41 biconvex lens ray diagram
How to use the Optically Fabricated Hologram to correct ... The system considered in this article (StartingLens.zmx) consists of a simple biconvex lens operating at 0.633 nm, with the Image plane at its paraxial focus. As can be seen from the OPD fan, spherical aberration is the dominant aberration. Ray Optics Optical Instruments - Practically Study Material A biconvex lens is known as converging lens. A biconcave lens is known as diverging lens. ... Ray diagrams: To construct the ... The ray diagrams for a convex and a concave lens are shown below. For Convex lens. i) When object lies at infinity: The real image is formed at the focus (F) of the lens as shown in fig. The size of the image is very ...
Physics Store - Blogger Draw a ray diagram to show refraction of a ray of monochromatic light passing through a glass prism. ... Under what condition does a biconvex lens of glass having a certain refractive index act as a plane glass sheet when immersed in a liquid? 39. Two wires of equal length, one of copper and the other of manganin have the same resistance. ...
Biconvex lens ray diagram
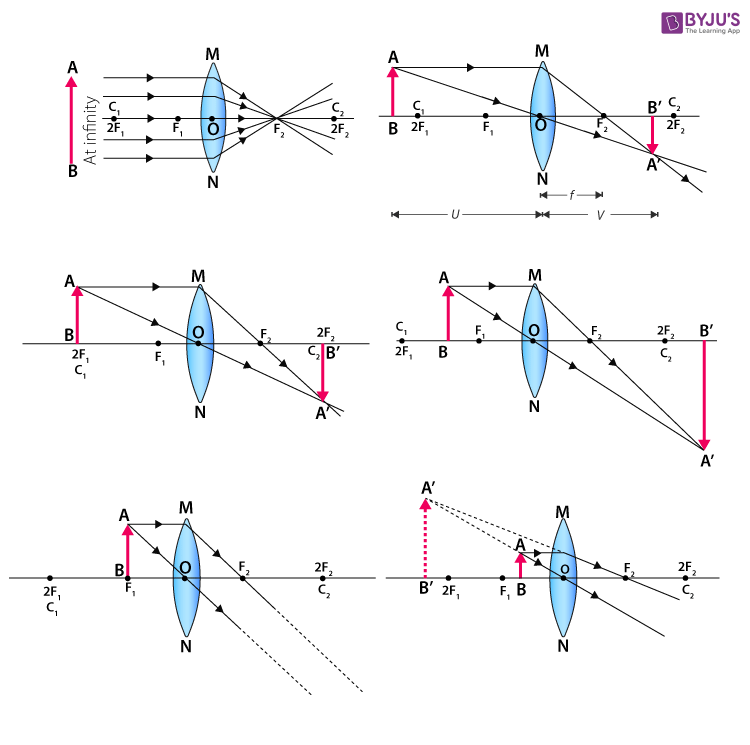
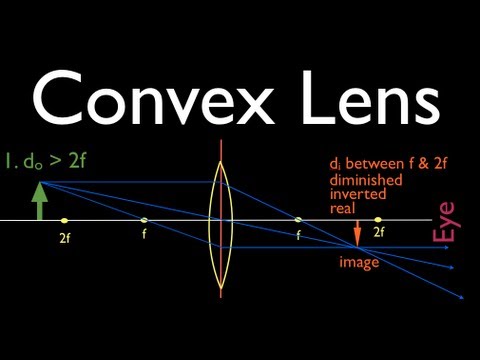
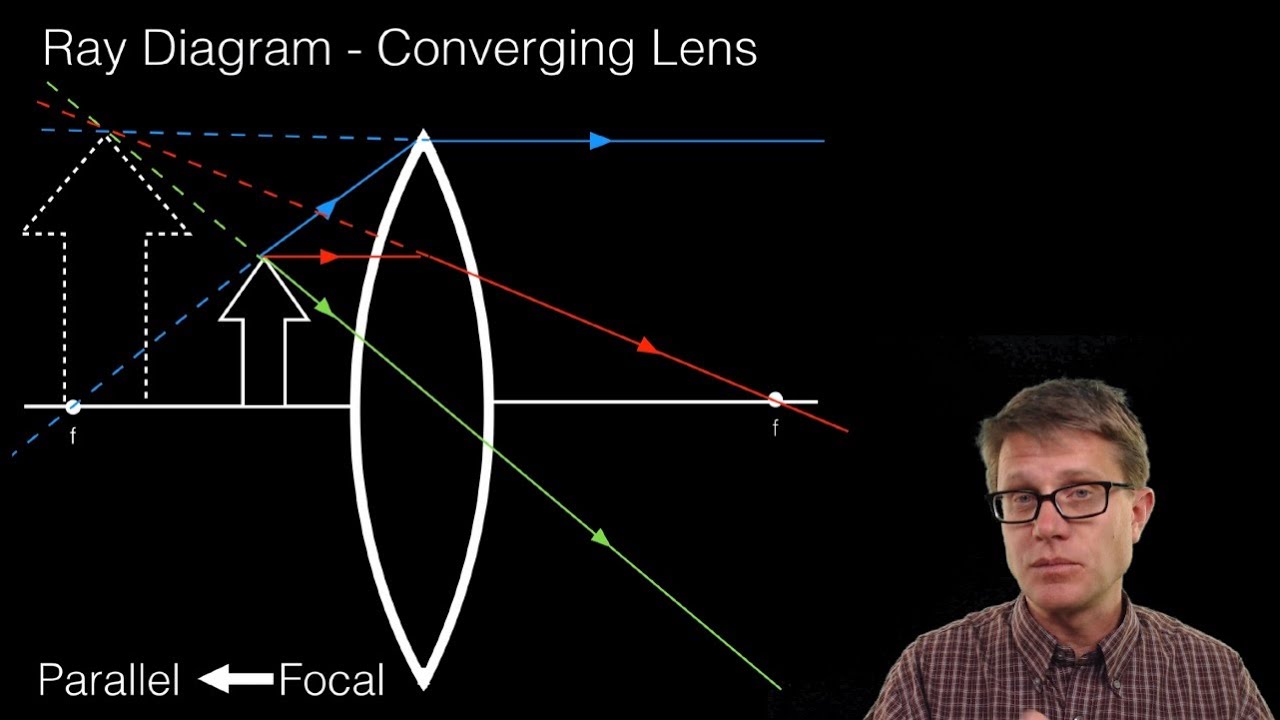
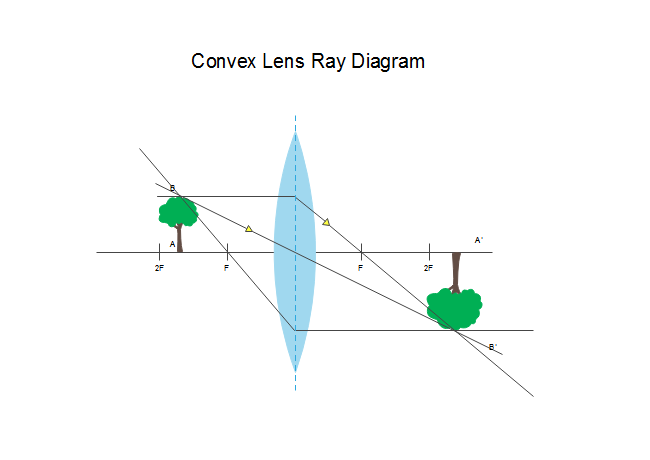
Thin Lens Ray Diagram - schoolphysics welcome, jacobs ... Thin Lens Ray Diagram. Here are a number of highest rated Thin Lens Ray Diagram pictures upon internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by giving out in the best field. We receive this nice of Thin Lens Ray Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending topic similar to we share it in google lead or facebook. Find the slope of a line which passes through points (3,2 ... A thin bi-convex lens made out of a material of refractive index is place in a medium of refractive index . A paraxial beam of light, parallel to the principal axis of the lens, is shown in the figure. 📐A ray diagram is shown. A tree acts as the object further ... A ray diagram is shown. A tree acts as the object further than 2 F away from a biconvex lens. The distance between 2 F and the object is labeled W. The distance between F and 2 F is labeled X. There I a light ray parallel to the principal axis is bent through F on the image side of the lens. There is a ray straight through the center of the lens.
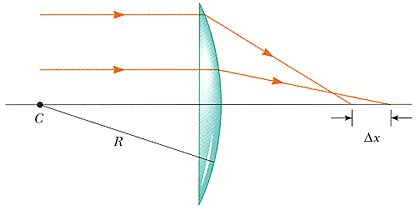
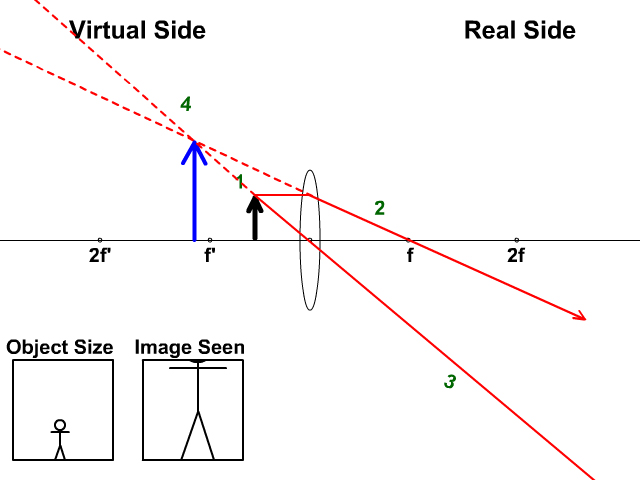
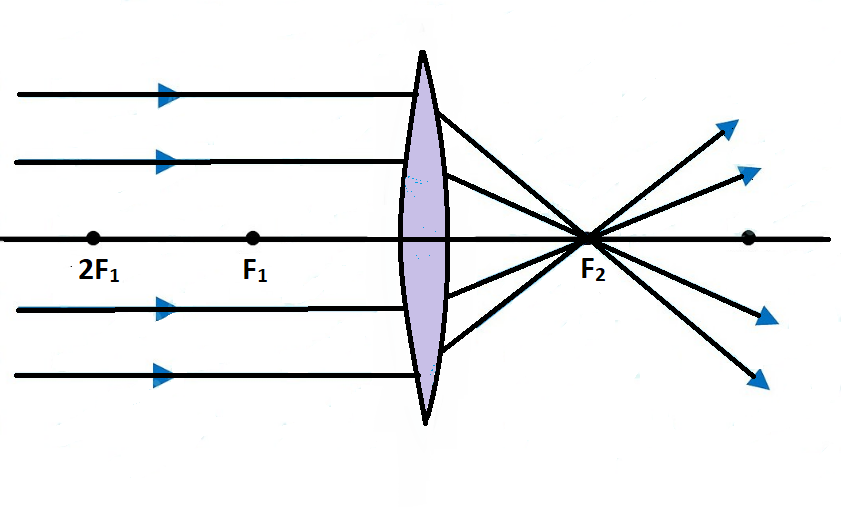
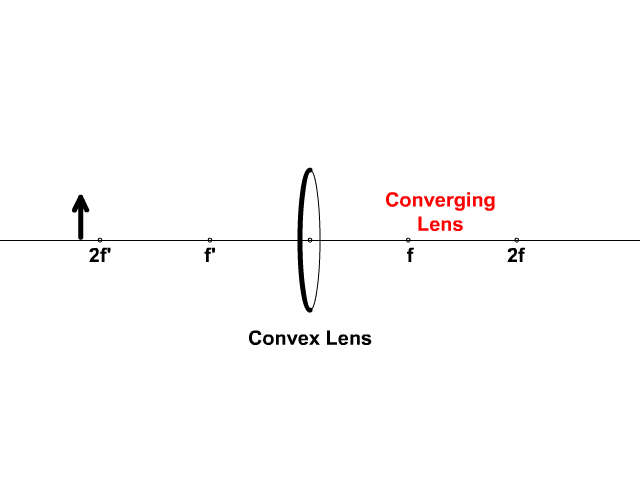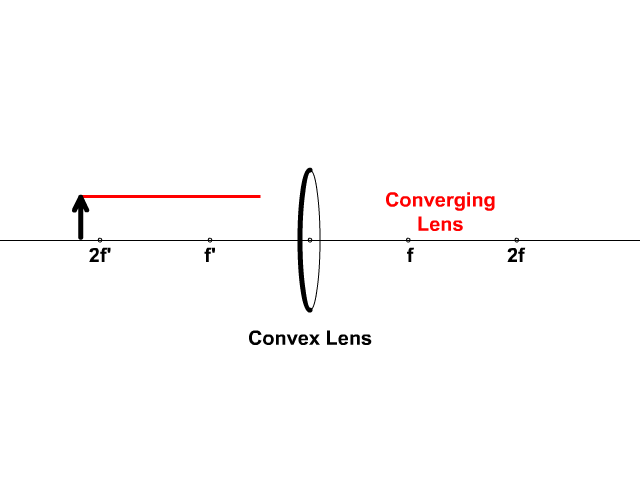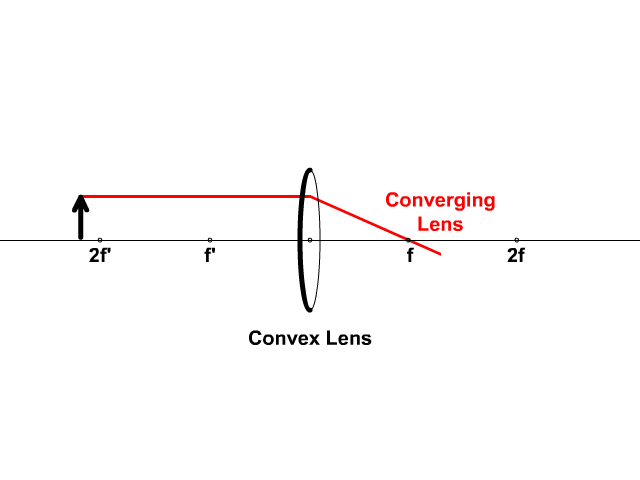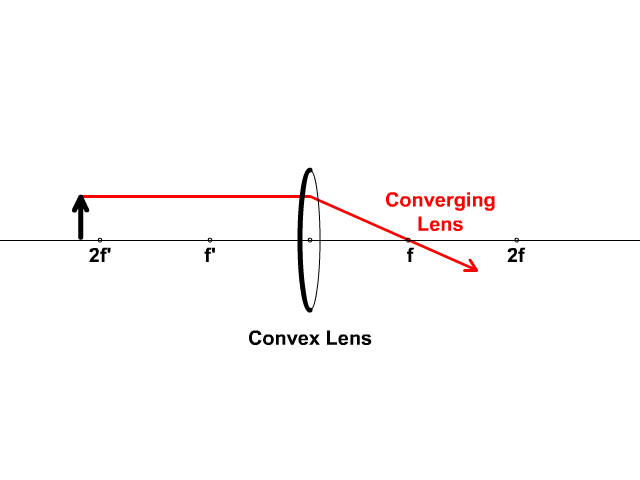
Biconvex lens ray diagram. what does not contribute to refraction in the eye ... Lenses serve to refract light at each boundary. As a ray of light enters a lens, it is refracted; and as the same ray of light exits the lens, it is refracted again. What is refractive power of eye? The total refractive power of the eye is about 63 diopters. The largest part of about 43 diopters is contributed by the cornea and the smaller ... Design a Camera with Python and PyRayT: Part One | Fotonix ... Creating a Simple Camera. To design our single-lens camera we only need two specs: system power and f/# ( F-number ). We want the system to have a focal length of 50mm, and since a lens' power is the inverse of focal length, our system power is 0.02. Our f/# will be 2.4, meaning the focal length should be 2.4x larger than the entrance aperture. Revision Notes for Refraction through a Lens Class 10 ... Principal Rays in Constructing a Ray Diagram First rule : A ray of light passing through the optical centre of the lens will emerge without any deviation. Second rule : A ray of light incident parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a convex lens, passes through the second focus F 2 . Is this given ray diagram for a biconvex lens correct? The rays on the diagram are roughly correct. An object in a plane at distance 2 f from the optical centre of the lens should form an image on the plane at a distance 2 f from the optical centre but to the other side of the lens. You can show this by putting u = 2 f into the equation 1 u + 1 v = 1 f [real-is-positive convention]
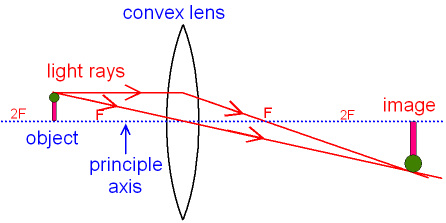
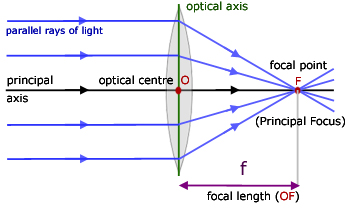
What is a Simple microscope? Applications ... - Forensic Yard F = Focal length of convex lens Explanation of Ray diagram of Simple microscope The object AB is placed between the principal focus F1 and the Optical center O of the convex lens. Now a ray of light parallel to the principal axis travels towards the convex lens from the point A and is refracted through the principal focus F2 of the convex lens. Thin Lens - scp 806 resurrection projection scp secure ... Biconvex Lens Diagram. Combination Of Lenses. Thin Lens Ray Diagram. Simple Lens. Lens Magnification Formula. Lens-Maker's Formula. Thin Lenses Physics. Convex Lens Focal Point. Convex Meniscus Lens. Mirrors And Lenses Physics. Meta Lens. Converging Lenses. Spherical Lens. Compound Lens. What is the power of a convex lens of focal length 0.20m ... Answer: Power of a lens is reciprocal of its focal length. P = 1 / f ( in m) = 100 / f ( in cm ) Focal length of a convex lens is positive so we will use f = +0.20m ( and if there is a concave lens use f = -0.20m). So, Power = 1 / 0.20 = 5 D Thanks for reading. Answer in Optics for Sam #248741 The first lens has an optical power of +50 D. The second lens is a biconvex lens of radii of curvature of 25 mm and 100 mm. Both lenses have a refractive index of 1.5. a. Describe the intermediate and resulting final image of this two-lens system. b. With the aid of ray diagram, sketch how the intermediate and final images are formed.
What are the 6 types of lenses? - Big Photography ... The two most common types of lenses are concave and convex lenses, which are illustrated below in Figure 1. A common bi-convex lens is considered a positive lens because it causes light rays to converge, or concentrate, to form a real image. An object is placed in front of a convex lens of 30 cm at ... Answer: > An object is placed in front of a convex lens of 30 cm at a distance of 60 cm from the convex lens, on the other side of that lens a plane mirror is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the lens, where will its final image be formed? Draw figure of the lens, the mirror and the object. U... How to model a Fresnel lens in OpticStudio - Knowledgebase To describe the different Fresnel lens models, we use the following definitions: Z s: the sag of the substrate; this is used to calculate the ray intercept with the surface;; Z f: the sag of the Fresnel surface; this is used to calculate the ray refraction or reflection.; Fresnel models available in Sequential Mode. Note that all models are ideal in Sequential Mode, which means that the ... Plano Convex Lenses - stage lighting for students ... Plano Convex Lenses. Here are a number of highest rated Plano Convex Lenses pictures on internet. We identified it from trustworthy source. Its submitted by government in the best field. We allow this kind of Plano Convex Lenses graphic could possibly be the most trending subject taking into consideration we part it in google gain or facebook.
Biconvex lenses | Physics classroom Treating this and drawing ray diagrams for a biconvex lens is essentially two refractions (one on the way into the lens and the other on the way out) along ...May 17, 2014 · Uploaded by Khash Afshar
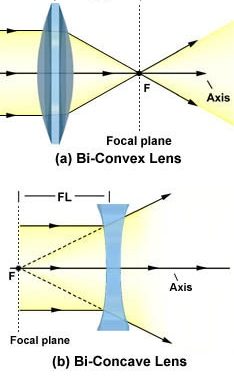
LensManipulate | Wolfram Function Repository returns a manipulable graphic of the ray diagram of a thin lens. ... Details and Options. The available thin lenses are biconvex and biconcave. ResourceFunction ["LensManipulate"] follows the sign convention for thin lenses from Hecht, Optics, Pearson, 2015: Object distance (+) real object (-) virtual object: Focal length
Refraction at Spherical Surfaces: Conventions, Formula ... From the ray diagram we get, ∠ A O M = α, ∠ A I M = β and ∠ A C M = γ. As the external angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the internal opposite angles, so γ is the external angle of the Δ A C I with r and β as the internal opposite angles. ∴ γ = r + β or r = γ - β
Difference Between Mirror and Lens (With Table) - Ask Any ... The lens is of the ellipsoid, biconvex shape. An ellipsoid is similar to a sphere but stretched out, like an olive, and biconvex means it's rounded outward on both sides. ... Ray diagrams can also be built on paper to predict the position of the image formed by a mirror. The diagrams can also be used to predict the shape, size, and distance ...
optics - Deriving the thin lens formula from the lens ... The thin lens formula is given as : 1 v − 1 u = 1 f. However, I also know the following formula for refraction at a curved surface : n 2 v − n 1 u = n 2 − n 1 R. Suppose, I consider a biconvex lens made of two such surfaces with R 1 and R 2 as the radii of curvature. The refractive index of this lens is n 2 and the surrounding is n 1.
describe how a lens magnifies an image - Lisbdnet.com The distinguishing feature of the magnifying glass is its structure—a bi-convex lens (one that is convex on both sides) situated in a frame and attached to a handle. ... To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. How Lenses Function. Thin Lens Equation Converging and Dverging Lens Ray Diagram & Sign Conventions. Convex and Concave Lenses.
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 Important ... A biconvex lens of refractive index μ1 focal length 'f and radius of curvature R is immersed in a liquid of refractive index μ 2. For (i) μ 2 > μ 1, and (ii) μ 2 < μ 1, draw the ray diagrams in the two cases when a beam of light coming parallel to the principal axis is incident on the lens. Also, find the focal length of the lens in ...
30 Interesting Convex Lens Facts for Learning Basic ... 3. A convex lens is one that is thin on the sides and thicker in the middle. The incoming light beams are converged by a convex lens to a certain spot. 4. The convex lens can be divided into two categories: Plano-Convex and Biconvex. 5. The opposite of a concave form is a convex shape.
What are two examples of a convex lens? - R4 DN A common bi-convex lens is considered a positive lens because it causes light rays to converge, or concentrate, to form a real image. What is convex lens explain with diagram? A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge . In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical ...
Finding Image Distance for Varying Object Distances using ... Ans. We know that 1/f = 1/v - 1/u. So, 1/f = 1/f + 1/v. Hence, 1/v = 0. v = infinity. Image will be formed at infinity and the nature of the image will be real and inverted. Ques. Explain with a neat ray diagram how a virtual image can be formed when convex lens is used. (5 marks) (SSLC 2013) Ans.
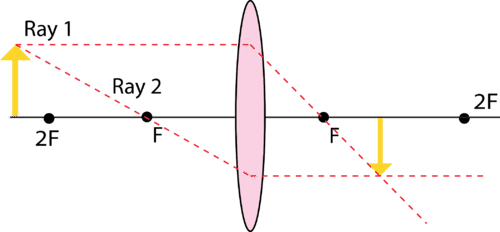
Unit 1: Converging and diverging lenses - National ... Draw your own ray diagram to find out what kind of image is formed if an object (a vertical arrow with its bottom on the principal axis) is placed at a distance between F F and 2F 2 F from a converging lens. Draw one or more ray diagrams to see what happens to the magnification and the position of the image as the object is moved closer to F F.
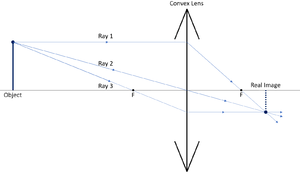
Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table ... For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
📐A ray diagram is shown. A tree acts as the object further ... A ray diagram is shown. A tree acts as the object further than 2 F away from a biconvex lens. The distance between 2 F and the object is labeled W. The distance between F and 2 F is labeled X. There I a light ray parallel to the principal axis is bent through F on the image side of the lens. There is a ray straight through the center of the lens.
Find the slope of a line which passes through points (3,2 ... A thin bi-convex lens made out of a material of refractive index is place in a medium of refractive index . A paraxial beam of light, parallel to the principal axis of the lens, is shown in the figure.
Thin Lens Ray Diagram - schoolphysics welcome, jacobs ... Thin Lens Ray Diagram. Here are a number of highest rated Thin Lens Ray Diagram pictures upon internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by giving out in the best field. We receive this nice of Thin Lens Ray Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending topic similar to we share it in google lead or facebook.
![Solved] Is this given ray diagram for a biconvex lens correct ...](https://i.stack.imgur.com/30U7X.jpg)
















0 Response to "41 biconvex lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment