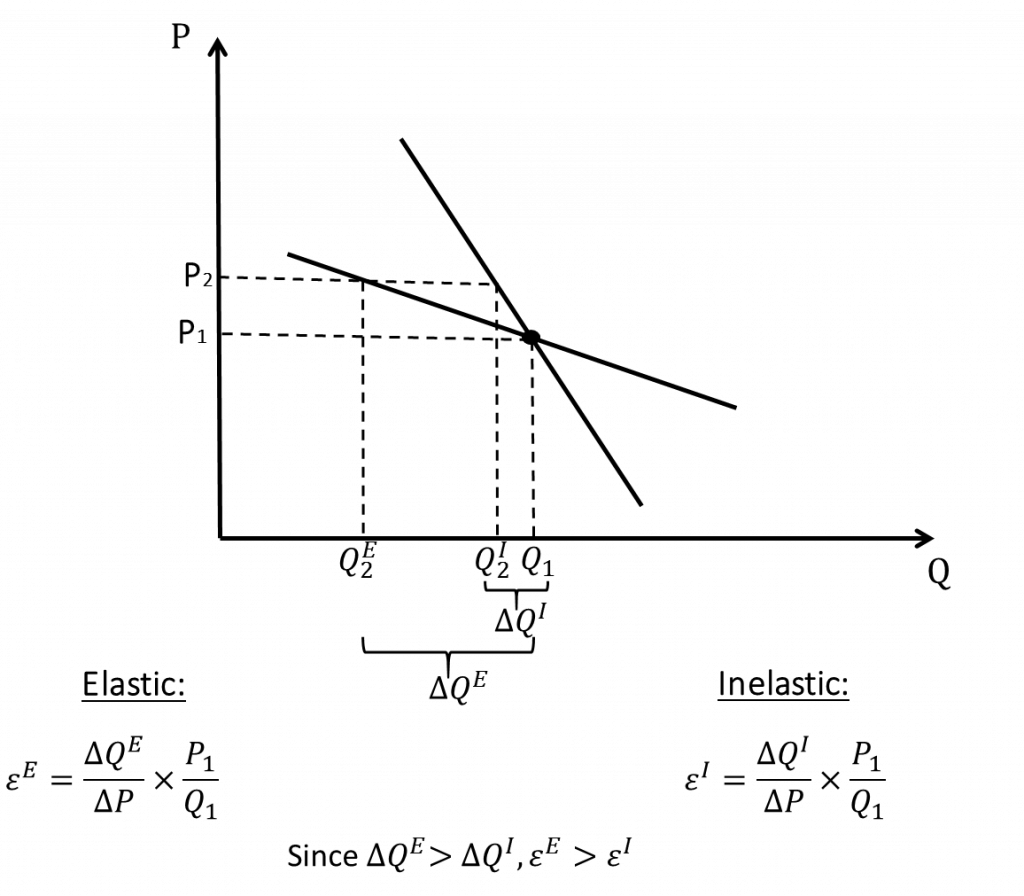
Transcribed image text: (Advanced analysis) The equation for the supply curve in the below diagram is approximately 30- -Q Ο 20 40 60 80 100 Multiple Choice Ο P= 4 - 30. Ο P= 4 + 0.30. Ο Ο P=4 + 20. Ο Ο P=4 + 0.50. · Price Q, QQ, Quantity Demanded Refer to the diagram. In the P1P2 price range, demand is Multiple Choice relatively elastic perfectly elastic 0 relatively inelastic. 0 of unit elasticity Variable Y Ο 3 6 9 12 15 18 Variable X Refer to the provided graph.
Spatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos ...
Because economists associate a rise in confidence with higher consumption and investment demand, it will lead to an outward shift in the AD curve, and a move of the equilibrium, from E 0 to E 1, to a higher quantity of output and a higher price level, as Figure 2 (a), below, shows.
Similar to the demand curve, optimal scenarios are not always the case, such as in monopolistic markets. The theory of supply and demand relates not only to physical products such as television sets and jackets but also to wages and the movement of labor.
Nov 17, 2019 · 1. Introduction. This paper revisits the classic issue of price elasticities of demand for health care services, a topic of central importance for understanding moral hazard and optimal insurance plan design, as well as having important implications for health plan choice, access to care, health care cost containment, risk adjustment, and financial risk.
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the supply curve in the below diagram is approximately P = 4 + 1/3Q Other things equal, if the price of a key resource used to produce product X falls, the: product supply curve of X will shift to the right. Macroeconomics is mostly focused on the economy as a whole
The demand curve for most, if not all, goods conforms to this principle. There may be rare examples Analysis is then done to see what "trade offs" are made in the "market", which is the negotiation Cross elasticity of demand is measured as the percentage change in demand for the first good that...
The supply curve shows the relationship between: . 72. A firm's supply curve is upsloping because: 3-17. Chapter 03 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium (+ Appendix) 78. If producers must obtain higher prices than before to produce a given level of output, then the following has occurred: A. a...
A shift to the right in the demand curve for product A can be most reasonably ... (Advanced analysis) The equation for the supply curve in the below diagram ...
In presenting the idea of a demand curve, economists presume the most ... (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram:.
ADVANCED ANALYSIS Suppose the equation for the demand curve for some product X is P= 8 – 0.6 Q and the supply curve is P= 2 + 0.4Q. a. What are the equilibrium price and quantity? Instructions: Enter your answer for equilbrium price rounded to 2 decimal places and enter your answer for quantity as a whole number. Price = $ Quantity = b.
In the indifference curve analysis, demand curve is derived without making these dubious The above demand schedule which has been derived from the indifference curve diagram can be easily It is easier to understand the derivation of demand curve if it is drawn rightly below the indifference...
In economics, a demand curve is a graph depicting the relationship between the price of a certain commodity (the y-axis) and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price (the x-axis). Demand curves can be used either for the price-quantity relationship for an individual consumer...
In Economics, Demand Function is the relationship between the quantity demanded and price of the commodity. Two Types: Linear and Non-linear. In the linear demand function, the slope of the demand curve remains constant throughout its length. A linear demand equation is mathematically...
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: A. is P = 70 Q. B. is P = 35 2Q. C. is P = 35 .5Q.
Guide to what is the demand curve and its definition. Demand Curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the prices of goods and demand quantity and is usually inversely proportionate. that means higher the price Below is the elastic demand curve for the above data



/supply-and-demand-graph-482858683-0d24266c83ee4aa49481b3ca5f193599.jpg)












0 Response to "37 (advanced analysis) the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram"
Post a Comment